We are thrilled to announce the launch of Part A of our brand new online course series, Medical Therapeutic Yoga!
This course was written and is instructed by Ginger Garner, MPT, ATC and presents an evidence- based method for using yoga as medicine in rehabilitation and wellness. Ginger has been lecturing on this topic throughout the United States since 2000. Her medical yoga graduate and post-graduate program, Professional Yoga Therapy, which teaches non-dogmatic, evidence-based care through fostering an east/west multi-disciplinary team approach, is a first of its kind in the US.
In addition to this brand new online course, H&W will be sponsoring two live seminars taught by Ginger in 2013: Yoga as Medicine for Labor and Delivery and Postpartum, which will be offered in Arlington, VA in October, and Yoga as Medicine for Pregnancy, which we will be offeing in Greenville, SC in September.
We are thrilled be offering these brand new courses!
Have you packed your bags for Combined Sections Meeting? This year, many faces of the Pelvic Rehab Institute faculty and friends will be present and will be sharing thoughts, information, and cool products.If you would like to freshen your tech skills (or learn some completely new ones) check out the social media and technology presentation by Tracy Sher and Sandy Hilton. They will be training participants in how to gather information from Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, RSS feeds, in how to locate on-line exercise programs, health and research blogs, and in how to access the international on-line physical therapy community.
Planning on taking the Women's Health board certification offered through the American Board of Physical Therapy Specialties? Elizabeth Hampton, Stacy Tylka and colleagues will enlighten attendees about exam application, completing the case study, exam eligibility, and about the roles and responsibilities of the WCS in the clinic. An added touch: "Chocolates and encouragement are both provided..." Nice!
Dustienne Miller will share her knowledge integrating yoga for patients who have pelvic pain. The session is at maximum capacity, so if you signed up for it- get there early! Tracy Spitznagle and Christina Holladay will present cases and educate the participant in caring for the complicated patient, which is certainly necessary for therapist who treat patients who have pelvic dysfunction and multiple system involvement. Tracy will also present with Ryan DeGeeter on abdominal pain during running and how to differentiate between gastrointestinal symptoms versus mechanical symptoms.
Dawn Sandalcidi, who many of you will know from the pediatric bowel and bladder training coursework, will present on another of her valuable skills: trigger point dry needling. And if you plan to treat men or women with pelvic complaints, you absolutely must check out the table that faculty member Brandi Kirk designed for use in the clinic. The table optimizes body mechanics and allows the therapist to comfortably treat patients with pelvic dysfunction. The table has removable supports for the patient's lower extremities as well. You can find the table to check out at the Current Medical Technologies booth in the exhibitor hall (Booth 1403). There will be a demo of the table from 2-2:30 pm Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday.
One last mention: in a combined effort, the APTA Section on Women's Health and The Shae Foundation are hosting an event that will explore collaborative healthcare models in women's and men's health. The event is on January 22nd at 6 pm and it will be moderated by Karen Brandon. More details can be located here. Hope to see you at CSM!
Pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain (PPGP) has received increased interest in the news and in the research community in the past few years. PPGP can cause significant movement dysfunction both during and after pregnancy, and therapists can play a valuable role in prevention, intervention and rehabilitation. In the news lately are several recent studies that I will summarize and for which I have provided abstract links below.
Is pelvic girdle pain predictable?
The International Association for the Study of Pain reports on predictors of pelvic girdle pain in the working mom. In the study, 548 pregnant Dutch working women were recruited, and at 12 weeks postpartum nearly half of the women reported pain in the pelvic girdle. The pregnancy-related predictors for pelvic girdle pain at 12 weeks were low back pain history, increased somatisation, 8 hours or more sleep or rest/day, and uncomfortable postures at work. Pregnancy and postpartum-related predictors included increased disability and having pelvic girdle pain at 6 weeks, higher somatisation, higher baby birth weight, uncomfortable postures at work, and number of days of bed rest. The authors concluded that when a woman has pelvic girdle pain during pregnancy, increased attention should be given to the woman to prevent serious pelvic girdle pain in the postpartum period and beyond.
Research addressing mode of delivery and pelvic girdle painin 10,400 women who had singleton pregnancies found an association between cesarean section and persistent pelvic girdle pain following birth. A planned c-section was associated with 2-3 times higher rates of pelvic girdle pain at 6 months postpartum. The authors conclude that for women who have pelvic girdle pain in pregnancy, unless there is a compelling medical reason for c-section birth, a vaginal birth is recommended. In a study by the same lead author,Dr. Bjelland of Norway, women were found overall to have high rates of recovery from pelvic girdle pain in the postpartum period, yet women who experienced significant emotional distress during 2 times points in pregnancy had an independent association with persistent pelvic girdle pain.
Another Norwegian study asked if women were following exercise guidelines in pregnancy and how that was related to pelvic girdle and low back pain. The authors conclude that most pregnant women in Norway do not follow the current exercise guidelines in mid-pregnancy. For women who exercised at or more than 3x/week, they had a lower rate of pelvic girdle pain. In the women who exercised 1-2x/week, rates of low back pain and depression were lessened. The study findings suggest that exercising during pregnancy may lower the risk of pelvic and low back pain.
The more we understand about the relationship between pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain and postpartum persistent pelvic girdle pain, the better prepared we are as pelvic rehab providers to offer support and healing. The research addressing best rehabilitation approaches for pelvic girdle pain continues, with reviews of the literature often concluding that we need more and better research.
A recent Cochrane summary about feedback and biofeedback for urinary incontinence has been published that supports patient perception of benefit for symptoms. The summary was first published on-line in July of 2011. 24 trials were included in this review, and the authors compared research of pelvic floor muscle training with studies that included feedback or biofeedback to augment the pelvic floor muscle training. Women who received biofeedback in their rehabilitation for urinary incontinence were less likely to report that they did not improve. Interestingly, compared to those who did not receive biofeedback, there was no significant difference in cure rates or in leakage episodes.
So why would a woman perceive that she has increased recovery of her symptoms simply through the addition of biofeedback to her rehabilitation program? The authors report that in the studies in which biofeedback was included, the subjects spent more time with the therapists. Is it this fact that leads to the increased rate of reported benefit? Speaking from professional experience, I utilized biofeedback consistently when I began working with patients who have urinary incontinence, and as I gained more skills, I used the biofeedback less. (Keep in mind that biofeedback is a global term accompanying any type of information, such as visual or auditory, and that in this article biofeedback refers to electromyographic (EMG) measurement of muscle activity.) As I resumed use of biofeedback, I was reminded of the value of having the patient really "see" the effects of their attempts at muscle activation. Perhaps the internal validation on the patient's part that he or she has a true impact on the machine via the body is quite powerful in itself.
We do know for a fact from the wide body of literature on the topic that urinary incontinence and the perceived interruption in function impacts quality of life ratings. Perhaps the patients who have an increased awareness of their own empowerment through muscular effort, home program practice, and therapist validation of patient effort with biofeedback training also affects the perceived impact of urinary incontinence. If a patient perceives increased benefit from therapy, does that perception then influence quailty of life?
An important take-home point from this research summary is this: the literature supports biofeedback as a tool that augmentspelvic floor muscle training. Biofeedback is not a tool that stands alone in rehabilitation; EMG training is utilized as a part of the process, following synthesis of information gained from the examination and evaluation of the patient. Some providers who refer for pelvic rehabiltation seem to think that biofeedback alone should be utilized, while other providers do not believe we should be using biofeedback with their patients. The needs of the specific patient should drive that decision making, and we as pelvic rehab providers must continually educate our providers about the various tools we have to treat urinary incontinence and other pelvic floor disorders.
There are only five seats left in the Pelvic Floor Level 2A course in Boston on March 22-24!
This course will be offered at Marathon Physical Therapy and is the designed as a next step (after Pelvic Floor Level One) in completing the clinicians’ ability to comprehensively evaluate the female and male pelvic floor by learning colorectal examination and treatments.
Don't miss this chance to build you clinical skill set and take advantage of the only Northeast offering of this course in 2013 - REGISTER today!
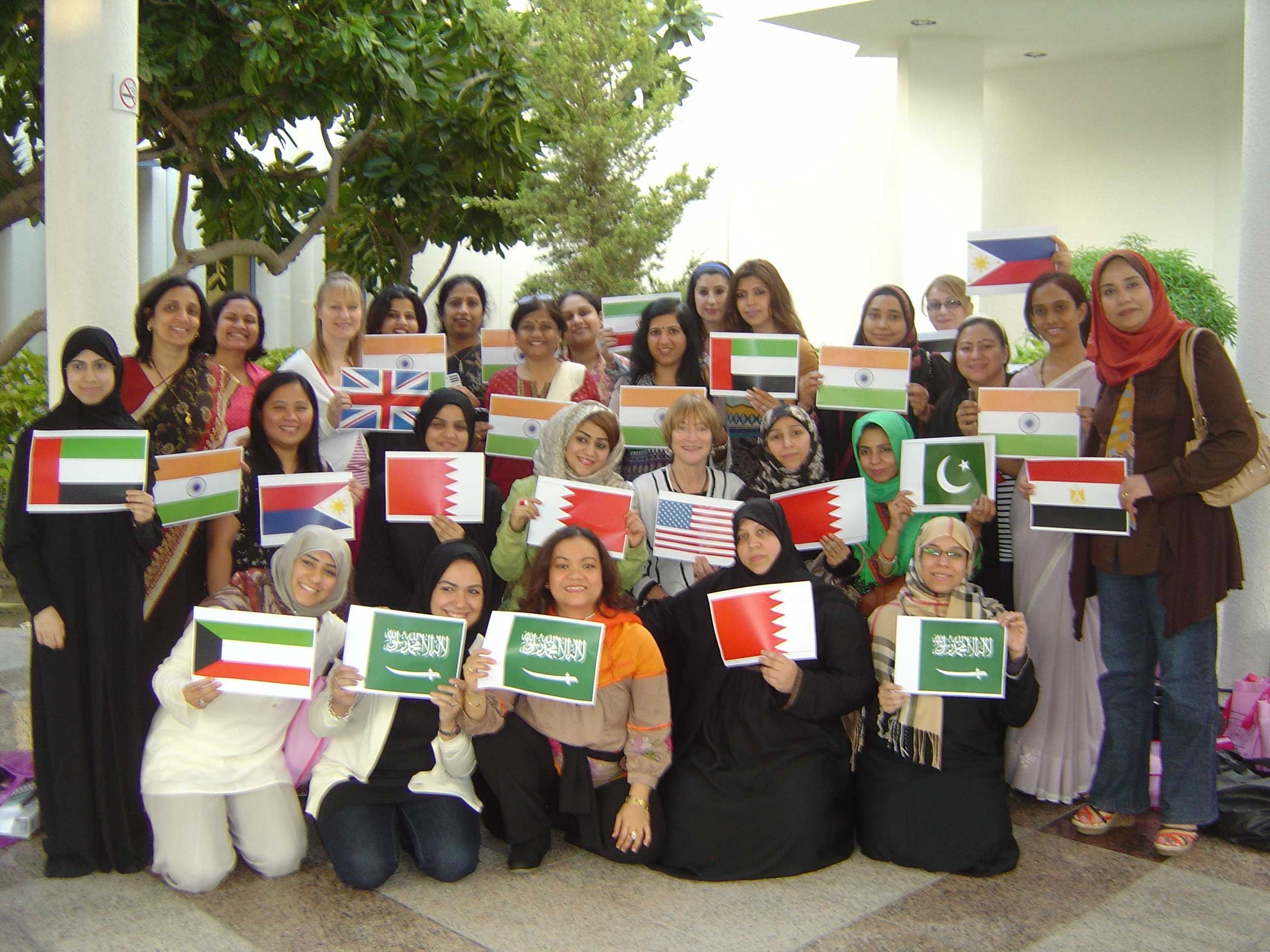

Our host asked the participants of the most recent 11-day pelvic rehab training seminar in Dubai, United Arab Emirates to hold the flag of their home country. Look at the "global village" that attended this course! These physiotherapists will be returning to their home countries as Herman & Wallace-trained "Pelvic Ambassadors".
There's Institute-founder, Holly Herman, who instructed this course, in the middle.
If you have been following research in pelvic pain, you may be aware of the diagnostic terms interstitial cystitis (IC) as well as painful bladder syndrome (PBS). And there's always bladder pain syndrome (BPS), or hypersensitive bladder syndrome. While you may have heard at some point that health care providers should use PBS preferentially over IC, that recommendation does not seem to have stuck, and the Interstitial Cystitis Association (ICA) has decided to utilize "IC" until a more definitive diagnostic criteria and test are developed. Much of the literature you will continue to see published will choose to include both IC and PBS together in the title, and recent research has attempted to further define the diagnosis as having a relationship to ulcers versus no ulcers.
Recognized subtypes of IC include ulcerative (5-10% of those with IC) and non-ulcerative (90% of those with IC). According to the ICA, patients who have non-ulcerative IC have tiny glomerulations or hemorrhages on the bladder wall, indicative of inflammation, but not specific to IC. In patients who have ulcerative IC, Hunner's ulcer's or patches of red, bleeding areas are noted on cystoscopy. Recent research aimed to find out if female patients with ulcerative versus non-ulcerative IC have different symptoms or characteristics. 214 women (36 with ulcerative IC, 178 with non-ulcerative IC) were included in this research. While both groups reported triggers such as certain foods, exercise, and stress, more patients who had non-ulcerative IC reported pain with intercourse.
On the Brief Pain Inventory, one of the outcomes tools used in this study, both groups reported similar numbers of painful areas, with lower abdominal and pelvic pain followed by low back pain. Words used to describe the pain were, however, different among the two subtypes of IC: patients with non-ulcerative IC reported aching, cramping, and tenderness, while patients in the ulcerative group reported sharp, stabbing, and hot burning pain. Aside from these differences, the patients in the two groups did not share significant differences in the outcomes measured. The authors suggest that further research is needed to provide more information about the different presentations of patients who have IC/PBS.
For those of us in pelvic rehabilitation, the most important aspect of our care is to treat what is found, and that can only be accomplished through excellent examination and evaluation techniques. If you are interested in learning more about IC, the ICA website provides a wide array of tools for patients and providers. Until then, we will continue to see IC, PBS, BPS, and other abbreviations that point out that there is much yet to learn about this disabling condition.
Even if you currently are not treating male patients in your pelvic rehabilitation program, continue to read for critical information about testicular pathology. Any male patient (or family member, friend, or loved one) can present with a sudden onset of symptoms that require medical follow-up. Testicular pathology, as pointed out in this article from Medscape, can be benign or life-threatening. (If you are not able to view the article, you can first create a free user account for Medscape and then view the information. Medscape is also a great resource as they will send you weekly article reviews on various medical topics.) The article has images of testicular pathology throughout the presentation which can help in understanding the anatomy and pathology present. Following are a few diagnoses that are highlighted in the article, and that may mimic clinical symptoms of thoracolumbar radiculopathy or pelvic pain.
Testicular torsion: Commonly occurring in adolescent males, torsion happens when the testicle twists, impairing the blood flow to and from the testicle. If the twisting last 4-6 hours or longer, the testicle can become necrotic and no longer be viable. Pain, swelling, and erythema are common in this condition, and any patient who presents with acute onset of scrotal pain must be examined for this condition.
Testicular fracture: Blunt trauma can cause significant injury to the testicles, and conservative management may be all that is required. The testicle itself can fracture, or be degloved, and a significant hematoma can occur. Surgical intervention may be required for preservation of the testicle.
Hydrocele: Fluid can collect either in the scrotum or in the spermatic cord (the "tube" that extends from the lower abdominal wall to the scrotum, carrying neurovascular and other structures). A painless lump may be the first sign of this condition. Aspiration or surgical resection may be required.
Varicocele: An enlargement of the veins within the scrotum can lead to a varicocele. While this may not cause dysfunction for the patient, a varicocele can lead to infertility and possibly discomfort due to the dragging sensation and increased pressure from enlargement.
Epididymitis: Testicular swelling, redness, and tenderness may be caused by an infection to the epididymis, a structure within the scrotum. A patient who presents with these symptoms may also have a fever and should be evaluated medically.
In addition to the above diagnoses, a testicular tumor might be first noted as a firm, painless nodule in either testicle. According to the Medscape article, a testicular tumor is the most common solid tumor found in men ages 20-35. Men need reminders just as women do for completing testicular self-exams and reporting any concerns to the physician. Here is a link to information on testicular self-exams, in case you find it helpful for patient education purposes. Keep the above information in mind when a patient presents with a change in symptoms or sudden, severe pain in the testicles.

The first ever Herman & Wallace course in the United Arab Emirates wraps up next week, and the Institute is eagerly looking forward to brining our mission to some other exciting international locations in the next few months.
In early January, Herman & Wallace faculty member Michelle Lyons will be teaching Oncology and the Pelvic Floor, a course covering gynocological, colorectal, prostate and testicular cancers and current cancer treatments and their implications for the pelvic floor at Mullingar General Hospital in Westmeath, Ireland.
Following that course, Michelle will be traveling to Kuwait City, Kuwait to teach a similar seminar to a group of women's health physiotherapists. The Kuwait course will focus on Oncology and Women's Health and will cover gynocologic, colorectal and breast cancer treatment.
In February, Michelle will return to Ireland to teach Herman & Wallace's Pelvic Floor Level One course at the School of Health Sciences at the University of Ulster.
We are so proud to have an international faculty member spreading the pelvic rehab gospel across the globe!
If you would like to catch Michelle teaching stateside, she will be instructing Care of the Pregnant Patient in Houston, TX in April and Care of the Postpartum Patient in Salt Lake City in October, two courses she helped develop with the rest of our team of faculty Pregnancy and Postpartum experts, or, as we call them, "Preg-perts". These courses are brand new in 2013 and we are excited to be offering these expanded course topics!

The Women's Action Initiative is an organization whose mission is to "empower women to prioritize pelvic and perinatal health as an integral element of their overall well being and quality of life". Founded in 2008 by Angela Hughes Halliwell, a mother of two, the WAI is currently waging a campaign to combat the effects of obstetric fistula in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Currently, millions of women in the Congo are living with unrepaired obstetric fistula caused by inadequate medical care during labor and delivery. The consequent tearing between the vagina and bladder, the vagina and rectum, or both causes leakage between the tissue that results in urinary and fecal incontinence.
Women with fistula are often mocked, ridiculed and isolated for their incontinence, and are sometimes abandoned by their families and husbands.
The WAI is currently raising money to send a team of three women's health physical therapists and a urogyn surgeon to Goma to treat, rehabilitate and educate these women. Their goal is to raise $50,000 for this endeavor.
Herman & Wallace support this mission and has made a donation towards this project. If you would also like to donate, you can do so here.
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://hermanwallace.com/