Allison Ariail, PT, DPT, CLT-LAANA, BCB-PMD is one of the creators of the Herman & Wallace Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Course Series. Allison Ariail is a physical therapist who started working in oncology in 2007 when she became certified as a lymphatic therapist. She worked with breast cancer, lymphedema patients, head and neck cancer patients, and the overall oncology team to work with the whole patient to help them get better. When writing these courses, Allison was part of a knowledgeable team that included Amy Sides and Nicole Dugan among others.
When diagnosed early, testicular cancer can be very curable and have more favorable outcomes. However, the US Preventative Services Task Force recommends against regular screening for testicular cancer. It is classified as a Grade D recommendation. This means they do not recommend clinical screening in asymptomatic individuals, or teaching patients to perform self-exams because they do not have certainty that screening has a benefit. However, recently several authors are asking for reconsideration to change the rating to a Grade B. A grade B classification is recommended when there is a benefit from doing the screening. These researchers are arguing that new studies support the benefits of regular screening by patients and their physicians. They further argue that not only will earlier diagnosis help with more favorable outcomes but that the current grade confuses individuals about the importance of self-care and wellness and reinforces negative cultural attitudes about wellness and screening.
We have several self-screens that we should be doing regularly; dermatological skin checks, vulvar skin checks, and self-breast exams. It makes sense to me to include a quick check of the testicles as well.
This made me wonder, how often individuals were being educated in how to perform self-testicular exams? I surveyed 10 individuals with testicles from different regions across the country on whether or not they had been educated on how to perform a self-testicular exam or had a testicular exam performed during their annual physical. Of the 10 people I interviewed, only 1 was educated by their physician on how to perform a self-testicular exam, and he was a little “hazy” about the instructions of what to do. Another two had been proactive and looked up instructions of how to do this on the internet, both of them initiated the search after a friend was diagnosed with testicular cancer. Another 3 more mentioned that their physician had performed a testicular exam during their physical. The other 4 individuals only mentioned that a prostate exam was performed.
A testicular exam does not take long to perform. Knowing how our bodies feel in health will allow us to know if there are changes over time. Feeling what the testicles feel like at baseline will allow individuals to know if there is atrophy, swelling, lumps, or shape changes occurring. As pelvic rehab professionals, we can teach our patients how to perform self-testicular exams, and to teach patients to advocate for themselves to be sure their physicians are performing testicular exams during their annual exam. Testicular cancer is most common between the ages of 15 and 35. It is important for teens to learn to do this exam as well! Here are some simple directions you can provide your patients:
- It is best to perform this test monthly.
- It is easiest to perform this test in the shower. The warm shower will relax the muscles holding the testicles, making it easier to perform.
- Gently grip the top of the scrotum with the thumb on top and fingers underneath. Slightly pinch this area so that the testicle stays put and won’t move while you do the exam. You will feel the spermatic cord between your fingers and thumb. The spermatic cord connects the testicle to the rest of your body.
- With your other hand, gently roll the scrotum between your fingers and thumb to feel the surface of the testicle. Glide your thumb and fingers from top to bottom, do this on front to back and on the sides.
- Check for any lumps, or bumps, and report to a physician if you find something unusual. Lumps could be as small as a piece of rice or a pea.
- Make note of size changes over time. Swelling of the testicle or scrotum should be reported to a physician.
- If you feel any dull soreness or heaviness in the testicle, report this as well.
- Check both sides.
- It is easy to mistake the epididymis for something unusual. The epididymis is a set of tubes that are coiled and line the back and top of each testicle. You will feel this as a normal lump on the top back portion of the testes. It may feel tender to the touch, but this is normal.
- You can learn more specifics on testicular cancer in Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2A (OPF2A). We not only discuss testicular cancer, but also go in-depth learning about penile cancer, prostate cancer, anal, and colorectal cancers. The next offering of OPF2A is May 20-21.
References:
- Fadich A, Giorgianni SJ, Rovito MJ, et al. USPSTF testicular examination nomination-self-examinations and examinations in a clinical setting. Am J Mens Health. 2018; 12(5): 1519-1516. Doi: 10.1177/1557988318768597
*Certified Lymphatic Therapists may skip Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1 and move on to the Level 2A and Level 2B courses.*

Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1 - no partner needed for registration
Price: $550.00 Experience Level: Beginner Contact Hours: 17.5 hours
The basics of the lymphatic system will be covered, as well as when to refer the patient to a lymphatic specialist for further treatment. Red flags and warning symptoms will be discussed so the participant feels comfortable with knowing when to refer the patient back to their medical provider for further assessment.
This introductory course is aimed to get the participant comfortable with working with oncology patients and as part of an interdisciplinary oncology team.
Course Dates: July 8-9 and December 2-3

Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2A - partner needed for registration
Price: $495.00 Experience Level: Intermediate Contact Hours: 17.25 hours
This course was designed to build on the information that was presented in Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1.
Information will be provided focusing on male pelvic cancers, colorectal cancer, and anal cancer including risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. The participant will also understand the sequelae of the medical treatment of cancer and how this can impact a patient's body and quality of life. Other topics include rehabilitation and nutritional aspects focusing on these specific cancers, as well as home program options that patients can implement as an adjunct to therapy.
Course Dates: May 20--21

Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2B - partner needed for registration
Price: $600.00 Experience Level: Intermediate Contact Hours: 19.25 hours
This course was designed to build on the information that was presented in Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1.
Information will be provided focusing on gynecological and bladder cancers including risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. The participant will also understand the sequelae of the medical treatment of cancer and how this can impact a patient’s body and quality of life. Other topics include rehabilitation and nutritional aspects focusing on these specific cancers, as well as home program options that patients can implement as an adjunct to therapy.
Course Dates: December 9-10

Aparna Rajagopal, PT, MHS, WCS, PRPC, Capp-OB Certified is the lead therapist at Henry Ford Macomb Hospital's pelvic dysfunction program, where she treats pelvic rehab patients and consults with the sports therapy team. Her interest in treating peripartum patients and athletes allowed her to recognize the role that breathing plays in pelvic dysfunction.
Leeann Taptich DPT, SCS, MTC, CSCS leads the Sports Physical Therapy team at Henry Ford Macomb Hospital where she mentors a team of therapists. She also works very closely with the pelvic team at the hospital which gives her a very unique perspective of the athlete.
Aparna and Leeann co-authored the course, Breathing and the Diaphragm: Pelvic and Orthopedic Therapists, which helps clinicians understand breathing mechanics and their relationship to the pelvic floor.
Abdominal bloating and distension are two very commonly reported GI symptoms in the pelvic practice setting. However, these symptoms are not commonly recognized in other physical therapy settings. While many people experience occasional bloating/discomfort it does not necessitate medical intervention, but repeated and long-standing bloating/distention can impact the quality of life.
One diagnosis which is associated with these symptoms is Abdomino-Phrenic dyssynergia where patients develop a paradoxical abdomino-phrenic response. Normally, as a response to an increase in intraluminal gas, the diaphragm relaxes, and the abdominal musculature contracts. When dyssynergia is present, the opposite happens and the diaphragm contracts, and the abdominals relax. Abnormal pelvic floor function is also associated with this diagnosis. Treatments typically used are biofeedback therapy and breathing techniques.
Where Leeann and I work, we are seeing patients increasingly referred with this diagnosis. Recently we treated a 72-year-old female patient with a long-standing history of troublesome bloating and distention, with the diagnosis of Abdomino phrenic dyssynergia.
- The patient had complaints of bloating and abdominal distension all day long, worsening toward evening
- She reported limiting her food intake in the evenings on account of the discomfort and "tightness" in the abdomen
- She rated the discomfort as 3-5/10 in the morning time with an increase to 8/10 by late evening
- She also reported poor sleep because of how "hard and tight" the abdomen felt by bedtime
Upon examination, amongst other findings, the patient demonstrated:
- Significant tightness in her posterior chain and her erector spinae in both thoracic and lumbar regions
- Decreased thoracic rotation/mobility
- Increased connective tissue restrictions in both upper abdominal quadrants, especially in the epigastric area and inferior to the rib cage
- Decreased lower rib cage mobility
- Poor ability to prolong exhale or to exhale strongly
- Decreased ability to relax the pelvic floor musculature after a contraction
In addition to biofeedback and visceral mobilizations, treatment techniques included joint mobility techniques inclusive of simple rib and thoracic spine mobilizations, soft tissue mobility techniques including gentle diaphragm releases, breath training, and breathing techniques to aid in pelvic floor relaxation.
The patient received 9 treatment sessions and a home maintenance program which she followed with good compliance. She reported a 70% overall improvement and was now able to sleep through the night and eat in the evenings without discomfort.
In our course, Breathing and the Diaphragm: Pelvic and Orthopedic Therapists, you will learn:
- Explain normal diaphragmatic breathing and the role of the internal and external oblique musculature.
- Assess and treat dysfunctional breathing patterns including but not limited to chest, abdominal, and paradoxical breathing patterns.
- Understand the concept of Intra-Abdominal Pressure (IAP) and the control and use of IAP with the diaphragm in a lowered position as a stabilizing mechanism for the spine.
- Understand the concept of regional interdependence and its application in the treatment of back or pelvic pain patients.
- Recognize the effects of postural patterns and the linkage to the diaphragm and pelvic floor.
- Understand the muscles and myofascial components involved in dysfunctional breathing and techniques to effectively treat the same.
- Understand and demonstrate mobilizations of the rib and thoracic spine and develop a comprehensive treatment program.
- Develop an exercise progression for dysfunctional breathing for use in the clinic and in-home programs.
- Integrate diaphragmatic breathing and mobility in the athletic clientele

Course Dates: April 22-23
Price: $450
Experience Level: Beginner
Contact Hours: 14
Description: This remote course is an integrated approach where participants will learn how the diaphragm, breathing, and the abdominals can affect core and postural stability through intra-abdominal pressure changes while looking at structures from the glottis and the cervical region to the pelvic floor.
This course includes assessment and treatment of the barriers by addressing thoracic spine articulation and rib cage abnormalities in the fascial system of muscles related to breathing and the diaphragm. Instructed techniques are applicable to patients who present with Diastasis Rectus Abdominis, pelvic pain, incontinence, and prolapse, as well as cervical, thoracic, scapular, and lumbar pain.

Join me on April 22 to begin this quest to learn more about signs, symptoms, and the journey that individuals with eating disorders endure. We will also explore ways that we as Pelvic Health Professionals can assist them on this journey in Eating Disorders and Pelvic Health Rehabilitation. This course will not have all the answers; rather will be a step forward for clinicians to expand their understanding and to seek out additional resources to learn more and provide evidence-based treatment for these individuals.
We, as pelvic health practitioners are NOT going to treat eating disorders… we are NOT going to diagnose eating disorders… but we CAN and SHOULD be asking questions… encouraging patients to seek additional support… and helping them find appropriately trained providers. We can ALSO provide support and speak with words that promote validation, wellness, and healing rather than words that are unintentionally triggering, harmful or nonvalidating. IN ADDITION, we can provide these individuals with manual skills, activities, and educational “tools'' to assist in GI distress, constipation, abdominal bloating, urinary dysfunction, pelvic pain, sexual dysfunction, POP issues, postural / body mechanics, abdominal canister coordination/function, tightness in trunk, hips, shoulders, rib cage, etc. These individuals would benefit from pelvic health professionals being an additional part (not the lead) of their treatment team.
We, as pelvic health professionals, need to: know what eating disorders are and are not, understand how this mental illness creates issues in all body functions, and what we can do to provide relief or reduction in some of their symptoms.
These case scenarios may be familiar or may have occurred without our awareness. These scenarios are based on real lives…and we likely see similar situations like this almost every day…
_____________________________________________________________________
Hope
Hope is a 31-year-old woman with an eight-year-old daughter with special needs. She is in your office for the second episode of care as she had COVID and her grandmother became terminally ill. Hope had come to PT before for severe abdominal pain and bowel dysfunction after a perforated colon during an ovarian cyst removal which resulted in a perforation in her colon, hemicolectomy, sepsis, and traumatic ICU hospitalization.
She had offered to you during her first episode of care that she had a history of anorexia. She was walking 7-9 miles a day, doing yoga 5 days a week, and seeing chiropractic care for fibromyalgia and chronic pain in the back/neck. She had been seeing an eating disorder mental wellness therapist and an eating disorder dietician for a while but had not seen them for some time. At the time of her first couple of visits, she was encouraged to make an appointment with both a mental wellness therapist and a dietician who both focused on eating disorders with who she was comfortable in the past. She agreed to do this but then stopped coming to therapy as mentioned above due to COVID and family emergencies.
When she came back to therapy, she looked much different. Her eyes were sunken, she had a thin layer of hair (lanugo) over her cheeks (what could be seen with the mask) and over her abdomen. Her fingernails were brittle and split.
She reported today that she has lost 25 more pounds because she thought that would help with the abdominal pain. Her new dietician (NOT an ED dietician) had her keeping a log of her food and has told her, according to Hope, that her body does not need more than 1500 calories a day and that she was eating “way too much”. She now logs everything she eats and counts calories.
Hope describes how she is now staying with her grandmother during the day in a skilled nursing facility and is supporting her grandfather. She is also caring for her 8-year-old daughter with special needs who is now in school during the day. She continues to exercise every day no matter what and is now not only walking the 7-9 miles but she is now doing strength training 4 days a week and yoga about 3-5 days a week. She seems to be almost superhuman as she juggles and manages all of these difficult situations.
After assessment of orthostatics, and standing blood pressure - her systolic BP dropped 25 mmHG and diastolic BP dropped 10 mmHg and her heart rate increased by 25 bpm after 5 minutes standing.
What might be some red flags here? What might your recommendations be? Who would you contact?
_____________________________________________________________________
Faith
Faith is a 24-year-old woman who came to pelvic floor physical therapy for urinary incontinence and dyspareunia which began after the cesarean section birth of her first child six months ago. She does not understand why she has all of the extensive "stretch marks" on her abdomen and why her cesarean section scar looks so large. She is very unhappy about how her body looks after giving birth.
Upon further conversation, she shares that she only eats a “super clean diet” and has cut out major food groups such as dairy, sugar, and meat because those foods are "high in calories" and "not healthy". She sparingly consumes any carbs and mainly eats vegetables and some fish sometimes.
She has experienced episodes of lightheadedness and near syncope for years. She reports that has been very “bendy” and was a cheerleader in high school. Faith has had painful joints and subluxations in her hips and knees for as long as she can remember.
Faith also shares that it is always so tiring. She also reports that she worries a lot about her newborn and is having a hard time juggling all of the demands of work, home, and caring for her baby. Her husband is helpful though has to work a lot.
After the assessment of orthostatics, Faith becomes lightheaded when standing. She was orthostatic for heart rate (>20 bpm) after 1, 3, and 5 minutes in standing. Her blood pressure also drops a bit in standing (<10 mmHg systolic) though was not considered orthostatic. She also has a Beighton score of 7 out of 9, has piezogenic papules on both of her heels, and soft velvety skin which is easily stretched.
Faith is asked if she would consider trying some salty snacks and some Gatorade to see if this helps with her lightheadedness. She responds that she will not eat pretzels or salty snacks because they are too high in carbs and she will not consider Gatorade because she doesn't drink beverages that are high in calories.
She keeps touching her abdomen and is uncomfortable about the “stretch marks'' that she has. She also keeps looking at herself in the mirror that is in the treatment room pulling her baggy sweater over her body.
She shares that she has always had constipation and abdominal pain - however this has really worsened lately. Faith also reports pelvic pressure at times and hopes that she does not have to deal with a pelvic organ prolapse like her mother had a few years ago.
During her first visit, she speaks very quickly and appears quite anxious.
This is only part of the history…but what might be helpful to say, do, explore, and assess?
_____________________________________________________________________
Brian
Brian is a 17-year-old wrestler who is coming to pelvic floor physical therapy for abdominal and pelvic pain. He shares that when he has to make "weight" before each meeting he will restrict water, and food and will exercise with layers of clothing on. He will drink about a cup of water during the day on those days and sometimes will just eat some chocolate, such as a peppermint patty, for dinner. After the meeting, he will sometimes eat a lot. He will often have significant abdominal pain and it will make him double over sometimes. He went to the GI doctor and was told that he has gastroparesis. He does not not know what he is supposed to do. If he doesn't eat, his abdomen hurts, and if he does eat it hurts too.
He also shares that he doesn't like school so much anymore. There is a lot of pressure to get a college scholarship and he is waiting to hear from a couple of his top choices. He doesn't feel like hanging out with some of his friends so much anymore. They always want to go out to eat and he can't do that. He typically will spend time with other wrestlers or will just stay at home. He reports being exhausted and having a hard time concentrating on his schoolwork.
Brian shares with you that he has to strain so much to have a bowel movement that he sometimes feels a bulging from his anus. He has a bowel movement about once a week and it is painful.
He does have urinary urgency and reports urinating "a little bit" many times during the day. His urine is tan in color.
When further questioned about Brian's response on the male genitourinary pain index (GUPI), he reports that he does not have pain with sexual climax because he does not have any desire to be sexually active anymore.
This is just a glimpse of Brian's journey... What other questions might you have? What can we do to help? What else would you be assessing?
_____________________________________________________________________
Joy
Joy is a 34-year-old musician with a history of binge eating disorder, which has been well-controlled for over five years. She comes to you with pelvic pain, dyspareunia, abdominal pain, and a history of constipation and urinary incontinence.
Joy saw a pelvic pain specialist who recommended a tricyclic antidepressant for pelvic pain. Joy also has bipolar disorder. She is in DBT treatment weekly (group and individual) and is well supported by her psychiatrist.
She is reporting new binge-related urges that are becoming hard to control since beginning the new medication. She is concerned about these new urges and this is causing additional anxiety. Her pelvic pain is actually worsening now with the additional anxiety and she is beginning to leak urine more frequently. Bowels are becoming firmer and harder to pass.
What are some next steps with Joy? What can we do to assist with her situation?
_____________________________________________________________________
Eating Disorders and Pelvic Health Rehabilitation: The Role of a Rehab Professional is a live remote course (including lab and lecture) with required seven-hour pre-course content accessible on Teachable. During the live course, there will be lectures, interactive discussions, and lab activities. We recommend, if possible, having another human available during the lab activities to practice the techniques discussed.
I look forward to seeing you on April 22!
Eating Disorders and Pelvic Health Rehabilitation
Course Dates: April 22
Price: $395
Experience Level: Beginner
Contact Hours: 13.25
Description: This course explores types of eating disorders including anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge eating disorder, ARFID (Avoidant Restrictive Feeding Intake Disorder), and OSFED (Otherwise Specified Feeding and Eating Disorder). We will also discuss conditions that do not yet have formal diagnostic criteria such as orthorexia and diabulimia and we will touch on Pica and Rumination Disorders. Most healthcare professionals understand very little about eating disorders and disordered eating. There is a weight stigma with health care identifying “health” in terms of weight, BMI, body appearance, exercise, and activity. As rehabilitation professionals, it is our responsibility to understand that health looks and feels different for everyone. In addition, we may be able to identify signs and symptoms of eating disorders and be able to provide support for these individuals through proper referral and modification of our rehabilitation plan of care.
What is a TA? In the world of the Herman & Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute, a TA is an abbreviation for teaching assistant. Herman & Wallace has always had teaching assistants (TAs) at lab courses to guide hands-on lab time to be extra hands and helpers for the instructors. Having exemplary instructors and the addition of more people on the teaching team in the room to answer questions, guide, and give clinical pearls is what creates the optimal learning experience through Herman & Wallace.
During COVID, the demand for quality pelvic health education was still high, but COVID limited travel and group gatherings. The Institute was able to pivot and reformat some courses into fully remote offerings. This allowed continuing education to continue but did not answer the question of the core series of pelvic floor courses and all of the other course offerings. This required some creativity. Some labs could be taught virtually, but some educational topics and skills could not be covered without in-person, hands-on learning in which participants got to practice on real bodies..The next pivot was to create a hybrid model of learning, in which some didactic skills were reformatted into pre-recorded content, and the labs were offered in smaller satellites around the country. Herman & Wallace had always been a leader in education because of the hands-on skills provided and learned during in-person labs. The question arose, who would help guide them and be the “boots on the ground” for lab skills?
Enter the teaching assistant team! Each satellite class for the Satellite Lab Courses comes with an experienced TA. These are practitioners who apply for the position or are invited by the Herman & Wallace staff because of their exemplary performance during other courses or their CV full of continuing education in the pelvic floor field. A teaching assistant must have taken the core classes including Pelvic Floor Levels 1, 2A, and 2B through Herman & Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute. They must feel comfortable learning along with the participants, guiding participants through labs, and sharing the clinical pearls they have as they relate to the content being taught.
TAs had always had an important role in courses, but as the primary educators during lab time, they were now a vital part of the learning experience for participants. In keeping with this bigger role, Herman & Wallace, created an elevated role called a Lead Teaching Assistant (Lead TAs). In addition to completing the education required of a teaching assistant, Lead Teaching Assistants have assisted at 5 or more classes with Herman & Wallace within a 2 year period, with a stellar record of not canceling on short notice after committing (TA cancellation is a big scheduling nightmare for the Institute). They have earned consistently positive feedback on surveys from their participants.
Lead TAs commit to TAing a minimum of 4 events per year and even will travel to do so if needed by HW. Lead TAs also have access to many of the bonus learning experiences and presentations that the Herman & Wallace Faculty have access to. Lead TAs are like super, fancy, ultra teaching assistants because it is literally their job to provide the best lab experiences for participants.
What are the benefits of being a TA? You get access to all of the updated course content. When you TA, you get Teachable access to the most up-to-date version of that class. Herman & Wallace is always updating, revising, and adding, so you get to learn all those new gems for FREE! If you’re like most participants, looking to take 20 other courses but trying to figure out how to afford it (without selling your firstborn), being a TA is the solution. You get paid in Herman & Wallace course credit, which means that if you TA a class you are pretty close to taking another class on the house! The chance to network with other therapists is another perk TAs often list. You also earn CEUs for the classes you assist, as long as you complete the course through Teachable. The last benefit comes if you are studying for a certification like your PRPC because it is a great way to “retake” and review the content. Did I mention the credit you receive from TAing can also be used to pay for your PRPC certification?
 What are the benefits of being a Lead TA? Really all of the above but it comes with more opportunities. Lead TAs become employees of Herman & Wallace which means that you can choose to be paid in course credit or money. You also get to attend monthly skill-building educational bonus opportunities created just for TAs. Lead TAs also get invitations to certain “Faculty Only” exclusive Herman & Wallace presentations. If you want to be able to write your own class or teach for the series, this is a great way to build your career towards this goal.
What are the benefits of being a Lead TA? Really all of the above but it comes with more opportunities. Lead TAs become employees of Herman & Wallace which means that you can choose to be paid in course credit or money. You also get to attend monthly skill-building educational bonus opportunities created just for TAs. Lead TAs also get invitations to certain “Faculty Only” exclusive Herman & Wallace presentations. If you want to be able to write your own class or teach for the series, this is a great way to build your career towards this goal.
Can I be a TA if I have not taken my education through H&W? Sadly, the answer is no. The Herman & Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute acknowledges that other education can have the ability to provide the same level of education and pelvic health knowledge. However, it is the Institute’s stance that teaching assistants for Herman & Wallace should be intimately familiar with the manner in which lectures and labs have been taught to participants through the Institute. Education through other avenues, while informative and valuable, does not provide these opportunities.
How do I know I am ready to be a Teaching Assistant? Are we ever really ready? As a therapist, I feel the more I learn, the more I learn what I don’t learn. But when you are working with participants, they want your reassurance and guidance during learning, not for you to know every single thing. I like to say “do your best until you know the rest” to participants (and myself) as we are all ALWAYS learning. You are ready when you feel you can come into the experience with a growth mindset of being as prepared as you can be and also have a plan for if you need help in teaching/supporting participants.
What if I don’t know the answer to a question? As someone who has been a TA to over twenty classes, I can say, you will not always have the answers. What you learned in college or when you took a class a few years ago may have changed or been updated. BUT you can be a resource and a guide to help work with participants in their learning to find those answers with the course instructor, research, and other pelvic health resources. Herman & Wallace offers a teaching team and you are one member of that team!
How can I be compensated? If you are a teaching assistant you will be compensated at a specific rate of Herman & Wallace course credits per day of service. If you are a Lead TA, you will also have the option to be paid in course credit or a cash rate. These rates will be discussed with the teaching assistant coordinator during the application process.
How do I pick what class to TA? Start with something you are comfortable with. This may be your favorite Herman & Wallace class, a clinic you are familiar with, or a topic you are really passionate about. It has to be a class you have taken through Herman & Wallace, but otherwise, you have quite a few choices! Please remember that you have to have completed all three of the H&W core pelvic floor courses to TA any of them. Other classes also have requirements to TA them. The best way to find out if you are qualified and what you are qualified to TA is to fill out the application.
Are you convinced to join the team as a Teaching Assistant? Click here to apply to be a Teaching Assistant.
Are you already a Teaching Assistant and ready for a promotion to Lead Teaching Assistant? Please email Megan Farr at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. and let her know you would like to be considered for a Lead TA role.
Would you like to chat with a Lead Teaching Assistant to find out if one of these tracks is right for you or to have some mentorship in your lab skills journey - please feel free to contact Megan Farr and she’ll help you get that conversation started too!

Allison Ariail, PT, DPT, CLT-LAANA, BCB-PMD is one of the creators of the Herman & Wallace Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Course Series. Allison Ariail is a physical therapist who started working in oncology in 2007 when she became certified as a lymphatic therapist. She worked with breast cancer, lymphedema patients, head and neck cancer patients, and the overall oncology team to work with the whole patient to help them get better. When writing these courses, Allison was part of a knowledgeable team that included Amy Sides and Nicole Dugan among others.
March is Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month. Did you know that the incidence rate of colorectal cancers is increasing? According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1.9 million new cases of colorectal cancer were identified worldwide in 2020. This number is expected to grow even more. It is predicted that by 2040 the number of new cases of colorectal cancer will rise to 3.2 million new cases a year, and 1.6 million annual deaths worldwide. Additionally, did you know due to the fact that the incidence rate is increasing and it is being diagnosed in younger individuals, the age for screening for colorectal cancer has lowered to 45? At age 45 individuals should begin regular screening for colorectal cancer either via stool-based testing or visual-based screening via a colonoscopy. If someone has risk factors they may need to begin screening at a younger age.
Colorectal cancer can often be preventable through modifiable risk factors. Changing some of these risk factors, alongside the detection and removal of precancerous lesions can lower someone's risks. However, if a diagnosis is made, treatment can help to prolong the life of the patient. The treatment can include various surgeries, chemotherapy, and radiation. All of these treatments can cause changes to a patient's body. A rehab professional that has knowledge about both the body and how the medical treatment of cancer causes changes, can make all the difference in the world for that patient returning to activities that they enjoy and love after treatment.
There are not many opportunities for rehab professionals to learn about these changes and how we can help these patients. However, Herman & Wallace has a series focused on helping oncology patients. In this series, techniques are learned that can help colorectal cancer patients recover from their diagnosis and the medical treatment they go through. The oncology series is online and offered several times a year. You can attend the upcoming oncology courses on: Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1 scheduled for July 8-9 and December 2-3, Level 2A scheduled for May 20--21, and Level 2B scheduled for December 9-10.
Reference:
Morgan E, Arnold M, Gini A, et al. Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Colon. 2023; 72(2).
*Certified Lymphatic Therapists may skip Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1 and move on to the Level 2A and Level 2B courses.*

Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1 - no partner needed for registration
Price: $550.00 Experience Level: Beginner Contact Hours: 17.5 hours
The basics of the lymphatic system will be covered, as well as when to refer the patient to a lymphatic specialist for further treatment. Red flags and warning symptoms will be discussed so the participant feels comfortable with knowing when to refer the patient back to their medical provider for further assessment.
This introductory course is aimed to get the participant comfortable with working with oncology patients and as part of an interdisciplinary oncology team.
Course Dates: July 8-9 and December 2-3

Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2A - partner needed for registration
Price: $495.00 Experience Level: Intermediate Contact Hours: 17.25 hours
This course was designed to build on the information that was presented in Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1.
Information will be provided focusing on male pelvic cancers, colorectal cancer, and anal cancer including risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. The participant will also understand the sequelae of the medical treatment of cancer and how this can impact a patient's body and quality of life. Other topics include rehabilitation and nutritional aspects focusing on these specific cancers, as well as home program options that patients can implement as an adjunct to therapy.
Course Dates: May 20--21

Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2B - partner needed for registration
Price: $600.00 Experience Level: Intermediate Contact Hours: 19.25 hours
This course was designed to build on the information that was presented in Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1.
Information will be provided focusing on gynecological and bladder cancers including risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. The participant will also understand the sequelae of the medical treatment of cancer and how this can impact a patient’s body and quality of life. Other topics include rehabilitation and nutritional aspects focusing on these specific cancers, as well as home program options that patients can implement as an adjunct to therapy.
Course Dates: December 9-10

Nari Clemons - Actually, I used to have a meditation and neuroscience class for Herman Wallace. It was a shorter class. But, I felt it was lacking in tools for the provider. For example, as an empathic provider, I felt I was very aware, very mindful that I was losing energy, that I was "picking things up" from my patients, and that I was really not enjoying my job or life balance as much as I used to. I became ill and burnt out, working in this intensive field. It felt like the joy of my life was kind of being sucked up by my job. Jen and I launched our own journeys, together, trying to understand how this world of boundaries and balance could help us in our own lives. So much changed and grew from that. So, in time we decided to combine the two into one class, to help practitioners integrate meditation into their practice and life, but also how to come back to loving their jobs with balance, as we were able to.
What are the top 3 takeaways a practitioner could hope to gain from this class?
NC - 1. Better self-care in and out of the clinic. 2. A more effective and less taxing way to interact with clients, share responsibility, and communicate in more helpful ways for both practitioner and patient. 3. enjoying their life and having more energy for their life outside of work.
JVV - 1. You don’t have to do it all. 2. We want to support you with tools to help your patients take more responsibility for their care and their outcomes. 3. YOU ARE VALUABLE…and here are ways you can care for yourself, have healthy boundaries, and align your actions with your priorities so you can leave work at work and truly enjoy your life outside of work.
Who do you think needs to take this class?
NC - Any practitioner who is finding work more and more emotionally taxing or draining. Really, there are a few patterns that benefit from this class. People who over-give and over-function in relationships in their life, including patient relationships. Often there can be a bit of a people-pleasing tendency in these situations. Also and especially if a participant is one of those people who have always been a little sensitive to energy: feel things, pick up things, notice their energy changes when they interact with others. I feel like this is the only class I know of that specifically gives tools and strategies for this kind of provider.
JVV - EVERYONE! LOL. People who are wrestling with healthy work/life balance, who find themselves staying late after work or working through lunch, health care providers who tend to care more for their patients than they do for themselves, those of us who leave work drained and only have meager offerings of energy for our families.
What was your favorite feedback from participants in taking this class?
NC - We hear a lot from participants that other classes made them have better clinical skills, but this class has helped them to enjoy their own life and their job more and to feel more balanced and professional as they employ better boundaries and shared responsibility.
JVV - Ahhh, it is true joy when participants are empowered and equipped to set healthy boundaries, care for themselves, and feel more joy in their lives.
How is this class different from other classes through H&W?
NC - Kind of along the same lines, this class does give you skills for use with patients, but they are the skills that help your life feel better, and your job feels better. They give you permission to change your paradigm of treatment from "how much can I possibly give" to "how do I shift my job, self, and communication, to allow my job to be just one part of my life that is enjoyable and doesn't take so much energy away from the other parts of my life."
JVV - This is the only class that focuses both on skills to use for patients and skills to use FOR YOURSELF. To keep yourself healthy, balanced, and whole as a medical provider in a demanding, challenging role.
Why are there two parts to this class?
NC - Because it is a lot of information, a lot of life changes to integrate. It takes time. We like the idea of a month of growth and change. Participants do pre-work to prepare for the first weekend, which starts the process of change. Then, they do work in the following month and really work on the intensive integration, new habits, new patterns, and new neuronal networks. Then, we come back for another day for the second part of learning that participants will be ready for after integrating some of the basics of the first weekend.
JVV - We just had SO MUCH we wanted to share!! And we found having two classes spaced a month or so apart really lets participants ingest and apply one level of change before being ready and hungry for the next level. The first part focuses on establishing good boundaries with patients, self-care practices including meditation, and identifying areas of their lives that need support or intervention to be healthier. The second class dives deeper into thoughts, emotions, and actions. Practices like gratitude, visualization, and deeper mediation practices.
Boundaries, Self-Care, and Meditation - Part 1

Course Dates: March 18
Price: $400
Experience Level: Intermediate
Contact Hours: 12.5
Description: The instructors recommend completing this series in two parts to allow time to process and implement one leg of the journey before undertaking the next. Both Part One and Part Two have a significant amount of pre-work to digest and practice before meeting via Zoom. Please plan for up to 12 hours of pre-course work. This sets the stage for you to find your path to experiencing more joy, energy and balance.
In Part One, participants begin their process of study, meditation, and self-reflection in the weeks prior to the start of the class. Pre-work includes focus on the neuroscience of pain trauma, PTSD, and meditation. Participants will learn about the powerful influence both negative and positive experiences have on our nervous system’s structure and function. Personal meditation practice and instruction will create changes in the participant's own nervous system. Participants will also learn how to prescribe meditation for various patient personalities and needs, as well as analyze yourself through inventories on coping, self-care, empathy, burnout, values, as well as track how you spend your time. Commitment to pre-work will facilitate rich discussion as we put what you have learned into practice around building a shared responsibility model of patient care, language to support difficult patients, and both visualizing and planning steps to create new, healthier patterns in your life and in your practice.
Lila Abbate, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, WCS, PRPC is a Board-Certified Specialist by the American Physical Therapy Association in Orthopedics (OCS) 2004 and Women’s Health (WCS) 2011. She has obtained the Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner (PRPC) in 2014. She is a Diane Lee/LJ Lee, Integrated Systems Model (ISM) graduate and completed the New York series in 2012. Dr. Abbate is Senior Faculty with Herman & Wallace and can be found instructing the Pelvic Floor Series as well as her own courses Coccydynia and Painful Sitting and Bowel Pathology and Function.
Pain with sitting is a common complaint that patients may present to the clinic with. While excess sitting has been shown to be detrimental to the human body, sitting is part of our everyday culture ranging from sitting at a meal, traveling in the car, or doing work at a desk. Often, physical therapists disregard the coccyx or tailbone as the possible pain generator, simply because they are fearful of assessing it, have no idea where it is, or have never learned about it being a pain generator in their education.
Coccydynia is the general term for “pain over the coccyx.” Patients with coccydynia will complain of pain with sitting or transitioning from sitting to standing. Despite the coccyx being such a small bone at the end of the spine, it serves as a large attachment site for many important structures of interest that are important in pelvic floor support and continence:¹
- Anterior Tip: Iliococcygeus and pubococcygeus, Sacrococcygeal ligament
- Lateral: Coccygeal muscles which runs parallel with the sacrospinous ligament
- Posteriorly: Fibers of gluteus maximus and sacrotuberous ligament
Along with serving as a major attachment site for the above structures it provides support for weight bearing in the seated position and provides structural support for the anus. However, the coccyx is only 10% weightbearing, so what seems to go wrong that this bone is taking the brunt of the weightbearing? Women are five times more likely to develop coccydynia than men, with the most common cause being an external trauma like a fall or an internal trauma like a difficult childbirth.1,2 In a study of 57 women suffering from postpartum coccydynia, most deliveries that resulted in coccyx pain were from the use of instruments such as forceps delivery or vacuum-assisted delivery. A BMI over 27 and having greater than or equal to 2 vaginal deliveries resulted in a higher rate of coccyx luxation during birth. ³ Other causes of coccyx pain can be non-traumatic such as rapid weight loss leading to loss of cushioning in sitting, hypermobility or hypomobility of the sacrococcygeal joint, infections like a pilonidal cyst, or pelvic floor muscle dysfunction.¹ When assessing a patient with coccyx pain, it is also of the utmost importance to rule out red flags, as there are multiple cases cited in the literature of tumors such as retro rectal tumors or cysts being the cause of coccyx pain. These masses must be examined by a doctor to determine if they are malignant or benign and if excision is necessary. Quite often, these masses can be felt as a bulge on rectal examination.4,5
A multidisciplinary approach including physical therapy, ergonomic adaptations, medications, injections, and, possibly, psychotherapy leads to the greatest chance of success in patients with prolonged coccyx pain.1 Special wedge-shaped sitting cushions can provide relief for patients in sitting and help return them to their social activities during treatment. Physical therapy includes manual manipulation and internal work to the pelvic floor muscles to alleviate internal spasms and ligament pain. Intrarectal coccyx manipulation can potentially realign a dislocated sacrococcygeal joint or coccyx.1 Unique taping methods demonstrated in video by Dr. Abbate, can be used as a follow-up to coccyx manipulation to help hold the coccyx in the new position and allow for optimal healing. Often coccyx pain patients have concomitant pathologies such as pelvic floor muscle dysfunction, sacroiliac or lumbar spine pain, and various other orthopedic findings that are beneficial to address. When conservative treatments fail, injections or a possible coccygectomy may be considered.
Luckily conservative treatment is successful in about 90% of cases.¹ Join Lila Abbate in her upcoming Coccydynia and Painful Sitting remote course on March 31st. By learning how to treat coccyx pain appropriately, you will be a key provider in solving many unresolved sitting pain cases that are not resolved with traditional orthopedic physical therapy.
References:
1. Lirette L, Chaiban G, Tolba R, et al. Coccydynia: An overview of the anatomy, etiology, and treatment of coccyx pain. The Ochsner Journal. 2014; 14:84-87.
2. Marinko L, Pecci M. Clinical Decision Making for the Evaluation and Management of Coccydynia: 2 Case Reports. JOSPT. 2014; 44(8): 615
3. Maigne JY, Rusakiewicz F, Diouf M. Postpartum coccydynia: a case series study of 57 women. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2012; 48 (3): 387-392.
4. Levine R, Qu Z, Wasvary H. Retrorectal Teratoma. A rare cause of pain in the tailbone. Indian J Surg. 2013; 75(2): 147-148.
5. Suhani K, Ali S, Aggarwal L, et al. Retrorectal cystic hamartoma: A problematic tail. J Surg Tech Case Rep. 2104; 6(2): 56-60.
Coccydynia and Painful Sitting

Course Dates: March 31, June 17, September 22, and December 10
Price: $175
Experience Level: Intermediate
Contact Hours: 5.5
Description: Coccyx pain is a common, frustrating condition for the patient who often has difficulty sitting, one of the most important tasks necessary for daily activity. Patients who find help from a pelvic rehabilitation provider have often experienced pain near the tailbone for long periods of time, leading to chronic pain in addition to neuromusculoskeletal dysfunctions. This one-day, remote continuing education course allows the therapist to focus on this vital, sensitive area to learn and refine skills in assessment and treatment. Anatomy, pathology, and palpation skills of the coccyx region are instructed.
This course includes a video lab on both internal and external neuromuscular taping techniques which can immediately be applied in the clinic. This course also includes a review of seating options to reduce pain.
Fun fact: Did you know that the pelvis fans and folds just like the hand and foot?
Ischial tuberosities change position and move medial to lateral and back based on the functional task. Pelvic floor muscles length and fascial integrity and its ability to conform to demands become an important factor in treating painful sitting.
The one-day course gives you a basic anatomy review and discusses the biomechanics of sitting and the difference of quadruped and its assessment. External coccyx treatments are explained and reviewed through video format along with a discussion to assist patients in making good decisions using sitting relief pillows. You will learn 5 basic tips to know if your patient has true coccydynia or if the pain is being driven from elsewhere up or down the chain. A review of the literature and how the medical community views basic coccydynia and which medical interventions can assist patients with long-standing sitting pain.
Pelvic Rehab Report
The official Herman & Wallace blog. New blogs post every Friday on topics relating to the field of pelvic floor dysfunction.
Sarah Hughes PT, DPT, OCS, CF - L2 has been practicing PT since 2007 and opened her private practice, Arrow Physical Therapy in 2016. She now owns and operates Arrow remotely while residing in the Chicago area and practicing at Outlier Physical Therapy. Her specialties include dance medicine, the CrossFit and weightlifting athlete and conditions of the hip and pelvis such as femoroacetabular impingement and labral tears. Dr. Hughes earned a BS in exercise science from Gonzaga University and a DPT from the University of Washington, she wrote and instructs Weightlifting and Functional Fitness Athletes.
Mobility. What is it and how can we get more of it?? In the CrossFit world, athletes can be really fixated on mobility.
- This feels tight.
- That feels restricted.
- I can’t squat below parallel because my ankles are tight.
- I can’t press fully overhead because my lats are locked up.
- I know I just need to foam roll more.
- I’ve been doing this mobility program but I still can’t make progress

Don’t let these athletes fool you. They may be strong and look capable in their functional fitness, but often there is a REASON they feel tight, and it’s not because they need more passive motion. Many CrossFit athletes spend their warm-up time lying on foam rollers, stretching with heavy resistance bands, static stretching, and using percussion guns and other mobility tools.
But, what IS mobility? Mobility is defined as the ability of a joint to move actively through a range of motion. Mobility is about controlling your body through a full range of active movement; much different than passively stretching into a position. And, mobility can only be achieved with strength training, neuromotor retraining, appropriate exercise prescription and PRACTICE. Keep these athletes in your sights as they perform the exercises. Don’t get caught giving them too much freedom to only see you for manual work and then do a home program alone. No online program that they can purchase will ever replace your education and ability to help them with mobility drills.
Are your patients stretching and stretching without the increased mobility they are looking for? Are you doing manual work that is targeted and effective but only getting you so far with them? Try some stability drills and strength training exercises! In the Weightlifting and Functional Fitness Athletes - Remote Course we will look at different CrossFit requirements and what these athletes need. HINT: it's not more foam rolling!!
Weightlifting and Functional Fitness Athletes

Course Dates: March 4, May 13, and October 14
Price: $295
Experience Level: Beginner
Contact Hours: 9
Description: When it comes to Crossfit and Weightlifting, opinions are divided among Physical Therapists and other clinicians. Why is it that these sports cause such strong differences among rehab professionals? In this half-day, remote continuing education course, instructor Sarah Haran PT, DPT, OCS, CF-L2 looks at the realities and myths related to Crossfit and high-level weight-lifting with the goal of answering “how can we meet these athletes where they are in order to keep them healthy, happy and performing in the sport they love?"
This course will review the history and style of Crossfit exercise and Weightlifting, as well as examine the role that therapists must play for these athletes. Common orthopedic issues presented to the clinic will be examined. Labs will introduce and practice the movements of Crossfit and Weightlifting, discussing the points of performance for each movement. The practitioner will not only learn how to speak the language of the athlete but will experience what the movement feels like so that they may help their client to break it down into its components for a sport-specific rehab progression. The goal of this course is to provide a realistic breakdown of what these athletes are doing on a daily basis and to help remove the stigma that this type of exercise is bad for our patients. It will be important to examine the holes in training for these athletes as well as where we are lacking as therapists in our ability to help these individuals. We will also discuss mindset and culture issues such as the use of exercise gear (i.e. straps or a weightlifting belt), body image, and the concept of "lifestyle fitness". Finally, we will discuss marketing our practices to these patients.

Rachna Mehta, PT, DPT, CIMT, OCS, PRPC, RTY 200 is the author and instructor of the Acupressure for Optimal Pelvic Health course. Rachna brings a wealth of experience to her physical therapy practice and has a personal interest in various eastern holistic healing traditions.
As I walked into the room to greet a new patient, I quickly glanced at the prescription for Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy in her chart. The words “urinary retention” caught my attention. As I gathered her history, I learned that this patient had a history of high anxiety and had been to the ER twice within a few weeks with symptoms of urinary retention. She was now taught to self-catheterize herself to manage her symptoms. After comprehensive testing by her urologist ruled out obstructive and neurological causes, she was referred to pelvic floor therapy with a diagnosis of pelvic floor muscle tension and inability to relax her pelvic floor muscles.
Urinary retention, or the inability to voluntarily void urine, is one of the most prevalent presenting urologic complaints in the emergency department. Voluntary urination requires close coordination between muscles of the pelvic floor, bladder, and urethra, as well as the nerves innervating them.
Female urinary retention is either acute or chronic and can be categorized according to the International Continence Society as:
- Complete (full retention) or partial (high post-void residuals)
- Acute or chronic
- Symptomatic or asymptomatic
- Mechanism (obstructive or non-obstructive)
Two of the most common causes of chronic urinary retention in women are bladder muscle dysfunction and obstruction. The condition is important as it can lead to significant clinical problems if left untreated, such as bladder decompensation, hydronephrosis, renal failure, vesicoureteral reflux, nephrolithiasis, and urinary tract infections, as well as symptoms including suprapubic pain, feelings of incomplete emptying, weak urinary stream, urgency, and incontinence1.
The patient was anxious and worried and could not step out more than an hour away from her home as she feared she would need to return home to void. She could only void at her own home and her social life was extremely limited due to these voiding restrictions. Given her high anxiety, I initiated Acupressure points for Anxiety in her program as an evidence-based holistic practice.
Acupressure is widely considered to be a powerful Complementary & Alternative Medicine (CAM) therapy and is gaining acceptance within the medical community as part of an Integrative medicine approach. It draws its roots from Acupuncture which is part of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) believed to be over 3000 years old. TCM is based on Meridian theory where key Acupressure points (or Acupoints ) lie along specific meridian lines and are connected to the visceral functions of vital organ systems.
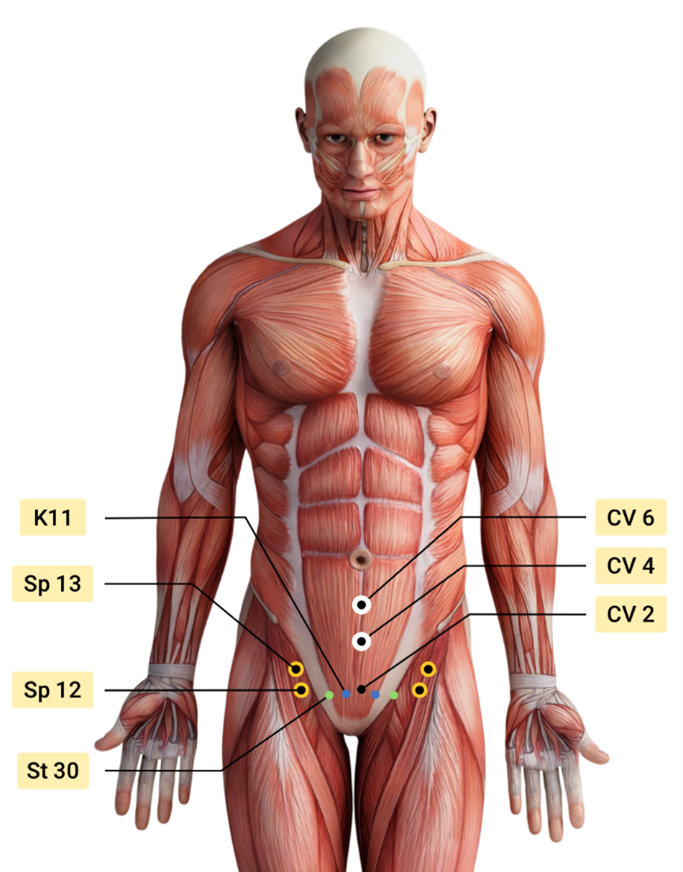
Research shows that Acupressure points have been used with Emotional Freedom Techniques (EFT) as well as for the management of pain, anxiety, nausea, fatigue, urinary incontinence, constipation, and symptom management. Studies over the past few decades have found that Acupressure points transmit energy or the vital Qi (life force energy ) through interstitial connective tissue with potentially powerful integrative applications through multiple systems.
Acupressure has demonstrated the ability to improve heart rate variability, and thus decrease sympathetic nervous system activity. By decreasing sympathetic nervous system stimulation, the release of stress hormones such as epinephrine and cortisol is decreased, and the relaxation response can be augmented, which may correlate with decreasing levels of pain, stress, and anxiety2.
Over the next few weeks, the patient was treated by a multidisciplinary team including her Primary Care Physician, Psychologist, Acupuncturist, and Pelvic floor Physical Therapist. Integrating Acupressure along with manual therapy, behavioral modifications, exercises, breath work and stretching, key potent points in the Central Channel, Kidney, Stomach, Spleen, and Bladder meridians were utilized to down-regulate her nervous system and improve the physiological functioning of her vital organs.
The patient was also taught to use perineal acupressure points for the management of intermittent constipation. The patient learned and practiced daily an Acupressure Anxiety points regimen along with traditional rehabilitation exercises, and became calmer and more mindful with complete resolution of urinary retention symptoms. She could now step outside her home and use public bathrooms which socially was a big achievement for her.
The course Acupressure for Optimal Pelvic Health next offered on Feb 4th -5th 2023 explores Acupressure as an evidence-based modality for the management of Anxiety, Stress, Pain, and Symptom management. The course also teaches two programs with specific potent points for Anxiety and for Daily Wellness and introduces Yin Yoga as a complementary practice to Acupressure. This course is curated and taught by Rachna Mehta PT, DPT, CIMT, PRPC, RYT 200. Rachna has integrated Acupressure as part of her rehabilitation toolbox for several years now bringing holistic healing and wellness to her patients.
References
- Leslie SW, Rawla P, Dougherty JM. Female Urinary Retention. [Updated 2022 Nov 28]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538497/
- Monson E, Arney D, Benham B, et al. Beyond Pills: Acupressure Impact on Self-Rated Pain and Anxiety Scores. J Altern Complement Med. 2019;25(5):517-521.
- Au DW, Tsang HW, Ling PP, Leung CH, Ip PK, Cheung WM. Effects of acupressure on anxiety: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupunct Med. 2015;33(5):353-359. doi:10.1136/acupmed-2014-010720
- Son CG. Clinical application of single acupoint (HT7). Integr Med Res. 2019;8(4):227-228.
- Kwon CY, Lee B. Acupuncture or Acupressure on Yintang (EX-HN 3) for Anxiety: A Preliminary Review. Med Acupunct. 2018;30(2):73-79.
- Abbott, R., Ayres, I., Hui, E. et al. Effect of Perineal Self-Acupressure on Constipation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J GEN INTERN MED30, 434–439 (2015).
Acupressure for Optimal Pelvic Health

Course Dates:
February 4-5, June 3-4, October 14-15
Price: $450
Experience Level: Beginner
Contact Hours: 12.50
Description: This continuing education course is a two-day seminar that offers participants an evidence-based perspective on the application of Acupressure for evaluating and treating a host of pelvic health conditions including bowel, bladder, and pelvic pain issues. The course explores a brief history of Acupressure, its roots in Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), and presents current evidence that supports the use of complementary and alternative medicine as an adjunct to western medicine. TCM concepts of Meridian theory and energy channels are presented with scientific evidence of Acupoints transmitting energy through interstitial connective tissue with potentially powerful integrative applications through multiple systems.
Lectures will present evidence on the use of potent Acupressure points and combinations of points for treating a variety of pelvic health conditions including chronic pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, constipation, digestive disturbances, and urinary dysfunctions to name a few. Key acupoints for decreasing anxiety, stress, and bringing the body back to a state of physiological balance are integrated throughout the course.
Participants will be instructed through live lectures and demonstrations on the anatomic location and mapping of acupressure points along five major meridians including the spleen, stomach, kidney, urinary bladder, and gall bladder meridians. Key associated points in the pericardium, large intestine, small intestine, lung, and liver meridians as well as the governing and conception vessels will also be introduced. The course offers a brief introduction to Yin yoga and explores Yin poses within each meridian to channelize energy through neurodynamic pathways to promote healing across multiple systems. Participants will learn how to create home programs and exercise sequences and will be able to integrate acupressure and Yin yoga into their orthopedic and pelvic health interventions.