Akinesia is a term typically used to describe the movement dysfunction observed in people with Parkinson disease. It is defined as a poverty of movement, an impairment or loss of the power to move, and a slowness in movement initiation. There is an observable loss of facial expression, loss of associated nonverbal communicative movements, loss of arm swing with gait, and overall small amplitude movements throughout all skeletal muscles in the body. The cause of this characteristic profile of movement is due to loss of dopamine production in the brain which causes a lack of cortical stimulation for movement.
 If the loss of dopamine production in the brain causes this poverty of movement in all skeletal muscles the body, how does the pelvic floor function in the person with Parkinson disease and what should the pelvic floor rehabilitation professional know about treating the pelvic floor in this population of patients?
If the loss of dopamine production in the brain causes this poverty of movement in all skeletal muscles the body, how does the pelvic floor function in the person with Parkinson disease and what should the pelvic floor rehabilitation professional know about treating the pelvic floor in this population of patients?
Let’s take a closer look referencing a very telling article about Parkinson disease and skeletal muscle function. In the Italian town of L’Aquila, a major devastating 6-point Richter scale earthquake occurred on April 6, 2009. 309 people died and there was destruction and collapse of many historical structures, some greater than 100 years old. The nearby movement disorder clinic had been following 31 Parkinson disease patients in the area, 17 of them higher functioning and the other 14 much lower functioning. In fact, of those 14, 10 of them were affected by severe freezing episodes with severe nighttime akinesia requiring assistance with bed mobility tasks, 1 was completely bedridden and the others with major fluctuations in motor performance. 13 of the 14 patients also had fluctuating cognitive functioning.
This devastating earthquake occurred at 3:30 am. All 14 of these patients were able to escape from their homes during or immediately following the event. Caregivers reported that in the majority of the cases, the person with Parkinson’s disease was the first one to be alerted to the earthquake, the first one to get out of the house, ability to alert relatives to run for safety, physically assisting relatives out of the collapsing buildings, and in some cases independently escaping down 1-2 flights of stairs.
Paradoxical kinesia is thought to be the reason for this all but sudden ability to move normally within the presence of an immediate threat to their life and lives of loved ones. Paradoxical kinesia is defined as “a sudden and brief period of mobility typically seen in response to emotional and physical stress in patient’s with advanced idiopathic Parkinson’s disease.” There are a few mechanisms hypothesized to play a role, such as, adrenaline, dopaminergic reserves activating the flight reaction, and compensatory nearby cerebellar circuitry.
There is no pathological evidence that in Parkinson disease there is any break in the continuity of the motor system. The neurologic pathways are all intact and the ability to produce muscle power is retained however requires a strong base of clinic knowledge of the disease to help these patients activate these intact motor pathways. I look forward to sharing the neurologic basis of these deficits in Parkinson disease and strategies in pelvic floor rehab to do just that!
Erica Vitek, a specialist in treating patients with neurologic dysfunction, is the author and instructor of Neurologic Conditions and Pelvic Floor Rehab, taking place September 14-16, 2018 in Grand Rapids, MI.
Bonanni, L., Thomas, A., Anzellotti, F., Monaco, D., Ciccocioppo, F., Varanese, S., Bifolchetti, S., D’Amico, M.C., Di Iorio, A. & Onofrj, M. (2010). Protracted benefit from paradoxical kinesia in typical and atypical parkinsonisms. Neurological sciences, 31(6), 751-756.
The following is a guest submission from Alysson Striner, PT, DPT, PRPC. Dr. Striner became a Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner (PRPC) in May of 2018. She specializes in pelvic rehabilitation, general outpatient orthopedics, and aquatics and treats at Carondelet St Joesph’s Hospital in the Speciality Rehab Clinic located in Tucson, Arizona.
Recently, I had a patient present with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) on his right foot. He stated that the pain had started about 10 days after his prostatectomy when someone had fallen onto his right foot. He reported a bunionectomy on that foot 7 years prior and noted an episode of plantar facilities before his prostatectomy. CRPS is defined as “chronic neurologic condition involving the limbs characterized by severe pain along with sensory, autonomic, motor, and trophic impairments” in a 2017 article "Complex regional pain syndrome; a recent update" by Goh, En Lin. The article goes on to discuss how CRPS can set off a cascade of problems including altered cutaneous innervation, central and peripheral sensitization, altered sympathetic nervous system function, circulating catecholamines, changes in autoimmunity, and neuroplasticity.
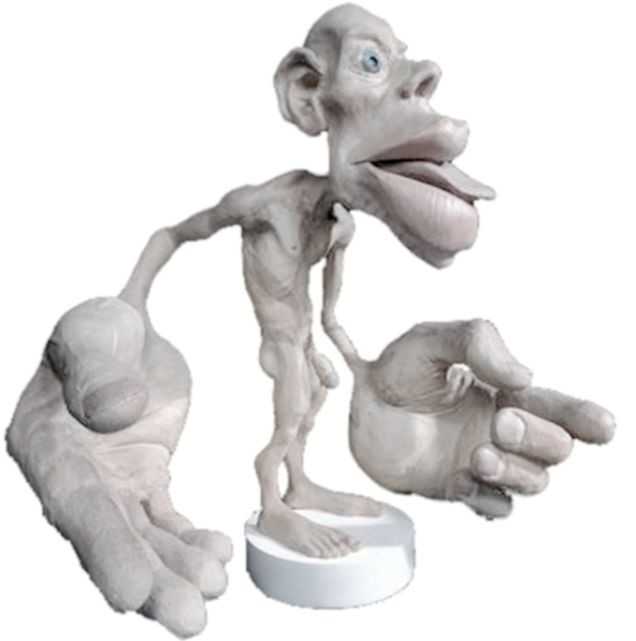 A recent persistent pain theory to explain the relationship between pelvic floor and his foot could be overflow or ‘smudging’ in his homunculus. The homunculus is the map of our physical body in our brain where the feet are located next to the genitals. Possibly when one has pain, there can be ‘smudging’ of our mental body map from one area into another. I have heard this explained as though a chalk or charcoal drawing has been swipes their hand through the picture. A recent study by Schrabrun, SM et al “Smudging of the Motor Cortex is Related to the Severity of Low Back Pain” found that people with chronic low back pain had a loss of cortical organization which and that this loss was associated with the severity and location of LBP.
A recent persistent pain theory to explain the relationship between pelvic floor and his foot could be overflow or ‘smudging’ in his homunculus. The homunculus is the map of our physical body in our brain where the feet are located next to the genitals. Possibly when one has pain, there can be ‘smudging’ of our mental body map from one area into another. I have heard this explained as though a chalk or charcoal drawing has been swipes their hand through the picture. A recent study by Schrabrun, SM et al “Smudging of the Motor Cortex is Related to the Severity of Low Back Pain” found that people with chronic low back pain had a loss of cortical organization which and that this loss was associated with the severity and location of LBP.
There are many ways to improve the organization of the homunculus and create neuroplasticity. One such way was suggested is with Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) to the bottom of the foot to affect bladder spasms and pain. In recent study, “Transcutaneous electrical stimulation of somatic afferent nerves of the foot relieved symptoms related to postoperative bladder spasms,". Zhang, C et al. 2017 found that participates that had either a bladder surgery or a prostate surgery had improvement in bladder spasm symptoms and VAS scores on day two and three. Their protocol was to use two electrodes over the bottom of the foot at 5 Hz with 0.2 millisecond pulse width until a muscle twitch was achieved and was increased, but still comfortable for an hour (there is a picture of electrode placement in the article). The authors note that this neuromodulation of the foot sensory nerves may inhibit interactions between the somatic peripheral neuropathway and autonomic micturition reflex to calm the bladder and pain.
No matter what we do to help calm nervous systems from the top down; pain neuroscience education, mindful based relaxation, graded motor imagery, or from the bottom up; de-sensitization, biofeedback, or good old-fashioned TENS. The result is the same; a cortical organization and happier patients.
En Lin Goh†, Swathikan Chidambaram† and Daqing Ma. "Complex regional pain syndrome: a recent update". Burns & Trauma 2017 5:2.https://doi.org/10.1186/s41038-016-0066-4"
Schabrun SM, Elgueta-Cancino EL, Hodges PW. "Smudging of the Motor Cortex Is Related to the Severity of Low Back Pain." Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017 Aug 1;42(15):1172-1178. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000938
Chanjuan Zhang, et al. "Transcutaneous electrical stimulation of somatic afferent nerves in the foot relieved symptoms related to postoperative bladder spasms". BMC Urol. 2017; 17: 58. doi: 10.1186/s12894-017-0248-9
In a previous post on The Pelvic Rehab Report, Sagira Vora, PT, MPT, WCS, PRPC explored the impact that pelvic floor exercises can have on arousal and orgasm in women. Today we hear part two of the conversation, and learn what factors can impact a woman's ability to achieve orgasm.
 “An orgasm in the human female is a variable, transient peak sensation of intense pleasure, creating an altered state of consciousness, usually with an initiation accompanied by involuntary, rhythmic contractions of the pelvic striated circumvaginal musculature, often with concomitant uterine and anal contractions, and myotonia that resolves the sexually induced vasocongestion and myotonia, generally with an induction of well-being and contentment.”
“An orgasm in the human female is a variable, transient peak sensation of intense pleasure, creating an altered state of consciousness, usually with an initiation accompanied by involuntary, rhythmic contractions of the pelvic striated circumvaginal musculature, often with concomitant uterine and anal contractions, and myotonia that resolves the sexually induced vasocongestion and myotonia, generally with an induction of well-being and contentment.”
Wow, that sounds like paradise! The question is--how to get there? Many of our cohorts and many our female patients have not experienced this or orgasm happens for them rarely. Findings from surveys and clinical reports suggest that orgasm problems are the second most frequently reported sexual problems in women. Some of the reasons cited for lack of orgasm are orgasm importance, sexual desire, sexual self-esteem, and openness of sexual communication with partner by Kontula el. al. in 2016. Rowland found that most commonly-endorsed reasons were stress/anxiety, insufficient arousal, and lack of time during sex, body image, pain, inadequate lubrication.
One factor that comes up consistently, is the ability of women to focus on sexual stimuli. This point has been brought up by various studies and presented in different ways. Chambless talks about mindfulness training and improvements in orgasm ability noted equally in women who practiced mindfulness vs. women who engaged in Kegels and mindfulness. Rosenbaum and Padua note in their book, The Overactive Pelvic Floor, “women who do not have a low-tone pelvic floor and who seek to enhance sexual arousal and more frequent orgasms have not much to gain from pelvic floor muscle training. Actually, a relaxed pelvic floor and mindful attention to sexual stimuli and bodily sensations seem a more effective means of enhancing sexual arousal and orgasm.” Various studies specifically studying the effect of mindfulness training have demonstrated both improved arousal and orgasm ability in women who practiced mindfulness. Brotto and Basson found their treatment group, which consisted of 68 otherwise healthy women, who underwent mindful meditation, cognitive behavioral training and education, improved in sexual desire, sexual arousal, lubrication, sexual satisfaction, and overall sexual functioning.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy appears to play a significant role in improving sexual function in women. Meston et. al. notes, “cognitive behavioral therapy for anorgasmia focuses on promoting changes in attitudes and sexually relevant thoughts, decreasing anxiety, and increasing orgasmic ability and satisfaction. To date there are no pharmacological agents proven to be beneficial beyond placebo in enhancing orgasmic function in women.”
Alas, there are no magic pills to create the above described “state of altered consciousness,” allowing women a sense of “well-being and contentment.” However, mindfulness training and cognitive behavioral therapy are both accessible and attainable for women who want to improve their ability to enjoy this much desired state. Many Pelvic floor therapist incorporate cognitive behavioral and mindfulness approaches in their practice.
The studies above mention pain as one of the factors for inability to experience arousal and orgasm. Hucker and Mccabe even noted that their mindfulness treatment group demonstrated significant improvements in all domains of female sexual response except for sexual pain. Dealing with sexual pain is a daily battle pelvic floor therapist face each day. So, how do women with sexual pain dysfunction differ from women who are experiencing sexual dysfunction but not pain? Let’s explore this in our next blog…
Chambless DL, Sultan FE, Stern TE, O’Neill C, Garrison S. Jackson A. Effect of pubococcygeal exercise on coital orgasm in women. J Consult CLin Psychol. 1984; 52:114-8
Bratto LA, Basson R. Group mindfulness-based therapy significantly improves sexual desire in women Behav Res Ther. 2014 Jun; 57:43-5
Hucker A. Mccabe MP. Incorporating Mindfulness and Chat Groups Into an Online Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Mixed Female Sexual Problems. J Sex Res. 2015;52(6):627-33
Kontula O., Mettienen A. Determinants of female sexual orgasms. Socioaffect Neurosci Psychol. 2016 Oct 25;6:31624. doi: 10.3402/snp.v6.31624. eCollection 2016
Meston CM1, Levin RJ, Sipski ML, Hull EM, Heiman JR. Women’s orgasm. Annu Rev Sex Res. 2004;15:173-257. Review
Rosenbaum, Talli Y., Padoa, Anna. The overactive Pelvic floor. 1st ed. 2016
Roland DL, Cempel LM, Tempel AR. Women’s attributions on why they have difficulty reaching orgasm. J. Marital Therapy. 2018 Jan 3:0
I’m Elizabeth Hampton PT, DPT, WCS, BCB-PMD and I teach “Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain”, which offers practitioners a systematic screening approach to rule in or rule out contributing factors to pelvic pain. This course helps clinicians to understand and screen for the common co-morbidities associated with pelvic floor dysfunction, like labral tears, discogenic low back pain, nerve entrapments, coccygeal dysfunction, and more. Importantly, it also coaches clinicians to organize information in a way that enables them to prioritize interventions in complex cases. I've noticed that there are some questions that course participants frequently have as they talk through common themes in their care challenges and wrote this blog to share some clinical pearls you may find to be helpful for your own practice or as an explanation to your clients.
Here are some of the most common questions that I get when teaching Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain:
1) Question: How do I even start to organize information when a client has a complex history and I am feeling overwhelmed?
I write down a road map with key categories: Bowel and bladder; Spine; Sacroiliac Joint/Pubic Symphysis; Hip; Pelvic floor muscles; biomechanics; respiration; neural upregulation; whatever details can be fit into ‘big buckets’ of information. I use it to both organize my thoughts for my notes, as well as educate the client as to what my findings are and the design of their treatment program.
2) Question: How do you get your clients to do a bowel and bladder diary?
I am proud to say that I can talk anyone into a 7 day bowel and bladder diary because I tell them how incredibly helpful it is to understand the way their body responds to what they eat, drink, and daily habits. It’s my secret weapon to snag clients to start connecting with their body and listening to their details, educate about defecation ergonomics and what happens in multiple systems when there is pelvic floor overactivity. It’s a great teaching tool that facilitates self-reflection and how their self-care choices impact their body’s behavior.
3) Question: How do you educate clients about pelvic floor function so they don’t focus so much on Kegels?
Pelvic floor muscles do three things:
-
They contract gently, or powerfully, with no discomfort, and totally normal breathing; PFMs should have the same kind of nuanced control like your voice does: they should be able to do a gentle contraction, like a “whisper” or a powerful contraction, like a “shout”, depending on the task position and intent.
-
They relax fully and completely when the body is resting in support, or they should be able to relax to a supportive level when they are needed posturally. Relaxation should be its own celebrated event!
-
They should be able to relax and gently lengthen.
Faculty member Elizabeth Hampton PT, DPT, WCS, BCB-PMD is the author and instructor of Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain, a course designed to help practitioners utilize differential diagnosis in evaluating pain. Join Dr. Hampton in Portland, OR on July 27-29, 2018 or November 2-4, 2018 in Phoenix, AZ.
Kelly Feddema, PT, PRPC returns in a guest post on Pregnancy Associated Ligamentous Laxity. Kelly practices pelvic floor physical therapy in the Mayo Clinic Health System in Mankato, MN, and she became a Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner in February of 2014. See her post on diastasis recti abdominis on the pelvic rehab report, and learn more about evaluating and treating pregnant patients by attending Care of the Pregnant Patient!
 Pregnancy associated ligamentous laxity is something that we, as therapists, are fairly well aware of and see the ramifications of quite often in the clinic. We know the female body is changing to allow the mother to prepare for the growth and birth of the tiny (or sometimes not so tiny) human she is carrying. We also know that the body continues to evolve after the birth to eventually return to a post-partum state of hormonal balance. Do we think much about what this ligamentous laxity can mean during the actual delivery? Does laxity predispose women to other obstetric injury?
Pregnancy associated ligamentous laxity is something that we, as therapists, are fairly well aware of and see the ramifications of quite often in the clinic. We know the female body is changing to allow the mother to prepare for the growth and birth of the tiny (or sometimes not so tiny) human she is carrying. We also know that the body continues to evolve after the birth to eventually return to a post-partum state of hormonal balance. Do we think much about what this ligamentous laxity can mean during the actual delivery? Does laxity predispose women to other obstetric injury?
A recent study in the International Urogynecology Journal assessed ligamentous laxity from the 36th week of pregnancy to the onset of labor by measuring the passive extension of the non-dominant index finger with a torque applied to the second metacarpal phalangeal joint. They collected the occurrence and classification of perineal tears in 272 out of 300 women who ended up with vaginal deliveries and looked for a predictive level of second metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP) laxity for obstetric anal sphincter injury (OASI). They concluded that the increased ligamentous laxity did seem associated with OASI occurrence which was opposite of their initial idea that more lax ligaments would be at less of a risk of OASI.
In another study from the same journal published in 2017, researchers studied if levator hiatus distension was associated with peripheral ligamentous laxity during pregnancy. This was a small study but they concluded that levator hiatus distension and ligamentous laxity were significantly associated during pregnancy. They did admit the relationship was weak and results would have to be confirmed with a larger study and more specific study methods. However, the likelihood of major levator trauma more than triples during the reproductive years from under 15% at age 20 to over 50% at age 40(University of Sydney) so it seems that these issues warrant continued study with the continued trend toward delayed child bearing in Western cultures.
Gachon, B., Desgranges, M., Fradet, L. et al. Int Urogynecol J (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-018-3598-2
Gachon, B., Fritel, X., Fradet, L. et al. Int Urogynecol J (2017) 28: 1223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-016-3252-9
University of Sydney. "Levator Trauma" sydney.edu.au. Accessed 25 April 2018.
Coaching Patients to Engage in Positive Activities to Improve Outcomes
Substantial attention has been given to the impact of negative emotional states on persistent pain conditions. The adverse effects of anger, fear, anxiety and depression on pain are well-documented. Complementing this emphasis on negative emotions, Hanssen and colleagues suggest that interventions aimed at cultivating positive emotional states may have a role to play in pain reduction and/or improved well-being in patients, despite pain. They suggest positive affect may promote adaptive function and buffer the adversities of a chronic pain condition.
 Hanssen and colleagues propose positive psychology interventions could contribute to improved pain, mood and behavioral measures through various mechanisms. These include the modulation of spinal and supraspinal nociceptive pathways, buffering the stress reaction and reducing stress-induced hyperalgesia, broadening attention, decreasing negative pain-related cognitions, diminishing rigid behavioral responses and promoting behavioral flexibility.
Hanssen and colleagues propose positive psychology interventions could contribute to improved pain, mood and behavioral measures through various mechanisms. These include the modulation of spinal and supraspinal nociceptive pathways, buffering the stress reaction and reducing stress-induced hyperalgesia, broadening attention, decreasing negative pain-related cognitions, diminishing rigid behavioral responses and promoting behavioral flexibility.
In a feasibility trial, 96 patients were randomized to a computer-based positive activity intervention or control condition. The intervention required participants perform at least one positive activity for at least 15 minutes at least 1 day/week for 8 weeks. The positive activity included such tasks as performing good deeds for others, counting blessings, taking delight in life’s momentary wonders and pleasures, writing about best possible future selves, exercising or devoting time to pursuing a meaningful goal. The control group was instructed to be attentive to their surroundings and write about events or activities for at least 15 minutes at least 1 day/week for 8 weeks. Those in the positive activity intervention demonstrated significant improvements in pain intensity, pain interference, pain control, life satisfaction, and depression, and at program completion and 2-month follow-up. Based on these promising results, authors suggest that a full trial of the intervention is warranted.
Rehabilitation professionals often encourage patients with persistent pain conditions to participate in activities they enjoy. This research highlights the importance of this instruction and patient guidelines can include the activities identified in the Muller article. In addition, mindful awareness training may further enhance a patient’s experience as he or she learns to pay close attention to the physical sensations, emotions and thoughts that accompany positive experiences. I look forward to discussing this article as well as sharing the principles and practices of mindfulness in my upcoming course, Mindfulness-Based Pain Treatment at Samuel Merritt University, Oakland, CA. Course participants will learn about mindfulness and pain research, practice mindful breathing, body scan and movement and expand their pain treatment tool box with practical strategies to improve pain treatment outcomes. I hope you will join me!
Hanssen MM, Peters ML, Boselie JJ, Meulders A. Can positive affect attenuate (persistent) pain? Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(12):80.
Muller R, Gertz KJ, Molton IR, et al. Effects of a tailored positive psychology intervention on well-being and pain in individuals with chronic pain and physical disability: a feasibility trial. Clin J Pain.2016;32(1):32-44.
Men who present with chronic pelvic pain frequently have symptoms referred along the penis and into the tip of the penis, or glans. Symptoms may include numbness, tingling, aching, pain, or other sensitivity and discomfort. The tip of the penis, or glans, is a sensory structure, which allows for sexual stimulation and appreciation. This same capacity for valuable sensation can create severe discomfort when signals related to the glans are overactive or irritating. One of the most common complaints with this symptom is a level of annoyance and distraction, with level of bother worsening when a person is less active or not as mentally engaged with tasks. Wearing clothing that touches the tip of the penis (such as underwear, jock straps, jeans, or snug pants) may be limited and may worsen symptoms. When uncovering from where the symptoms originate, the culprit is often the dorsal nerve of the penis, which is sensible given that the glans is innervated by this branch of the pudendal nerve. If we consider this possibility (because certainly there are other potential causes) we find that there are many potential sites of pudendal nerve irritation to consider. First, let’s visualize the anatomy of the nerve.
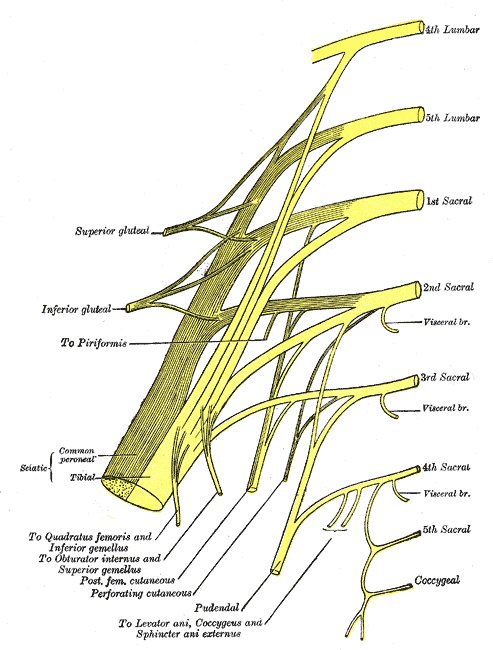
Following the usually accepted descriptions of the dorsal nerve, we know that it is a terminal branch of the pudendal nerve that primarily is created from the mid-sacral nerves. This can lead us to include the lumbosacral region in our examination and treatment, yet in my clinical experience, there are other sites that more often reproduce pain in the glans. As the dorsal nerve branches off of the pudendal, usually after the location of the sacrotuberous ligament, it passes through and among the urogenital triangle layers of fascia where compression or irritation may generate symptoms.
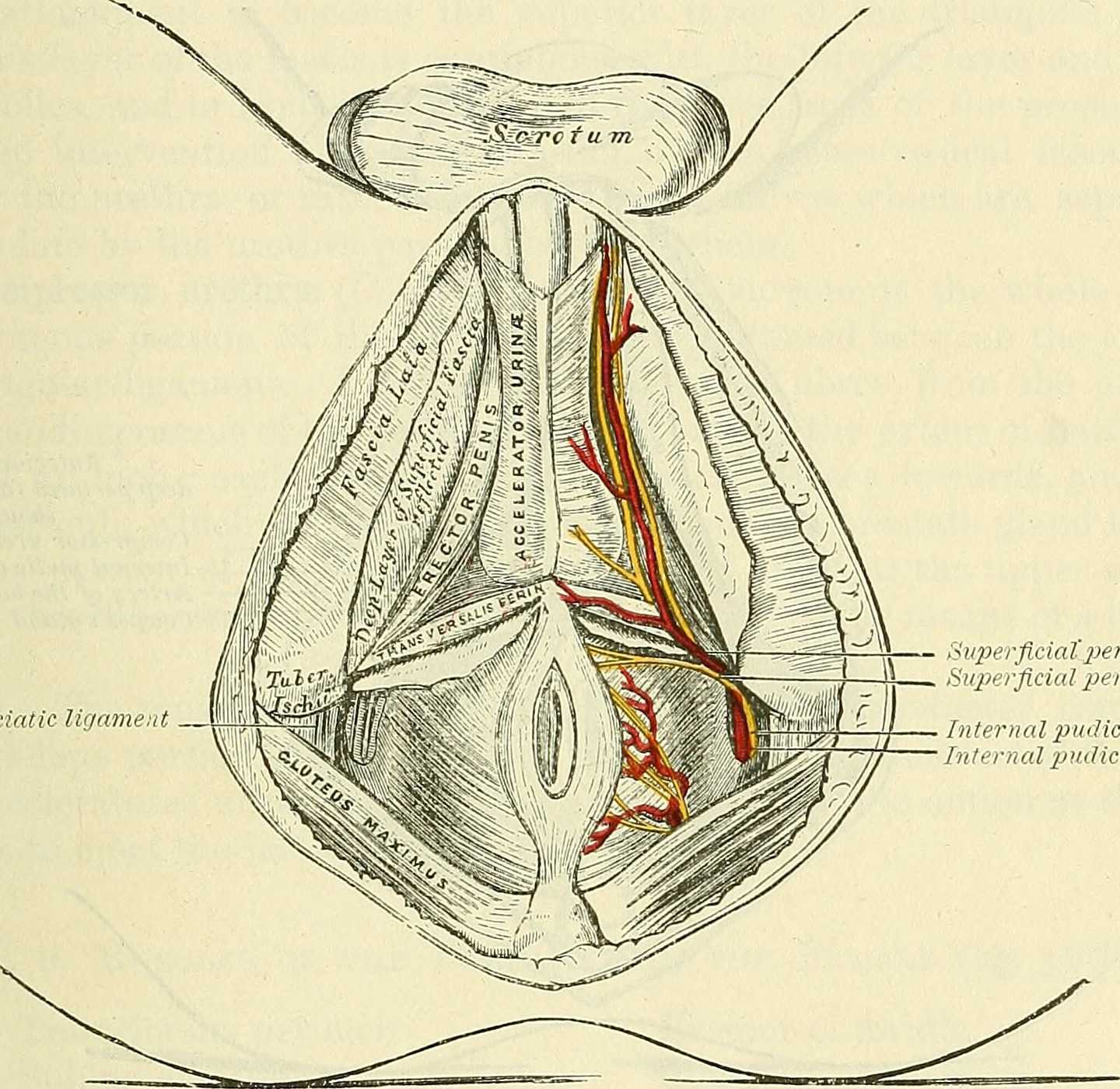
As the nerve travels towards the pubic bone, it will pass inferior to the pubic bone, a location where suspensory ligaments of the penis can be found as well as pudendal vessels and fascia. This is also a site of potential compression and irritation, and palpation to this region may provide information about tissue health. Below is a cross-section of the proximal penis, allowing us to see where the pudendal nerve and vessels would travel inferior to the pubic bone.
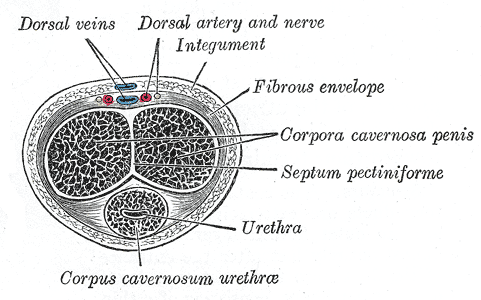
As the dorsal nerve extends along either side of the penis, giving smaller branches along its path towards the glans, the nerve may also be experiencing soft tissue irritation along the length of the penis or even locally at the termination in the glans.
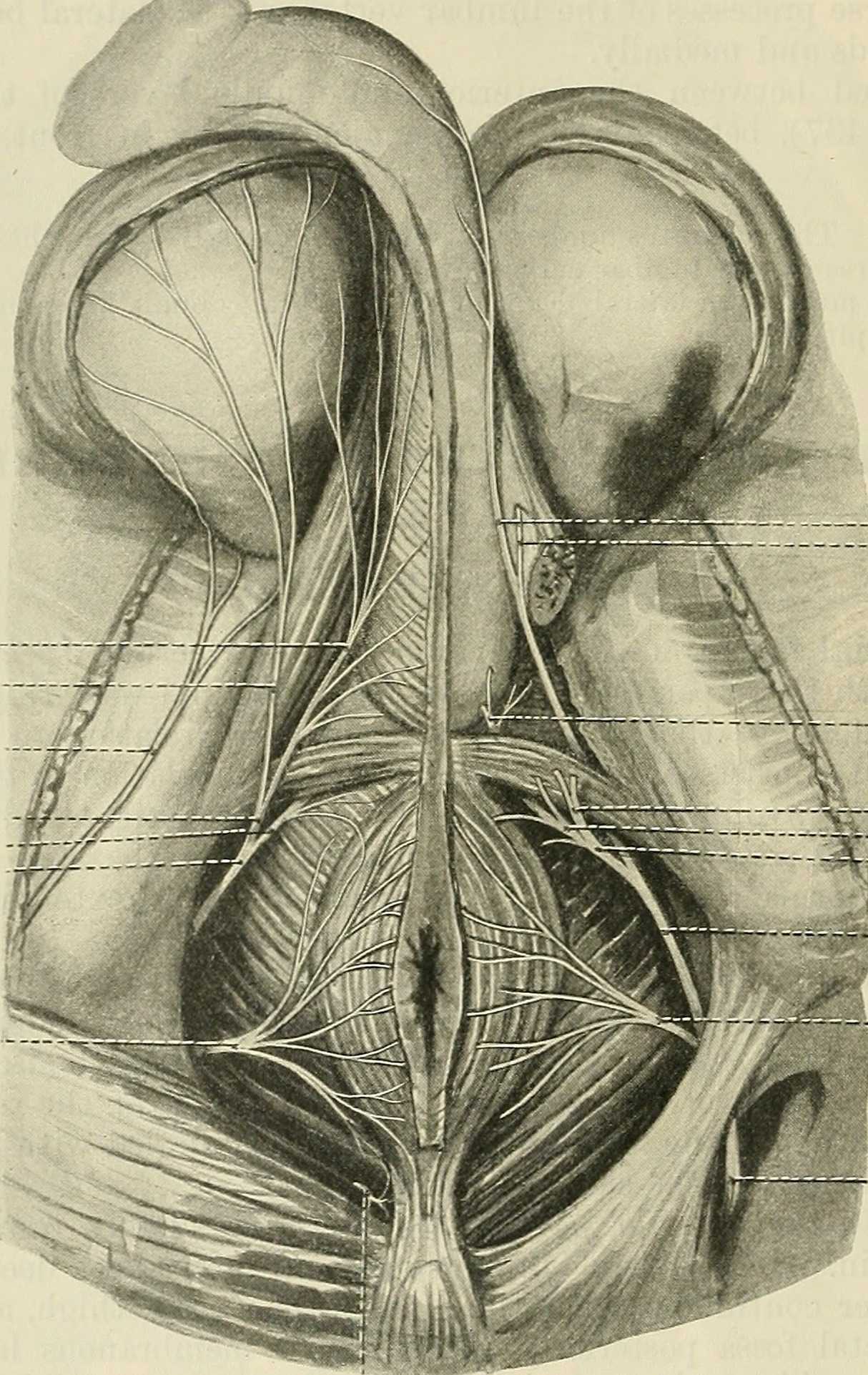
Palpation internally (via rectum) or externally may be a part of the assessment as well as treatment of this condition. Oftentimes, tip of the penis pain can be reproduced with palpation internally and directed towards the anterior levator ani and the connective tissues just inferior to the pubic bone. It may be difficult to know if the muscle is providing referred pain, or if the nerve is being tensioned and reproducing symptoms, however gentle soft tissue work applied to this area is often successful in reducing or resolving symptoms regardless of the tissue involved. In my experience, these symptoms of referred pain at the tip of the penis is often one of the last to resolve, and the use of topical lidocaine may be helpful in managing symptoms while healing takes place. Home program self-care including scar massage if needed, nerve mobilizations, trunk and pelvic mobility and strengthening, and advice for returning to meaningful activities can play a large role in resolution of pain in the glans.
If you would like to learn more about treating genital pain in men, consider joining me in Male Pelvic Floor: Function, Dysfunction, & Treatment. The 2018 courses will be in Freehold, NJ this June, and Houston, TX in September.
Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC is the author and instructor of Neurologic Conditions and Pelvic Floor Rehab, a new course coming to Grand Rapids, MI and Philadelphia, PA. This post is the next in her series on creating a course about neurologic conditions and pelvic rehabilititation.
Being a clinician, as we evaluate and treat people with pelvic health conditions, we typically take all systems of the body into account. We take the problem presented to us by the client and we examine, from all angles, how we might go about advice and treatment to best achieve their goals in alleviating the problem. We do a full review of medical history and pharmacology. We examine our client in-depth from a musculoskeletal perspective. We look at psychological contributions to the problem they are facing. We can look at their lifestyle and have them make a detailed diary to help us analyze their bladder, bowel, fluid intake and dietary habits. Do we also always include a look at the neurological components? Do we know what we are looking for? What are the best tools we can have in our toolbox as clinicians to look at our client’s problem through a “neuro brain”?
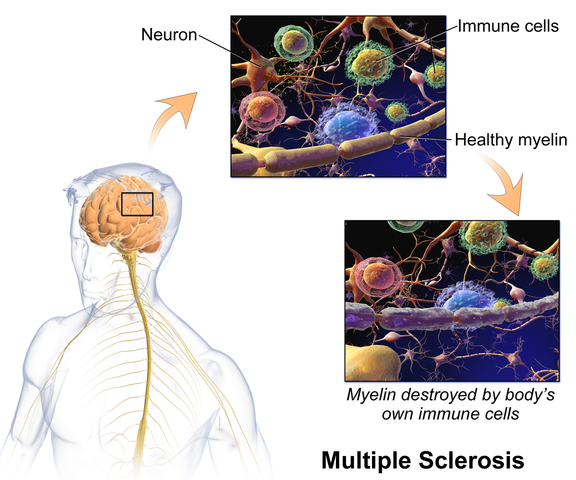 In writing each lecture of this course, I have had to step back each time I am developing a new concept and look at it with in-depth thought and contemplation about how I will use this in the clinic to assess my client’s concerns using a neuro-based approach. Taking the concepts and facts about the musculoskeletal system that we know well and then taking a look at the neurological systems contributions and relationship to that dysfunction can be challenging. The main reason for this challenge is that neuro system dysfunction is many times hard explain, presents with inconsistent or changing symptoms, may have motor or sensory deficits together or by themselves, may radiate to different locations than where the true dysfunction is located, and may have developed into central sensitization causing a hypervigilance to typically non-painful stimuli.
In writing each lecture of this course, I have had to step back each time I am developing a new concept and look at it with in-depth thought and contemplation about how I will use this in the clinic to assess my client’s concerns using a neuro-based approach. Taking the concepts and facts about the musculoskeletal system that we know well and then taking a look at the neurological systems contributions and relationship to that dysfunction can be challenging. The main reason for this challenge is that neuro system dysfunction is many times hard explain, presents with inconsistent or changing symptoms, may have motor or sensory deficits together or by themselves, may radiate to different locations than where the true dysfunction is located, and may have developed into central sensitization causing a hypervigilance to typically non-painful stimuli.
In brain storming our ideas for course creation, much was said about thinking back to college or other continuing education courses and “learning a little about a lot of things neuro” but not the in-depth knowledge one might want to have when focusing their attention on specific neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson disease, demyelinating diseases such as Multiple Sclerosis, injury to the brain due to cerebral vascular accident or incomplete or complete spinal cord injury.
As I progress deep into the development of this course, I have my “neuro brain” on and a persistent focus set on providing clinicians with as much in-depth information on neurological contributions to pelvic floor function and dysfunction. I want clinicians to walk away from this course feeling confident that through evaluation of a client that has been diagnosed with Parkinson disease, Multiple Sclerosis or suffered a spinal cord injury, they would have the tools to develop an in-depth treatment plan that would provide these clients with the best results possible to improve their quality of life. I also want clinicians to have the confidence to market themselves to their local neurologists. This is an entirely new avenue for developing a referral base in pelvic health work. Many times for clients who have chronic neurological conditions, the problem list is long and bladder, bowel and sexual health concerns might not even be broached within the very short physician appointment times. We can give our neurologists new treatments to be confident in and excited about to improve their patient’s quality of life!
When a woman is given a cancer diagnosis, her entire world is turned upside down and inside out. There are so many things to think about; medical treatments, financial concerns, family concerns, and emotional upheaval. Sex may be the last thing that a woman may think about when she is actively going through treatment. However, at what rate are survivors having issues after treatment is complete?
 A recent study published in the journal Cancer looked at just this. A 2-year longitudinal study was performed that tracked young adults (18-39 years old) through and after their cancer diagnosis. The most common cancers seen in the samples were leukemia, breast cancer, soft-tissue sarcoma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The patients completed the Medical Outcomes Study Sexual Functioning Scale at 4 months, 6 months, and 24 months after diagnosis. At 2 years after diagnosis over 50% of the patients surveyed reported some degree of sexual dysfunction. Women that were in a committed relationship had an increased likelihood for experiencing sexual dysfunction; while men had increased rate of reporting sexual issues regardless of their relationship status.
A recent study published in the journal Cancer looked at just this. A 2-year longitudinal study was performed that tracked young adults (18-39 years old) through and after their cancer diagnosis. The most common cancers seen in the samples were leukemia, breast cancer, soft-tissue sarcoma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The patients completed the Medical Outcomes Study Sexual Functioning Scale at 4 months, 6 months, and 24 months after diagnosis. At 2 years after diagnosis over 50% of the patients surveyed reported some degree of sexual dysfunction. Women that were in a committed relationship had an increased likelihood for experiencing sexual dysfunction; while men had increased rate of reporting sexual issues regardless of their relationship status.
Women that undergo cancer treatment have several reasons that could be influencing their sexual function. Fatigue is a complaint that is often expressed by cancer patients. Their body image is often altered due to surgeries that have been performed. Chemotherapy and hormonal therapy often push women into menopause which then leads to vaginal dryness. Additionally, radiation and surgical treatment can lead to scar tissue, fibrosis, and stenosis of the vagina and pelvic floor muscles.
This is where physical therapy can help! In the Pelvic Floor Series Capstone course we teach advanced techniques that help treat pelvic floor issues by working on both the muscles, and the fascia. We also cover techniques that decrease the tenderness in the muscles that then allow you to stretch the muscle with less discomfort.
All of the techniques taught in Capstone are gentle but effective. The cancer survivor is the perfect population to use these gentle techniques on! Think of how rewarding our job will be when we help relieve the pain that may be associated with intercourse, and therefore improve intimacy of a cancer survivor with her partner!
Come join us for Capstone and learn techniques that will take your treatment skills to the next level!
Acquati, Zebrack, Faul, et al. Sexual functioning among young adult cancer patients: A 2-year longitudinal study. Cancer. 2018; 124(2): 398-405.
A couple of years ago, I wrote a blog about an interesting article by Hides and Stanton that related size and strength of the multifidus to the risk for lower extremity injury in Australian professional football players.
 Now some of the same researchers are looking above. A prospective cohort study has recently been published that examined factors and their effects on concussions. Physical measurements of risk factors were taken in pre-season among Australian football players. These measurements included balance, vestibular function, and spinal control. To measure these outcomes the following tests were included: for balance the amount of sway across six test conditions were performed; vestibular function was tested with assessments of ocular-motor and vestibular ocular reflex; and for spinal control cervical joint position error, multifidus size, and contraction ability was tested. The objective measure was concussion injury obtained during the season diagnosed by the medical staff.
Now some of the same researchers are looking above. A prospective cohort study has recently been published that examined factors and their effects on concussions. Physical measurements of risk factors were taken in pre-season among Australian football players. These measurements included balance, vestibular function, and spinal control. To measure these outcomes the following tests were included: for balance the amount of sway across six test conditions were performed; vestibular function was tested with assessments of ocular-motor and vestibular ocular reflex; and for spinal control cervical joint position error, multifidus size, and contraction ability was tested. The objective measure was concussion injury obtained during the season diagnosed by the medical staff.
The findings were so interesting! Age, height, weight, and number of years playing football were not associated with concussion. Cross-sectional area of the multifidus at L5 was 10% smaller in players who went on to sustain a concussion compared to players that did not receive a concussion. There were no significant differences observed between the players that received concussion and those who did not with respect to the other physical measures that were obtained.
With all the recent evidence about the harmful effects of concussions amongst our athletes, I find this information amazing and am excited to see where the researchers take this in the future. The next question for the physical therapist is how do we train the multifidus? The multifidus can be difficult to retrain in some individuals. It is a hard muscle for some patients to learn to recruit. Biofeedback using ultrasound imaging can make this daunting task easier for many patients. With the cost of ultrasound units coming down, it is also a very reasonable tool for clinics to look at investing in.
Join me to learn more about the multifidus and how to use ultrasound imaging in the retraining process. Future course offerings include August in New Jersey, and November in San Diego. I look forward to seeing you there!
Hides, Stanton. Can motor control training lower the risk of injury for professional football players? Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014; 46(4): 762-8.
Leung, Hides, Franettovich Smith, et al. Spinal control is related to concussion in professional footballers. Brit J of Sports Med. 2017; 51(11).
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://hermanwallace.com/