The following post comes to us from Herman & Wallace faculty member Allison Ariail, PT, DPT, CLT-LANA, BCB-PMD, PRPC. Allison authored "Use of transabdominal ultrasound imaging in retraining the pelvic-floor muscles of a woman postpartum" and is a leading expert in the use of ultrasound imaging for pelvic rehab. She is the author and instructor of the Rehabilitative Ultrasound Imaging: Women’s Health and Orthopedic Topics offered with Herman & Wallace.
In the pelvic floor series we learn how to perform examinations for cystoceles and rectoceles. It can be more difficult for therapists to examine and quantify the degree of uterine descent. In the last few years translabial ultrasound imaging has also been used to identify what is happening in the anterior compartment upon Valsalva and pelvic floor contraction, including the uterus. This is helpful when trying to determine the degree of uterine prolapse. Degree of pelvic organ descent visible on by ultrasound has been shown to have a near-linear relationship with measures on the POPQ.
 Clinically we see that some patients with severe prolapses have few symptoms, while other patients with smaller prolapses will have more severe complaints of symptoms. This can be puzzling to the clinician who is trying to treat prolapse patients. Shek and Dietz performed a study to set cutoff measures of uterine descent that will predict symptoms of prolapse. Translabial ultrasound imaging was performed on 538 women with 263 women reporting prolapse symptoms. Seventy-five percent of the women presented with grade two or greater prolapse on the POPQ, with most of being cystoceles or rectoceles. The women with more complaints of symptoms of prolapse were more likely to have uterine prolapse. There was a strong association between degree of uterine descent and symptoms of prolapse. They determined that an optimal cutoff to predict symptoms of prolapse due to uterine descent is a cervix descending to 15 mm above the pubic symphysis.
Clinically we see that some patients with severe prolapses have few symptoms, while other patients with smaller prolapses will have more severe complaints of symptoms. This can be puzzling to the clinician who is trying to treat prolapse patients. Shek and Dietz performed a study to set cutoff measures of uterine descent that will predict symptoms of prolapse. Translabial ultrasound imaging was performed on 538 women with 263 women reporting prolapse symptoms. Seventy-five percent of the women presented with grade two or greater prolapse on the POPQ, with most of being cystoceles or rectoceles. The women with more complaints of symptoms of prolapse were more likely to have uterine prolapse. There was a strong association between degree of uterine descent and symptoms of prolapse. They determined that an optimal cutoff to predict symptoms of prolapse due to uterine descent is a cervix descending to 15 mm above the pubic symphysis.
This study intrigues me and makes me wonder how much we are focusing on cystoceles and rectoceles and not looking at uterine prolapses. Using translabial ultrasound imaging is a nice tool to allow the clinician to see what is going on with all of the pelvic organs. With one Valsalva maneuver you are able to assess a lot of information including support of the pelvic organs. It also gives the clinician another way to quantify the degree of prolapse. Ultrasound imaging is a wonderful tool that clinicians can use for assessment as well as a biofeedback tool. If you are interested in learning how to perform this type of assessment, I will be teaching Rehabilitative Ultrasound Imaging: Women’s Health and Orthopedic Topics May 1-3 in Dayton, OH.
Shek KL, Dietz HP. What is abnormal uterine descent on translabial ultrasound? Int. Urogynecol J. 2015; 26(12)1783-7.
Exercise in pregnancy is a loaded topic. We commonly see images of women doing vigorous exercise in late pregnancy accompanied by judgmental statements about the safety of such activity not only for the woman, but also for the baby. Many myths persist about exercise in pregnancy, and it’s our role as health care specialists to educate women about what is known about exercising. Holly Herman, co-founder of the Herman & Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute, has been educating providers about this topic for most of her career. Anyone lucky enough to take a course on pregnancy and postpartum issues from Holly Herman knows that her style of teaching is effective and her passion is contagious. From Holly’s use of patient stories to wonderful humor, you can really “get it” when it comes to clinical concepts and strategies. One of Holly’s clinical pearls that really stuck with me after learning about exercise and pregnancy is the research completed by James Clapp in his book “Exercise in Pregnancy”. In short, the book dispels the myth that women shouldn’t exercise in pregnancy and in fact reports on the benefits of exercise to both Mom and baby for labor, delivery, and beyond. In signature style, Holly held this book up in front of the class and to great laughter said, “And this is the book you should buy for your mother-in-law.”
 Another myth that has been perpetuated in relation to pregnancy, labor and delivery is the notion that exercising can make the pelvic floor muscles short, tight, and more narrow, making delivery more difficult. In an article we reported on previously about women being “too tight to give birth” the authors concluded that strong pelvic floor muscles do not lead to challenges with birthing. (Bo et al., 2013) In a more recent article that addressed this issue, Kari Bo and colleagues studied 274 women for levator hiatus (LH) width to see if exercising in late pregnancy did in fact narrow this space. At week 37 of gestation, the exercisers were measured to have a significantly larger LH than the non-exercisers. (Exercisers were defined as women who exercised 30 minutes or more 3 times per week versus the non-exercisers.) The authors conclude that there were not any significant differences in labor outcomes or in delivery outcomes between the groups. (Bo et al., 2015)
Another myth that has been perpetuated in relation to pregnancy, labor and delivery is the notion that exercising can make the pelvic floor muscles short, tight, and more narrow, making delivery more difficult. In an article we reported on previously about women being “too tight to give birth” the authors concluded that strong pelvic floor muscles do not lead to challenges with birthing. (Bo et al., 2013) In a more recent article that addressed this issue, Kari Bo and colleagues studied 274 women for levator hiatus (LH) width to see if exercising in late pregnancy did in fact narrow this space. At week 37 of gestation, the exercisers were measured to have a significantly larger LH than the non-exercisers. (Exercisers were defined as women who exercised 30 minutes or more 3 times per week versus the non-exercisers.) The authors conclude that there were not any significant differences in labor outcomes or in delivery outcomes between the groups. (Bo et al., 2015)
Without a doubt, the patient’s obstetrician gives primary direction to the patient when any high-risk issues are present. Most women however, are basing their exercise choices on experience, on misinformation, myths, or popular opinion. It is our responsibility to engage women in conversations about her health, wellness, and fitness, and to appropriately counsel on exercise during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Most of us lacked proper education about this important population in our primary graduate training, and therefore must seek out information to fill in the gaps. If you are interested in filling in any gaps, join us at one of our peripartum courses around the country. Your next opportunities to take these courses are:
Care of the Postpartum Patient - Seattle, WA
Mar 12, 2016 - Mar 13, 2016
Care of the Pregnant Patient - Somerset, NJ
Apr 30, 2016 - May 1, 2016
Care of the Pregnant Patient - Akron, OH
Sep 10, 2016 - Sep 11, 2016
Bø, K., Hilde, G., Jensen, J. S., Siafarikas, F., & Engh, M. E. (2013). Too tight to give birth? Assessment of pelvic floor muscle function in 277 nulliparous pregnant women. International urogynecology journal, 24(12), 2065-2070.
Bø, K., Hilde, G., Stær-Jensen, J., Siafarikas, F., Tennfjord, M. K., & Engh, M. E. (2015). Does general exercise training before and during pregnancy influence the pelvic floor “opening” and delivery outcome? A 3D/4D ultrasound study following nulliparous pregnant women from mid-pregnancy to childbirth. British journal of sports medicine, 49(3), 196-199.
Clapp, J. F., Cram, C. (2012) Exercising Through Your Pregnancy. Addicts Books
A few years ago, I was convinced my left hip pain was due to osteoarthritis. When my hip locked up after a 14 mile run, my manual therapist husband differentially diagnosed the pain as discogenic. Partly in denial and partly wanting to know the extent of the “damage,” I got an x-ray of my left hip, which was completely normal, and a lumbar MRI, which wasn't pretty. The source of my hip pain was a disc bulge at L3-4 and L4-5 with a Schmorl's node at L5-S1 to boot. Instead of riding the train of thought that we treat what hurts, therapists need to disembark and look further for the source, as suggested in the course, “Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain.”
 A case report published in the International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy by Livingston, Deprey, and Hensley (2015) documents the discovery of a deeper problem than the referring diagnosis of greater trochanteric pain syndrome. A 29 year old female had to stop running because of lateral hip pain that began 3 months after increasing the intensity and frequency of her running and low impact plyometrics. She had pain in sitting and while running. During the evaluation, she demonstrated a positive Trendelenburg, weak and painless hip abductors, and a positive single leg hop test on concrete. When the pain was not elicited with single leg hop on a foam surface, the patient was referred back to the physician for magnetic resonance imaging. The patient was later diagnosed with an acetabular stress fracture. The therapist’s thorough examination helped prevent possible avascular necrosis or a more traumatic fracture of the pelvis.
A case report published in the International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy by Livingston, Deprey, and Hensley (2015) documents the discovery of a deeper problem than the referring diagnosis of greater trochanteric pain syndrome. A 29 year old female had to stop running because of lateral hip pain that began 3 months after increasing the intensity and frequency of her running and low impact plyometrics. She had pain in sitting and while running. During the evaluation, she demonstrated a positive Trendelenburg, weak and painless hip abductors, and a positive single leg hop test on concrete. When the pain was not elicited with single leg hop on a foam surface, the patient was referred back to the physician for magnetic resonance imaging. The patient was later diagnosed with an acetabular stress fracture. The therapist’s thorough examination helped prevent possible avascular necrosis or a more traumatic fracture of the pelvis.
In a 2013 issue of the same journal, Podschum et al. presents a case report on deciphering the diagnosis in a female runner with deep gluteal pain with pelvic involvement. A 45 year old female marathon runner reported pulling her hamstring and complained of left ischial tuberosity pain with aching into the gluteal and pubic ramus regions that eventually forced her to stop running. She had pain in sitting and could not tolerate speed work. She had a history of low back and pelvic floor pain, with an MRI showing osteitis pubis, a lateral L3-4 bulge, and facet hypertrophy at L4-5. The physical therapist ruled out lumbar disc lesion, radiculopathy, sacroiliac joint dysfunction, and hip labral tear with special tests. Initial treatment focused on the differential diagnoses of hamstring syndrome and ischiogluteal bursitis based on subjective complaints and objective findings. After 4 visits, her deep ache shifted to the inferior pubic ramus in sitting as the ischial tuberosity pain diminished. A trained therapist then conducted a thorough pelvic floor exam. Pelvic floor hypertonic dysfunction was diagnosed and took over the “driver’s seat” as the focus for the rest of the treatment of this patient. Symptoms resolved and the patient returned to running marathons without any of her initial presenting symptoms.
If we let specific pain complaints guide our treatment, we will run out of steam with the lack of progress. Finding the true source of symptoms is critical in physical therapy. Sometimes so much is going on with our patients we have to sort through the weeds before we can access the actual road to recovery. The lumbar spine, hips, and pelvic floor create an intricate map of U-turns and two-way streets, so we need to deepen our understanding of how to navigate the regions. Only then will be able to confidently diagnose the “driver” and let the other areas call “shotgun.”
References:
Livingston, J. I., Deprey, S. M., & Hensley, C. P. (2015). DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSTIC PROCESS AND CLINICAL DECISION MAKING IN A YOUNG ADULT FEMALE WITH LATERAL HIP PAIN: A CASE REPORT. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, 10(5), 712–722.
Podschun, L., Hanney, W. J., Kolber, M. J., Garcia, A., & Rothschild, C. E. (2013). DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF DEEP GLUTEAL PAIN IN A FEMALE RUNNER WITH PELVIC INVOLVEMENT: A CASE REPORT. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, 8(4), 462–471.
There's a lot going on in the world of pelvic rehab, and continuing education is no exception! This March, Herman & Wallace is hosting NINE courses around the country. It's a lot to keep up with, so we thought you might appreciate a brief overview of what's coming up next!
Where's this pain coming from?
Pelvic pain can have many sources, and Elizabeth Hampton wants to help you quickly get to the source. Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain empowers you to play detective in order to help even the most complex patients. Don't miss out on Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain in San Diego, CA on March 4-6, 2016
What goes in eventually comes out
How important is a good diet? For most of us eating healthy is important, and for many pelvic rehab patients it is a necessity. That's why Megan Pribyl wrote her "Nutrition Perspectives for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist" course. This beginner level course is intended to expand the your knowledge of the metabolic underpinnings for local to systemically complex disorders. Don't miss out on Nutrition Perspectives for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist - Kansas City, MO - March 5-6, 2016!
There's fascia everywhere!
Fascial mobilization is a rising star in pelvic rehab treatment techniques, and Ramona Horton is excited to share it with you! "Mobilization of the Myofascial Layer: Pelvis and Lower Extremity" is the best opportunity you'll get to learn about the evaluation and treatment of myofascia for pelvic dysfunction. Check it out on our continuing education course page. Ramona will be teaching these techniques in Santa Barbara, CA on March 11-13.
Giving birth hurts
Sometimes the newborn is the one to get all the attention, but what about the new mother? Be sure that you can help postpartum women with symptoms like postural dysfunction, pelvic girdle dysfunction, diastasis recti abdominis and more by attending Care of the Postpartum Patient in Seattle, WA this March 12-13, taught by the wonderful Holly Tanner!
Vulvar pain is easy to have and hard to lose
12% of women in the US have vulvar pain for 3 or more months at some stage in their life. It takes a multidisciplinary approach to address all the causes and co-morbidities, and that is exactly what you'll get at Dee Hartmann's Vulvodynia: Assessment and Treatment in Houston, TX on March 12-13, 2016. Dee aims to address the vicious cycle of pain, visceral and sexual dysfunction, and the general hit to quality of life that patients with vulvodynia suffer from.
The challenge of SI joint pain
The sacroiliac joint, pelvic girdle, and pelvic ring sure can take a beating, and Peter Philip knows how to keep you moving. Through exercise and stabilization, the pelvic rehab practitioner can quickly treat pain in the lumbopelvic-hip complex. Learn all about the direct and indirect anatomy that influences the sacroiliac joint, and then get ready to find and treat the source of pain and dysfunction in Sacroiliac Joint Treatment in Minneapolis, MN on March 19-20, 2016.
Taxes and Menopause
The menopause transition is not something many people look forward to. For some women it goes more smoothly than others, and it's the less fortunate ones who need access to a well-trained pelvic care professional. Michelle Lyons is flying in from Ireland to help you to become that pro! Be it vaginal atrophy, sexual health dysfunction, pelvic organ prolapse, or any other of the myriad possible symptoms of menopause, you'll be equipped to handle them all after attending Menopause: A Rehabilitation Approach in Atlanta, GA on March 19-20, 2016.
The following post comes to us from Dee Hartmann, PT, DPT who is the author and instructor of Vulvodynia: Assessment and Treatment. To learn evaluation and treatment techniques for vulvar pain, join Dee in in Houston, TX this March 12-13. Early registration pricing expires soon!
 I recently heard a young, vivacious urologist present treatment options for overactive bladder to a group of nursing professionals (SUNA). To my delight as the only PT in the audience, I was pleased that physical therapy was her first line of treatment for this difficult population of chronic pelvic pain patients. As a women’s health PT, we know that chronic vulvar pain suffers experience many of the same dysfunctions, including pelvic floor muscle over-activity.
I recently heard a young, vivacious urologist present treatment options for overactive bladder to a group of nursing professionals (SUNA). To my delight as the only PT in the audience, I was pleased that physical therapy was her first line of treatment for this difficult population of chronic pelvic pain patients. As a women’s health PT, we know that chronic vulvar pain suffers experience many of the same dysfunctions, including pelvic floor muscle over-activity.
The physician’s presentation included two very emphatic statements—“physical therapy always hurts” and “no one in this group of patients should ever do Kegel exercises”. She went on to explain that anyone with pelvic floor muscle over activity should only be taught to relax; that “if they were seeing a practitioner who was telling them to do Kegels, they needed to find another PT”. As she’s not a PT, I challenged her on her second comment. I was too annoyed to address the first.
I appreciate that, as a urologist, she may not know that we learned some time ago that rest for chronic muscle tension, like chronic low back, has been proven ineffective[1]. Rather, research suggests that increased mobility and strengthening prove more effective in the long term to decrease pain by restoring normal muscle function. As pelvic floor muscles are voluntary, striated muscles, it only makes sense that the same findings apply. Those who oppose active pelvic floor muscle active exercise suggest that the over-active state of the pelvic floor muscles causes vulvar pain. I agree. However, simply relaxing dysfunctional pelvic floor muscles and expecting them to work effectively seems a bit short-sighted. Normal pelvic floor muscle function is integral to efficient core stability as well as sphincteric control, pelvic visceral support, and sexual function. Why not begin rehab for these ladies with an active exercise program, directed at renewing pelvic floor muscle motor control, with resulting decreased introital pain, improved function (sphincteric , supportive, and sexual), and improved core support?
As for the urologist’s first statement, mark me down as totally opposed. My professional experience suggests the need to replicate familiar vulvar pain and then find abnormal physical findings in the trunk, hips, viscera, and pelvis that are contributory. Rather than utilizing any treatment that causes additional pain, addressing associated abnormal findings that immediately decrease pelvic floor muscle resting tone and palpated vulvar pain, seems much more productive.
[1] Waddell G. "Simple low back pain: rest or active exercise?" Ann Rheum Dis 1993;52:317.
Kelley Thibault PT, NCS is an outpatient rehabilitation pro, having more than two decades of experience in that setting. She is a recent convert to Pelvic Rehabilitation, however, and she's jumped in head first! Her practice has shifted in that direction and she has four Herman & Wallace courses under her belt in just the last two years. We reached out to see what lessons she could share with us, and she was kind enough to give us her time today. Welcome to the field, Kelley!
Tell us a bit about your clinical experience:
I have been a physical therapist for 22 years and spent much of my career working in a hospital based outpatient clinic treating primarily neurologic diagnoses. I have worked in a transdisciplinary neurologic program for much of this time. I received my NCS from the APTA in 2004 and recertified in 2014. Over my career I have had an interest in Women’s Health Physical Therapy and attended a course with Holly Herman in the early 1990’s. I began treating more Women’s Health clients about 2 years ago to cover a maternity leave. 75% of my practice now is Women's and Men’s Health. I attended the pelvic floor level 1, 2A, 2B and 3 courses over the past year and have found them to be invaluable!!! I also have taken many of the pelvic courses on MedBridge.
What/who inspired you to become involved in pelvic rehabilitation?
I find it most rewarding to work with women who are postmenopausal and are experiencing dyspareunia and stress and/ or urge incontinence. I find with some education and behavioral modifications these clients can experience gains after the first visit. I also have enjoyed working with the chronic pelvic pain clients who require internal pelvic floor and myofascial work and seeing them return to function with less pain and more confidence.
What has been your favorite Herman & Wallace Course and why?
Pelvic floor rehabilitation works!!! There is so much that can be preventative as well as rehabilitative. I look forward to learning more and more!!! I think my favorite course thus far has been 2A mainly due to the fact that was the last course in the series that I took this past December 2015. The information on constipation and fecal incontinence as well as male pelvic anatomy, physiology and treatment was the piece I so felt I was missing in helping my clients.
What lesson have you learned from a Herman & Wallace instructor that has stayed with you?
I have found the “clinical pearls” given in each course to be invaluable!!! I have reviewed my manuals several times and will continue to do so.
What is in store for you in the future?
I hope to obtain my PRPC or WCS in the next several years and plan to continue to attend courses to improve my practice. I have been able to use my knowledge of pelvic health and treatment with my neurologic clients as well.
The following insight comes from Herman & Wallace faculty member Peter Philip, PT, ScD, COMT, PRPC, who teaches Differential Diagnostics of Chronic Pelvic Pain: Interconnections of the Spine, Neurology and the Hips for Herman & Wallace, as well as the Sacroiliac Joint Evaluation and Treatment course. Peter has been working with pelvic dysfunction patients for 15 years, and he has some insights and advice for male practitioners who are nervous about treating female patients.
 As a male treating female patients suffering with pelvic pain, many considerations must be taken to ensure that the patient is comfortable partaking in the patient/clinician relationship. As clinicians treating the most intimate of pain, we all must be highly aware of the sensitivities that each of our patients has as it relates to their genitalia. Many patients wish to maintain their modesty while simultaneously wishing to eliminate that which is ailing them. It is common that the observation, and contact to the pelvis and genitalia be a component of our patient’s evaluation and subsequent treatment in order for an accurate diagnosis to be made. So, in order to best protect our patients and ourselves it will behoove us to take a few simple steps.
As a male treating female patients suffering with pelvic pain, many considerations must be taken to ensure that the patient is comfortable partaking in the patient/clinician relationship. As clinicians treating the most intimate of pain, we all must be highly aware of the sensitivities that each of our patients has as it relates to their genitalia. Many patients wish to maintain their modesty while simultaneously wishing to eliminate that which is ailing them. It is common that the observation, and contact to the pelvis and genitalia be a component of our patient’s evaluation and subsequent treatment in order for an accurate diagnosis to be made. So, in order to best protect our patients and ourselves it will behoove us to take a few simple steps.
- During the course of the oral history, listen to what the patient is saying. What structures may be involved at referring to the outlined region in question? Can these structures be addressed externally and without exposure of the pelvis?
- If a pelvic examination appears to be warranted, provide the patient with an understanding of what you will be evaluating and why. How does your evaluation reflect their pain? What are your expected findings?
- Provide the patient the opportunity to read-and-sign a waiver that explicitly states that the evaluation may include: exposing, visualization and contact to the pelvic region inclusive of internal contact.
- Provide a means of audio-recording the evaluation and subsequent treatments. Federal guidelines dictates that there be signs on the doors of any room or office space that is recorded, and having the patient sign permission to the audio-recording further protects themselves and the clinician.
- Always ask permission to expose, visualize, and touch when and if any of the above are to be involved in the treatment of the day. Do this every visit, every time, and prior to initiating a new maneuver or treatment strategy.
- Sit aside the plinth. Once observations are complete, there will be nothing to visualize. Drape accordingly and allow the patient to maintain modesty.
- Test-retest. During the course of your evaluation, there will likely be an asterisks or correlational finding. Apply your treatment, and re-test. Appropriate treatments should provide both patient and clinician immediate feedback as to the efficacy and specificity of the functional diagnosis that the clinician is making.
- Hold the patient accountable for their actions, and importantly their corrective actions whilst not in physical therapy. Our patients may see us for two hours a week, and if they are not complicit in maintaining that which we provide their healing will be compromised.
- As for the male/female component. Some women and men will not be comfortable with a male clinician. Many women wish to maintain their modesty and/or have been violated and will have anxieties towards contact by a male clinician. The aforementioned strategies help not only to maintain a patient’s modesty, but also provide the ultimate control of who touches them, when and where. More importantly it provides the patient the opportunity to say “no” and to cease contact at their discretion. For the male:male patient:clinician relationship there may be equally as many difficulties. Some have been violated, and many have a subconscious concern of how well they ‘size up’ in comparison. Not that a comparison would ever be made, but the underlying anxieties will often be omnipresent.
- Be honest and sincere with your patients and yourself. If you’ve made a clinical assessment that did not produce the immediate pain relief expected, state that to the patient, and continue your evaluation. If you don’t know the exact driver of the pain, or dysfunction, refer out to a local specialist and discuss your findings so as to better address your suffering patient’s needs.
Food, at its basic level, provides us with nutrition and sustenance to perform our daily activities. Populations in tune with nature’s cycles of food tend to eat what is available locally based on climate and growth seasons. When societies move beyond simply eating food for energy, but also for flavor, pleasure, and even status, the face of nutrition changes. Whereas some diseases come from a lack of nutrition, many diseases we are faced with in the United States also come from an overabundance of food, with too many calories or too much sugar making up common causes of lack of health. The knowledge within the field of disordered eating is vast, and patients struggling with disordered eating may be fortunate enough to work with a specialist to help recover healthier habits. Even without a diagnosis of disordered eating, many us can identify with unhealthy eating habits, often guided by stress, fatigue, or emotions.
 Prior research has studied how we access willpower under different conditions of cognitive stress. In part of this research, participants were given a number to recall (either 2 digits or 7 digits) and then while walking to another location were offered a snack of either fruit salad or chocolate cake. The authors found that the participants who had to recall a 7 digit number more often chose the chocolate cake, leading the researchers to theorize about the role of higher-level processing and making choices. (Shiv et al., 1999) While we may be aware of a tendency to overeat (or make poorer food choices) during times of stress, fatigue, or emotional distress, changing the habits can be very challenging.
Prior research has studied how we access willpower under different conditions of cognitive stress. In part of this research, participants were given a number to recall (either 2 digits or 7 digits) and then while walking to another location were offered a snack of either fruit salad or chocolate cake. The authors found that the participants who had to recall a 7 digit number more often chose the chocolate cake, leading the researchers to theorize about the role of higher-level processing and making choices. (Shiv et al., 1999) While we may be aware of a tendency to overeat (or make poorer food choices) during times of stress, fatigue, or emotional distress, changing the habits can be very challenging.
Resources that discuss improving our eating choices in the face of “emotional eating” offers many alternatives, or ways to soothe ourselves without eating. In her books about this topic, clinical psychologist Susan Albers offers advice that may be helpful for our own habit building and for offering basic advice for our patients who struggle with the issue. (While offering advice to patients about healthy eating and habits is within our scope of practice, if a patient has need for a referral to a counselor, psychologist, or nutritionist, we can coordinate such a referral with the patient’s primary care provider.) In her book titled “50 More Ways to Soothe Yourself Without Food: Mindfulness Strategies to Cope with Stress and End Emotional Eating”, Dr. Albers offers many strategies for altering our habits. Some of these ideas include using acupressure points, breathing, rituals, self-massage, yoga, writing, dancing, art, tea, or sex to defer ourselves from poor eating habits. While eating can be enjoyable and pleasurable, when our patients are struggling with over-eating or eating foods that don’t support nutritional or healing goals, having a discussion about these issues may be useful.
If you are interested in learning more about nutrition, consider joining your pelvic rehab colleagues at one of the two Nutrition Perspectives for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist courses this year! Your first chance to attend will be in Kansas City on March 5-6, and later on in Lodi, CA June 25-26.
Albers, S. (2015). 50 More Ways to Soothe Yourself Without Food: Mindfulness Strategies to Cope with Stress and End Emotional Eating. New Harbinger Publications.
Shiv, B., & Fedorikhin, A. (1999). Heart and mind in conflict: The interplay of affect and cognition in consumer decision making. Journal of consumer Research, 26(3), 278-292.
This week we end with a fantastic interview with our featured pelvic rehab practitioner. Nancy Suarez, MS, PT, BCB-PMD, PRPC just joined the ranks of the elite Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioners! Check out our interview below:
 Describe your clinical practice:
Describe your clinical practice:
I work in a private practice specializing in women’s and men’s pelvic floor disorders including bowel and bladder issues, prolapse and sexual dysfunction, prenatal and postpartum rehabilitation, pre and postprostatectomy care, and lumbopelvic pain.
How did you get involved in the pelvic rehabilitation field?
As a physical therapist who regularly took continuing education courses following PT school, I happened to be looking for a course that might give me more knowledge to help some of my geriatric patients improve their urinary incontinence. I took my first Pelvic Floor course given by Hollis Herman and Kathe Wallace in 2000, and immediately began to make a difference in many of my patient’s lives.
What/who inspired you to become involved in pelvic rehabilitation?
Really it was my patients that inspired me to become involved in pelvic floor rehabilitation; I knew embarassingly little about it on my own until my first course! I was very fortunate to have been given the opportunity to join a pelvic floor specialty practice a few years after that first course, and there I honed my skills and began adding more pelvic floor courses to improve my practice.
What patient population do you find most rewarding in treating and why?
It is honestly difficult for me to choose one type of patient that I find MOST rewarding; it is such a privilege to see patients getting better when they may have thought there was no hope. I do find that I love helping middle aged and older women learn about their pelvic floor and learn how to overcome their incontinence, prolapse and pain.
After menopause, more than half of women may have vulvovaginal symptoms that can impact their lifestyle, emotional well being and sexual health. What's more, the symptoms tend to co-exist with issues such as prolapse, urinary and/or bowel problems. But unfortunately many women aren't getting the help they need, despite a growing body of evidence that skilled pelvic rehab interventions are effective in the management of bladder/bowel dysfunctions, POP, sexual health issues and pelvic pain.
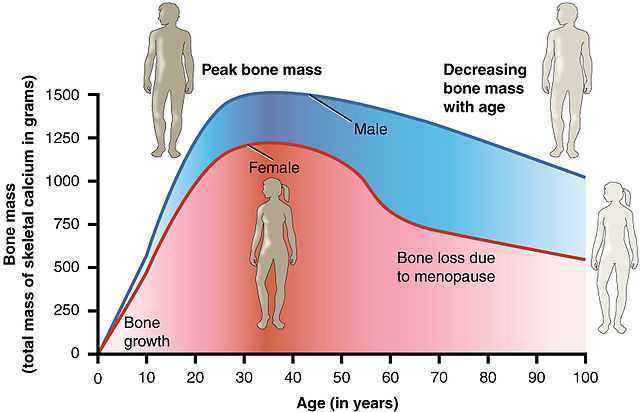 Vaginal dryness, hot flashes, night sweats, disrupted sleep, and weight gain have been listed as the top five symptoms experienced by postmenopausal women in North America and Europe, according to a study by Minkin et al 2015, and they also concluded ‘The impact of postmenopausal symptoms on relationships is greater in women from countries where symptoms are more prevalent.’ Between 17% and 45% of postmenopausal women say they find sex painful, a condition referred to medically as dyspareunia. Vaginal thinning and dryness are the most common cause of dyspareunia in women over age 50. However pain during sex can also result from vulvodynia (chronic pain in the vulva, or external genitals) and a number of other causes not specifically associated with menopause or aging, particularly orthopaedic dysfunction, which the pelvic physical therapist is in an ideal position to screen for.
Vaginal dryness, hot flashes, night sweats, disrupted sleep, and weight gain have been listed as the top five symptoms experienced by postmenopausal women in North America and Europe, according to a study by Minkin et al 2015, and they also concluded ‘The impact of postmenopausal symptoms on relationships is greater in women from countries where symptoms are more prevalent.’ Between 17% and 45% of postmenopausal women say they find sex painful, a condition referred to medically as dyspareunia. Vaginal thinning and dryness are the most common cause of dyspareunia in women over age 50. However pain during sex can also result from vulvodynia (chronic pain in the vulva, or external genitals) and a number of other causes not specifically associated with menopause or aging, particularly orthopaedic dysfunction, which the pelvic physical therapist is in an ideal position to screen for.
According to the North America Menopause Society, ‘…beyond the immediate effects of the pain itself, pain during sex (or simply fear or anticipation of pain during sex) can trigger performance anxiety or future arousal problems in some women. Worry over whether pain will come back can diminish lubrication or cause involuntary—and painful—tightening of the vaginal muscles, called vaginismus. The result can be a vicious circle, again highlighting how intertwined sexual problems can become.’
The research has demonstrated that the optimal strategy for post-menopausal stress incontinence is a combination of local hormonal treatment and pelvic floor muscle training – the strategy of combining the two approaches has been shown to be superior to either approach used individually (Castellani et al 2015, Capobianco et al 2012) and similar conclusions can be drawn for promoting sexual health peri- and post-menopausally.
The pelvic rehab specialist may be called upon to screen for orthopaedic dysfunction in the spine, hips or pelvis, to discuss sexual ergonomics such as positioning or the use of lubricant as well as providing information and education about sexual health before, during and after menopause.
To learn more about sexual health and pelvic floor function/dysfunction at menopause, join me in Atlanta in March for Menopause: A Rehab Approach.
Prevalence of postmenopausal symptoms in North America and Europe, Minkin, Mary Jane MD, NCMP1; Reiter, Suzanne RNC, NP, MM, MSN2; Maamari, Ricardo MD, NCMP3, Menopause:November 2015 - Volume 22 - Issue 11 - p 1231–1238
Low-Dose Intravaginal Estriol and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation in Post-Menopausal Stress Urinary Incontinence, Castellani D. · Saldutto P. · Galica V. · Pace G. · Biferi D. · Paradiso Galatioto G. · Vicentini C., Urol Int 2015;95:417-421
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://hermanwallace.com/











































