Peyronie’s disease is a condition in which there are fibrotic plaques (sometimes calcified) that can cause a curvature in the penis, most notable during erection. Pain as well as urinary and sexual dysfunction may occur with Peyronie's disease. Increased attention has been given in recent years to the relationship between male hormones, erectile dysfunction, and Peyronie's disease. According to the Mayo Clinic, testosterone, the predominant hormone affecting male physical characteristics, peaks during adolescence and early adulthood. Testosterone gradually decreases about 1% per year once a man reaches age 30-40. Some men experience symptoms from the decline in testosterone and these symptoms can include decreased sexual function, sleep disturbances changes in bone density and muscle bulk, as well as changes in cognition and depression. Because other factors and conditions can cause similar symptoms, patients with any of these changes should talk to their medical provider to rule out diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, depression, sleep apnea, and medication side effects, according to Mayo.
 In an article published in 2012, Iacono and colleagues studied the correlation between age, low testosterone, fibrosis of the cavernosal tissues, and erectile dysfunction. 47 patients diagnosed with erectile dysfunction (ED) were included, with 55% of the 47 men being older than age 65. Having increased fibrosis corresponded to having a positive Rigiscan test- meaning that a nocturnal test of penile rigidity demonstrated abnormal nighttime erections. Low levels of testosterone also corresponded to erectile dysfunction. (This is an open access article with full text available) Another published article agreed with the above in that low testosterone is associated with Peyronie’s disease and/or erectile dysfunction. The authors are cautious, however, in describing the association between the variables, as causation towards plaque formation characteristic of Peyronie’s is not known.
In an article published in 2012, Iacono and colleagues studied the correlation between age, low testosterone, fibrosis of the cavernosal tissues, and erectile dysfunction. 47 patients diagnosed with erectile dysfunction (ED) were included, with 55% of the 47 men being older than age 65. Having increased fibrosis corresponded to having a positive Rigiscan test- meaning that a nocturnal test of penile rigidity demonstrated abnormal nighttime erections. Low levels of testosterone also corresponded to erectile dysfunction. (This is an open access article with full text available) Another published article agreed with the above in that low testosterone is associated with Peyronie’s disease and/or erectile dysfunction. The authors are cautious, however, in describing the association between the variables, as causation towards plaque formation characteristic of Peyronie’s is not known.
The larger question about Peyronie’s disease is what a patient can do to improve the symptoms of the condition. Therapists who treat male patients are increasingly interested in this question, and many are working with their patients to address the known soft tissue dysfunction. Interventions may include teaching patients to perform soft tissue mobilizations and stretches to the restricted tissue, and educating the patient in what the available literature tells us about rehabilitation of this condition. Hopefully, as male pelvic rehabilitation continues to grow in popularity, more therapists will contribute case studies and participate in higher levels of research so that more men can add conservative care of Peyronie’s to their list of treatment options.
To learn more about what the literature tells us about Peyronie’s and other male pelvic rehabilitation conditions, the Male Pelvic Floor continuing education course is taking place in Seattle in November, and you won't want to miss it!
If you are familiar with the work of Diane Lee, you may have noticed the term “driver” used throughout descriptions of patient assessment techniques. One definition of “driver” is “a factor that causes a particular phenomenon to happen or develop.” When it comes to a patient’s pelvic dysfunction, we know that there may be a dramatic number of factors driving the symptom, so what is the value of trying to determine the level of significance of various factors?
 Let’s imagine that we meet a female patient who presents with pelvic pain, urinary incontinence, and difficulty holding back gas. In addition to providing a thorough subjective interview, screening for underlying medical conditions requiring attention, examining her neuromusculoskeletal system, and learning more about her daily habits, we need to figure out the best place to start with her care. What if, even though this particular patient has only experienced one major episode of leakage (after which all other symptoms started) you complete the exam to find that she is holding her pelvic muscles tense continuously? Perhaps you share this observation with the patient, only to hear her say that she is “so afraid of leaking again that she keeps her muscles tight to prevent it.” This type of rehabilitation sleuthing can help us get to the heart of the matter with our patients, regardless of the presenting complaints. For example, if we can educate this patient about the potential negative consequences of her fear of having another embarrassing episode (fear leads to muscle guarding which leads to pelvic pain and potentially dysfunctional voiding) then her thoughts can positively contribute to the other therapeutic recommendations we make.
Let’s imagine that we meet a female patient who presents with pelvic pain, urinary incontinence, and difficulty holding back gas. In addition to providing a thorough subjective interview, screening for underlying medical conditions requiring attention, examining her neuromusculoskeletal system, and learning more about her daily habits, we need to figure out the best place to start with her care. What if, even though this particular patient has only experienced one major episode of leakage (after which all other symptoms started) you complete the exam to find that she is holding her pelvic muscles tense continuously? Perhaps you share this observation with the patient, only to hear her say that she is “so afraid of leaking again that she keeps her muscles tight to prevent it.” This type of rehabilitation sleuthing can help us get to the heart of the matter with our patients, regardless of the presenting complaints. For example, if we can educate this patient about the potential negative consequences of her fear of having another embarrassing episode (fear leads to muscle guarding which leads to pelvic pain and potentially dysfunctional voiding) then her thoughts can positively contribute to the other therapeutic recommendations we make.
Other examples may include meeting a patient with pelvic dysfunction whose true “driver” is a kyphotic thoracic spine that compresses the abdominal organs, or a habit of wearing pants with a waistband so tight that bowel function is compromised (true story), foot pain that creates increased loading on the now painful side of the pelvis, or even emotions and thoughts such as fear and shame. I’m sure you can think of many other examples based on your own clinical experience. If you are a newer therapist, or perhaps wish to work through further examples of not only how to evaluate but to treat for finding the primary contributors to a patient’s dysfunction, check out Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute faculty member Elizabeth Hampton’s continuing education course that focuses on this Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain.
The next opportunity to take this course is in Houston in November of this year or March in San Diego.
Have you ever tried to make a fitted sheet reach all corners of a mattress when there is a small, defective seam stitched into the middle of the fabric? No matter how much you pull or tug, the sheet won’t hug the last corner just right. If you get it to stay, the opposite corner flips off from the extra tension. Unless you release the snag the stitching created, you won’t ever get the sheet to fit smoothly. This is like the myofascial system in the body, where a snag in one area can affect another proximally or distally when normal movement tries to occur.
 Even the pelvic floor can get myofascial restrictions and trigger points; however, this area is often ignored and seemingly insignificant when not fully understood. Pelvic floor fascial restrictions and trigger points can have paramount implications for the pelvic, abdominal, hip, and lumbar regions. This why pelvic rehabilitation practitioners should be equipped to evaluate and treat myofascial snags.
Even the pelvic floor can get myofascial restrictions and trigger points; however, this area is often ignored and seemingly insignificant when not fully understood. Pelvic floor fascial restrictions and trigger points can have paramount implications for the pelvic, abdominal, hip, and lumbar regions. This why pelvic rehabilitation practitioners should be equipped to evaluate and treat myofascial snags.
Pastore and Katzman (2012) published an article stating that 14%-23% of women with chronic pelvic pain have myofascial pelvic pain, and up to 78% of women with interstitial cystitis have myofascial trigger points. Once a trigger point in pelvic floor musculature is identified through palpation, it can refer pain to the perineum, vagina, urethra, and rectum, which seems obvious; however, pain may also refer to the abdomen, back, trunk, hip, buttocks, and lower leg. If palpation can provoke a referral pattern of pain, stretching and/or contraction of the musculature with that myofascial restriction will surely provoke a cascade of symptoms. How can we as clinicians just let statistics like this slide and figure “someone else should do that examination and fix it?” To demonstrate the efficacy in treating myofascial trigger points in pelvic musculature, consider the following study. Anderson et al (2015) had 374 patients follow a protocol of pelvic floor myofascial release of trigger points with an internal trigger point wand along with paradoxical relaxation therapy for 6 months. The goal was to see if patients with chronic pelvic pain syndrome could reduce their medication after following the protocol. At 6 months, a 36.9% reduction in medication use was noted in a complete case analysis, and a 22.7% reduction was revealed in the modified intention to treat (mITT) analysis. Patients no longer needing to take medication significantly correlated with the reduction of overall symptoms from following the protocol.
Knowing how to find and treat pelvic floor myofascial trigger points can lead to reduction of pain in women (and men) and even help reduce the need for medication for their chronic pelvic pain symptoms. Stop trying to make a bed without discerning if the base layer is free of snags. Learning how to go deeper to feel what’s under the covers can help unveil a source of potentially chronic, disabling pain. You can learn how to skillfully treat the “hidden” dysfunction by attending a Myofascial Release for Pelvic Dysfunction course with Ramona Horton.
References:
Pastore, E. A., & Katzman, W. B. (2012). Recognizing Myofascial Pelvic Pain in the Female Patient with Chronic Pelvic Pain. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing : JOGNN / NAACOG, 41(5), 680–691. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6909.2012.01404.x
Anderson , R., Harvey, R., Wise, D., Smith, J., Nathanson, B., Sawyer, T. (2015 March). Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: Reduction of Medication Use After Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy with an Internal Myofascial Trigger Point Wand. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. Volume 40, Issue 1, pp 45-52
The concept of patient compliance, or adherence (a more preferred term), has been the subject of many medical studies, and adherence in pelvic rehabilitation is an aspect of rehab of critical interest. Recently published results of a survey questioning providers and the public about adherence in pelvic floor muscle training offers an insightful perspective. Researchers Frawley, Dumoulin, and McClurg conducted a web-based survey which was published in published in Neurourology and Urodynamics. The survey was completed by 515 health professionals and by 51 individuals from the public. Interestingly, but perhaps not surprisingly, health professionals and public respondents placed different value on which factors related to rehabilitation contributed the most to adherence.
 Data collected in the study included topics such as barriers to adherence in pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT), perception of potential benefit of PFMT, therapy-related factors including therapeutic relationship, socioeconomic factors, and issues surrounding short-term versus long-term adherence, for example. For the providers, poor motivation was rated high as a barrier to short-term adherence, whereas the patients rated perception of minimal benefit from PFMT as the most important barrier. Facilitators of pelvic muscle training included aspects of access such as having appointments outside of the typical workday, or having childcare available, transportation, and not being bored by the exercise program or feeling that the therapist has adequate training and skills.
Data collected in the study included topics such as barriers to adherence in pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT), perception of potential benefit of PFMT, therapy-related factors including therapeutic relationship, socioeconomic factors, and issues surrounding short-term versus long-term adherence, for example. For the providers, poor motivation was rated high as a barrier to short-term adherence, whereas the patients rated perception of minimal benefit from PFMT as the most important barrier. Facilitators of pelvic muscle training included aspects of access such as having appointments outside of the typical workday, or having childcare available, transportation, and not being bored by the exercise program or feeling that the therapist has adequate training and skills.
As suggested by the authors, perhaps that most important variable agreed upon by both providers and public is that of perceived benefit. In other words, patients need to believe that the exercise program can alleviate symptoms and that what they are doing in their particular program is going to achieve positive results rather than wasting time on a home program that will not be effective. This issue is one that can be easily remedied through appropriate patient education, communication with the patient about whether or not they understand the potential value and expected recovery through program participation, and adequate training of the therapist that allows for proper diagnosis and treatment planning. The study concludes by emphasizing that health providers “need to be aware of the importance of long-term patient perception of PFMT…”
If you are interested in advancing your diagnostic or treatment planning skills, check out the pelvic floor series of continuing education courses and the many specialty courses that the Institute offers.
Oftentimes in the blog we address specific populations, perhaps involving pediatrics, post-prostatectomy patients, or patients who have oncology-related issues. Another population that deserves more focus is the geriatric population. If we consider who and where the women are who may be dealing with the highest level of pelvic dysfunction, we are led to the women in their later decades of life. A major challenge for geriatric women is that many pelvic rehab therapists are not reaching them: outpatient clinics tend to cater to younger patients, and for the women who are in living settings other than their own home, there are few therapists trained to address pelvic floor dysfunction such as incontinence or prolapse. Now seems like a great time to remedy these issues, as the Institute has created a course specific to geriatric patients.
What is different about pelvic floor evaluation and intervention in the geriatric population? This is a broad question with a range of important answers, but we can start with this one: what is different about the pelvic floor exam for women of geriatric age? Following are a few key thoughts. (You can find even more information about recommendations for pelvic exams and the use of speculums in the medical clinic in this article published in the Journal of Women’s Health.
 Geriatric patients may require assist for positioning on the examining table, including use of a high-low table or assistive devices for transitions. If a patient cannot tolerate the supine hooklying position for an exam, she may be able to tolerate either a frog-leg position (supine with with bent, heels together, knees abducted) or left sidelying with an assistant holding the top leg in a position for best viewing. Women of older age may have atrophic vaginitis, or thinning of the tissues that creates fragility, and a pelvic muscle assessment may need to be completed externally via observation, palpation, or with external sensors and biofeedback. Age-related changes such as difficulty with vision, hearing, or with complex instructions may require adaptations in exam strategies and sequencing.
Geriatric patients may require assist for positioning on the examining table, including use of a high-low table or assistive devices for transitions. If a patient cannot tolerate the supine hooklying position for an exam, she may be able to tolerate either a frog-leg position (supine with with bent, heels together, knees abducted) or left sidelying with an assistant holding the top leg in a position for best viewing. Women of older age may have atrophic vaginitis, or thinning of the tissues that creates fragility, and a pelvic muscle assessment may need to be completed externally via observation, palpation, or with external sensors and biofeedback. Age-related changes such as difficulty with vision, hearing, or with complex instructions may require adaptations in exam strategies and sequencing.
Another article which summarized guidelines for pelvic exams and cancer screening in women over age 65 discusses the importance of screening women of all ages. Because, as the authors point out, women over 65 are more likely to develop “late stage diagnoses of cancers, pelvic organ disease, incontinence, and infections…”, practitioners should encourage women to continue to seek expert care for screening of such diseases and conditions. The article also discusses the lack of access to gynecologic care in settings like nursing homes and assisted living, leaving women at risk for not having routine exams and screening.
There is much to learn about the pelvic rehabilitation process for geriatric patients of all genders. Herman & Wallace faculty member Heather Rader has offered her expertise in the field of geriatric pelvic rehab and is prepared to discuss not only the common conditions, modifications to evaluation and intervention, but also nuts and bolts topics like documentation, billing, and all things Medicare! You still have time to schedule a warm, sunny break for the coming winter as the continuing education course will take place in Florida in January!
Coccyx pain is a frequently encountered condition in pelvic rehabilitation practices. Although sitting is one of the primary limitations for patients who present with coccyx pain, or coccygodynia, defecation can be included in the list of functional complaints. This brings to mind the question: what does the coccyx do during defecation?
Coccygeal mobility was examined using MRI in this study by Grassi and colleagues. The authors included 112 subjects for the dynamic MRI research in positions of maximal contraction as well as straining for evacuation. Included in the study were subjects who complained of constipation, sense of incomplete evacuation of bowels, pain (not coccyx pain), organ prolapse, and minor trauma. Although the MRI was completed with the patient in supine (a non-functional defecation position), the authors reported that during a straining maneuver, the coccyx moves into extension, or backwards.
What if the coccyx does not move into extension during a straining maneuver? Is it possible for the coccyx to interfere with defecation? This appears to be true for a patient who appeared as the subject in the Journal of Medical Case Reports. The patient presented with an anteverted coccyx, and complained of “…worsening rectal pain developing an hour before defecation and lasting for several hours afterwards.” Pain was also reported during sitting on a hard surface. (See the linked article for an interesting image of the coccyx position and what is described as “rectal impingement.”) The patient was treated with coccygectomy which appeared to significantly reduce the symptoms (there are no outcomes tools reported in the case study, so progress reported is vague.) Although removal of the coccyx was the treatment in this particular case, the authors state that first-line treatment for coccyx pain includes conservative measures such as seat cushioning, coccygeal massage, stretching and manipulation, and injections, and that the majority of patients will respond favorably to these interventions.
There is more to learn about the coccyx and its role in defecation, sitting, and other daily functions. Faculty member Lila Abbate teaches a great course called Coccyx Pain, Evaluation & Treatment and it is a great opportunity to learn some new evaluation and treatment techniques. Join her this October 25-26 in Bay Shore, NY.
The abdominal canister is a model that we have used in rehab for a number of years, especially when it comes to discussing the (often controversial) topic of core stability. Traditionally regarded as encompassing the pelvic floor, diaphragm, deep abdominal muscles (particularly Transversus Abdominus), our definitions of ‘the canister’ or ‘core’ have of late expanded to include psoas, obturator internus, quadratus lumborum and the osseous components of the pelvic girdle (Chaitow 2012).
 Often, we in pelvic rehab bemoan the fact that the pelvic floor is not given the attention it deserves (when we know it really is the answer to everything…) but I do believe that we, as pelvic health specialists are just as guilty of not paying enough attention to the ‘roof’ of the canister, the diaphragm.
Often, we in pelvic rehab bemoan the fact that the pelvic floor is not given the attention it deserves (when we know it really is the answer to everything…) but I do believe that we, as pelvic health specialists are just as guilty of not paying enough attention to the ‘roof’ of the canister, the diaphragm.
The diaphragm and the pelvic floor are bound together structurally and functionally by both fascial and muscular connections (Chaitow 2012). The anatomical link between the diaphragm, psoas and the pelvic floor has been explored by Gibbons in 2001 ‘…The diaphragm’s medial arcuate ligament is a tendinous arch in the fascia of psoas major. Distally, the psoas fascia is continuous with the pelvic floor fascia, especially the pubococcygeus’. Newell in 2005 discussed the relationship between the diaphragm and transversus abdominus and Carriere in 2006 concluded that psoas spasm may influence diaphragmatic mechanics, and conversely that abnormal tensions in the medial arcuate ligament of the diaphragm may irritate psoas.
Paul Hodges has also concluded in his 2007 paper that breathing and continence may be more connected to low back pain than levels of activity or BMI, reinforcing Smith’s 2006 study looking at the link between breathing disorders, pelvic floor dysfunction and back pain in over 38,000 Australian women.
Of course, breathing, like pelvic floor functioning, can also be linked to psychological factors: when we are stressed, our breathing tends to become more apical (and our pelvic floors may hold excess tension). When that becomes habitual rather than a temporary stress response, a sub-optimal breathing pattern may develop, which disrupts the abdominal muscle balance and makes both back and pelvic pain more likely, with the added risk of pelvic venous congestion (Chaitow 2012). Myofascial trigger points may also develop because of restricted breathing patterns. We also know the opposite is true – such as using controlled breathing to calm down, to let go of tension and even to modify pain and autonomic responses (Busch 2012). Athletes may be at a particular risk of dysfunction, competing at high levels of intensity, both physically (in competition?) and psychologically (fear of losing a college scholarship?) Although more research is needed to confirm or disprove these connections, theoretically normalizing breathing patterns may improve outcomes in cases of low back or pelvic pain.
In my specialist course ‘The Athlete & the Pelvic Floor’ in Denver next month, we will look at specific manual therapy interventions for the diaphragm and its allies, the psoas and quadratus lumborum. As with any manual therapy techniques, we must always follow up with a clinical and home exercise program, or the effects will be only temporarily beneficial (Coronado 2011, Hegedus 2012) and so we will look at breath re-patterning, integration with the pelvic floor and how this is an often overlooked step when it comes to managing athletes with pelvic floor dysfunction. Hope to see you there!
References:
1. Chaitow, L & Jones, R (Eds) ‘Chronic Pelvic Pain and Dysfunction 2012 Elsevier Churchill Livingstone
2. Gibbons, S.G.T. 2001 The model of Psoas Major stability function. In: Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Movement Dysfunction, Sept 21-23 Edinburgh, Scotland
3. Newell, R. 2005 Anatomy of the post-laryngeal airways, lungs and diaphragm. Surgery 23 (11) 393-397
4. Carriere, B 2006 Interdependence of Posture and the Pelvic Floor. In: Carriere, B The Pelvic Floor, Thieme New York
5. Hodges, P, Sapsford, R, Pengel, L 2007 Postural and respiratory functions of the PFMs. Neorourol. Urodyn. 26 (3), 362-371
6. Smith, M, Russell, A, Hodges, P., 2006 Disorders of breathing and continence have a stronger association with back pain than obesity and physical activity. Aust. J. Physiother. 21(52) 11-16
7. Coronado, R, Bialosky, J & Cook, C. 2010 The temporal effects of a single session of high-velocity, low-amplitude thrust manipulation on subjects with spinal pain Physical Therapy Reviews Volume 15, Issue 1 (01 February 2010), pp. 29-35
Cognition in later years may be affected by premature menopause, according to an article published online in the British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. In the study 4,868 women at least 65 years old were assessed on a cognitive test battery and were evaluated for clinical dementia. Associations between the subject’s age at menopause, surgical versus natural menopause, use of menopausal hormone therapy, and cognitive function later in life were studied. According to introductory concepts described in the article, estrogen level changes postmenopause are associated with brain atrophy and memory complaints.
Tests were administered at baseline, and again at 2, 4 and 7 years from baseline. Tools included the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for global cognitive function, Benton’s Visual Retention Test (BVRT) for visual memory assessment, Isaacs Set Test for verbal fluency or semantic access, and the Trail Making Tests A and B for timed visual motor tasks of psychomotor speed and attention and executive function. Unrelated to cognitive function, The Rosow and Breslau mobility and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living scales, the Centre for Epidemiology Studies Depression Scale (CES-D), and other instruments were used to assess socioeconomic, demographic, lifestyle and health information. Dementia was also evaluated by a trained psychologist (or neurologist if subject was suspected to have dementia) and cases were assessed by a panel of dementia experts as a third step in the process.
Natural menopause was noted in 79% of the subjects, surgical menopause in 10%, and 11% due to other causes including radiation, chemotherapy, or unknown. Less than 1 in 7 women was currently using hormone therapy, and over 1/5 used hormone therapy at menopause (most commonly reported treatment was transdermal estradiol- median time of use was 10 years).
The authors concluded that variables such as verbal fluency, visual memory, psychomotor speed and global cognitive function can be negatively impacted by premature menopause. Specifically, premature menopause including premature ovarian failure or surgical menopause at 40 years of age or less was independently associated with increased risk of poor verbal fluency and visual memory later in life. Premature menopause was also associated with increased risk of psychomotor speed and global cognitive decline. The primary conclusion of the article is that when an ovariectomy is being considering in younger women, the potential negative impact on cognitive function should make up part of the risk/benefit discussion. Hormonal influence during various stages of a woman’s life can have a dramatic impact on many variables impacting quality of life and rehabilitation efforts. To learn more about menopause, the Institute offers several courses that contain information about rehabilitation for women throughout the lifespan.
Herman & Wallace offers an excellent course called "Menopause Rehabilitation and Symptom Management ", where you can learn about evaluating and treating menopause patients. Forward thinking therapists can provide an integrative, safe and effective/evidence based approach, such as menopausal weight loss, cardiovascular health promotion and mind body awareness, and Menopause: A Rehabilitation Approach - Atlanta, GA on March 19-20, 2016 is a great opportunity to learn such skills.
Within 1 week, I examined 2 women with the diagnosis of lumbar pain who each happened to mention having a hip labral tear. Of course, neither woman volunteered information about the pelvic floor dysfunction she has lived with since having children. When I took the extra step and openly asked if they had any “issues” in the pelvic floor region, both women initially looked surprised and then relieved as they shared (perhaps for the first time) the problems they’ve had. I started to wonder about the contribution of pelvic floor dysfunction to acetabular labral tears, or vice versa, and I knew each problem had to be addressed for the referring diagnoses to be treated completely and effectively.
Considering the anatomy of the acetabular labrum in relation to the pelvic floor structures, there is undeniably a connection. A thorough review of pelvic anatomy is given in the Functional Applications in Pelvic Rehabilitation course by Kathe Wallace. Just briefly, the acetabulum is the depression in the pelvis (os coxae) where the femoral head articulates. The labrum sits in the acetabulum, which faces anteriorly along with the femoral head, requiring the anterior aspect of the labrum to stabilize this portion of the hip that lacks bony contact. The obturator internus muscle, which is a deep hip external rotator and abductor, attaches to the posterior aspect of the obturator foramen and inserts on the medial surface of the greater trochanter. When this muscle is in spasm or inhibited, the pelvic floor and the hip can suffer.
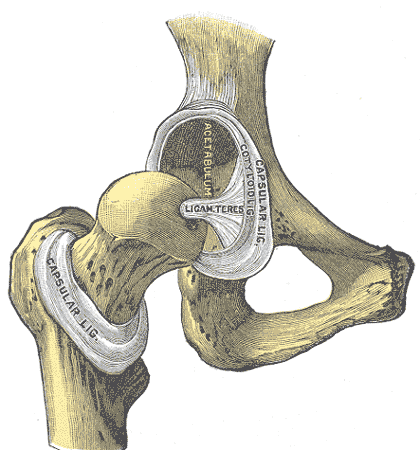 In 2009, Groh and Herrera published a review of hip labral tears, and the general consensus was that labral tears “occur more frequently in women than in men.” The fact that women have more hip dysplasia than men has been suggested as a cause for this finding; however, many of the women with labral tears do not have concomitant hip dysplasia. Alas, Hunt et al (2007) pointed out that women have a generally higher incidence of pelvic-floor pain, which could contribute to the higher incidence of labral tears.
In 2009, Groh and Herrera published a review of hip labral tears, and the general consensus was that labral tears “occur more frequently in women than in men.” The fact that women have more hip dysplasia than men has been suggested as a cause for this finding; however, many of the women with labral tears do not have concomitant hip dysplasia. Alas, Hunt et al (2007) pointed out that women have a generally higher incidence of pelvic-floor pain, which could contribute to the higher incidence of labral tears.
Interestingly, in a study by Brooks and Domb (2012), 10 women over 2 years presented post-partum with anterior hip pain and required labral surgery. The excessive hip external rotation needed for natural delivery was implicated in the pathology, and the authors encouraged obstetricians to have women evaluated prior to delivery and mobilized properly so they could prevent the tears. Hormonal changes in the ligaments as well as the posture assumed by pregnant women with increased lordosis placing more shearing on the anterior aspect of the hip are also factors to consider. Not to mention, the pelvic floor connection to the acetabular labrum certainly seems a reasonable culprit for making the labrum more susceptible to injury during pregnancy and/or delivery.
With the improved technology to diagnose acetabular labral tears, more are being found and treated surgically. The higher incidence of labral pathology in women makes the contribution of pelvic floor dysfunction a serious possibility to consider. If the labrum gets fixed but the pelvic floor is still an issue, becoming completely asymptomatic is less likely. Seeing 2 patients in 1 week who each presented with low back pain, labral tear, and pelvic floor dysfunction when I only work part time makes me think we cannot deny the importance of our subjective examination in uncovering all the possible causes of any suspected tissue in lesion.
Herman & Wallace faculty member Ginger Garner teaches an excellent course called "Extra-Articular Pelvic and Hip Labrum Injury: Differential Diagnosis and Integrative Management" which explores acetabular labral tears in depth. Join Ginger next May in Rochester, NY to learn some great evaluation and treatment techniques!
References:
Groh, M. M., & Herrera, J. (2009). A comprehensive review of hip labral tears.Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine, 2(2), 105–117. doi:10.1007/s12178-009-9052-9.
Hunt D, Clohisy J, Prather H. (2007). Acetabular tears of the hip in women. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am.,18(3):497–520.
Brooks AG, Domb BG. (2012). Acetabular labral tear and postpartum hip pain. Obstet Gynecol. 120(5):1093-8.
Megan Pribyl, MSPT is the author and instructor for Nutrition Perspectives for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist. Megan is passionate about nutritional science and manual therapy. Megan holds a dual-degree in Nutrition and Exercise Sciences (B.S. Foods & Nutrition, B.S. Kinesiology) from Kansas State University, and has actively sought to fill in missing links between orthopedics and nutrition.
APTA Landmark Motion Passes
RC 12-15: The Role of the Physical Therapist in Diet and Nutrition
 Is nutrition within our scope of practice? As the instructor for “Nutrition Perspectives for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist” offered through Herman & Wallace, I hear this question frequently! To me, the answer has always been a clear “yes*!”; now the APTA is endorsing this view. It’s an exciting time to be a rehab professional, especially for those looking to broaden clinical perspectives and scope of services to include basic nutrition and lifestyle information.
Is nutrition within our scope of practice? As the instructor for “Nutrition Perspectives for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist” offered through Herman & Wallace, I hear this question frequently! To me, the answer has always been a clear “yes*!”; now the APTA is endorsing this view. It’s an exciting time to be a rehab professional, especially for those looking to broaden clinical perspectives and scope of services to include basic nutrition and lifestyle information.
At the APTA House of Delegates in early June 2015, a landmark motion passed - RC 12-15: The Role of the Physical Therapist in Diet and Nutrition. As our profession advances towards a more integrative model, this motion symbolizes an acknowledgement of the rehab professional’s broader role as a health care provider. We, as physical therapists, are uniquely positioned to offer patients more comprehensive lifestyle-related education including discussion of nutrition. Both the World Health Organization (WHO, 2008) and the Physical Therapy Summit on Global Health (Dean, et.al, 2014) have called upon all health care providers to stand in unity to help the public with epidemics of lifestyle-related diseases; the APTA has given it’s nod of approval as well.
The motion states: “as diet and nutrition are key components of primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention of many conditions managed by physical therapists, it is the role of the physical therapist to evaluate for and provide information on diet and nutritional issues to patient, clients, and the community within the scope of physical therapist practice. This includes appropriate referrals to nutrition and dietary medical professionals when the required advice and education lie outside the education level of the physical therapist*.” Further, “this motion clearly incorporates the intent of the new Vision Statement for the Physical Therapy Profession by transforming society and improving the human experience.” (APTA, 2015)
This powerful development provides us with both challenge and opportunity. How can we, as pelvic rehab professionals, be armed with the most cutting edge nutritional information available? What nutrition information lies within our scope of practice? How can we apply this information to our pelvic rehab patient population? For the answer to these pressing questions and much more, plan now to attend Nutrition Perspectives for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist” March 5 & 6, 2016 in Kansas City, MO. It is my passion to share this information and I welcome you to join me for this timely CEU opportunity. It is designed to help you obtain the skills needed to confidently identify nutritional correlates in pelvic rehabilitation.
References:
ATPA (2015) http://www.apta.org/uploadedFiles/2015PacketI.pdf
Dean, E., de Andrade, A. D., O'Donoghue, G., Skinner, M., Umereh, G., Beenen, P., . . . Wong, W. P. (2014). The Second Physical Therapy Summit on Global Health: developing an action plan to promote health in daily practice and reduce the burden of non-communicable diseases. Physiother Theory Pract, 30(4), 261-275. (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24252072)
World Health Organization. (2008). 2008-2013 Action plan for the global strategy for the prevention and control of non communicable diseases. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO. (http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2015/noncommunicable-diseases/en/)
photo credit: Walmart’s locally grown produce via photopin (license)















































