Menopause and Hot Flashes
With menopause and the hormonal shifts that take place, some women suffer more than others with symptoms such as hot flashes. If you have ever been near someone during a hot flash, you know that this curious condition is more than feeling a little hot under the collar. During a hot flash, women will suddenly disrobe, wake from a deep sleep covered in sweat (so much so that they have to change the sheets!), or otherwise appear distressed and oftentimes suffer interference in whatever activity in which they were engaging. As we reported in an earlier post, women on average may have hot flashes for 5 years after the date of her last period. Some women (up to 1/3 in the referenced study) will report hot flashes for 10 or more years after menopause.
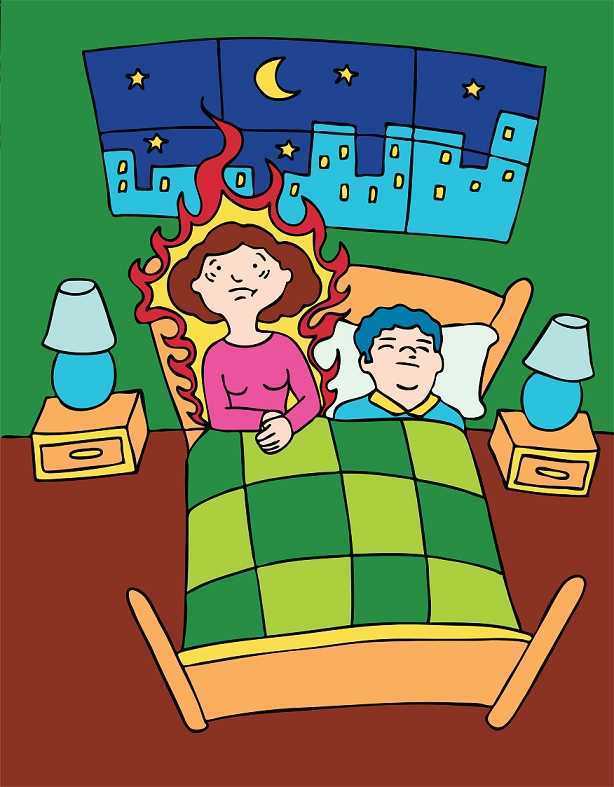 Hot flashes and night sweats also significantly disrupt sleep, according to research by Baker and colleagues. Menopausal women with insomnia may also have higher levels of psychologic, somatic, vasomotor symptoms, and score lower on the Beck Depression Inventory, and sleep efficiency and duration scores. Poor sleep can be associated with morbidity such as hypertension, stroke, diabetes and depression, so interrupted sleep is more than an inconvenience, but potentially a serious health issue.
Hot flashes and night sweats also significantly disrupt sleep, according to research by Baker and colleagues. Menopausal women with insomnia may also have higher levels of psychologic, somatic, vasomotor symptoms, and score lower on the Beck Depression Inventory, and sleep efficiency and duration scores. Poor sleep can be associated with morbidity such as hypertension, stroke, diabetes and depression, so interrupted sleep is more than an inconvenience, but potentially a serious health issue.
A more recent study linked anxiety as a potential risk factor for menopausal hot flashes. In 233 women who are premenopausal at baseline and who were followed for at least a year after their final menstrual cycle, anxiety symptoms, hormone levels, hot flashes and other psychosocial variables were assessed. During the 14 year follow-up 72% of the women reported having moderate to severe hot flashes, and the researchers correlated somatic anxiety as a potential predictive association with anxiety. Somatic anxiety refers to the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as stomach ache, increased heart rate, sweating, muscle aches.
In order to help a woman support her wellness during menopausal transitions, being able to address somatic anxiety and conditions like hot flashes is imperative. Teaching skills such as breathing, relaxation training, meditation, or mindfulness may positively impact the anxiety, and therefore have the potential to reduce hot flashes and other adverse symptoms. Herman & Wallace's Menopause Rehabilitation and Symptom Management course is an excellent opportunity to learn some of these valuable skills.
Baker, F. C., Willoughby, A. R., Sassoon, S. A., Colrain, I. M., & de Zambotti, M. (2015). Insomnia in women approaching menopause: beyond perception. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 60, 96-104.
Freeman, E. W., & Sammel, M. D. (2016). Anxiety as a risk factor for menopausal hot flashes: evidence from the Penn Ovarian Aging cohort. Menopause, 23(9), 942-949.
Freeman, E. W., Sammel, M. D., & Sanders, R. J. (2014). Risk of long term hot flashes after natural menopause: Evidence from the Penn Ovarian Aging Cohort. Menopause (New York, NY), 21(9), 924.
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://hermanwallace.com/