In this brief blog, I hope to explore several lifestyle medicine strategies (sleep hygiene, stress management, social connectedness) and how they may be included in therapeutic interventions to improve clinical outcomes. Frates and colleagues define lifestyle medicine as "The use of evidence-based lifestyle therapeutic approaches, such as a predominately whole-food and plant-based diet, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, stress management, avoidance of risky substance use, and other non-drug modalities to treat, oftentimes reverse, and prevent the lifestyle-related, chronic disease that's all too prevalent."1 Figure 1, adapted from the American College of Lifestyle Medicine, outlines the six pillars of lifestyle medicine.
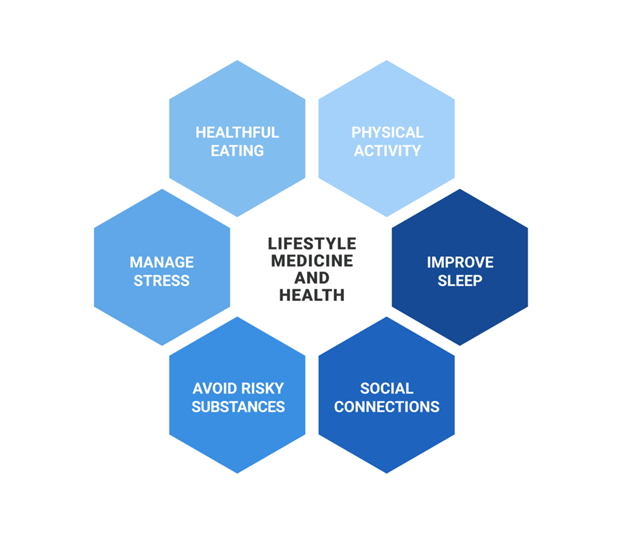
Figure 1. Components of lifestyle medicine
Sleep Hygiene in Patient Education
The following are some simple patient education strategies that may help patients improve sleep:2-5
- Establish a regular bedtime and waking hours (avoid or minimize "social jet lag" that may be due to work, school, or your personal schedule).
- Create a comfortable room that is cool, dark, and quiet.
- Sleep in a comfortable bed and make sure it's not too old.
- Use a supportive and comfortable pillow and ensure it's not too old.
- Eliminate nighttime caffeine and limit daytime caffeine.
- Do not wear tight or restrictive clothing during sleep
- Avoid alcohol within 3 hours of bedtime.
- Do not smoke or use nicotine.
- Eliminate/limit after-dinner and late-night snacking.
- Limit or avoid computer use and smartphone use near bedtime.
- Avoid intense exercise near bedtime. However, do exercise and be physically active during the day.
- Maintain a healthy body mass index (BMI).
- Avoid watching intense television shows before bedtime.
- Turn off the radio and television before going to sleep.
- Avoid bright light near bedtime, but do increase daytime exposure to sunlight.
- Consider reducing your fluid intake near bedtime to avoid (or minimize) getting up to go to the bathroom, but maintain adequate hydration during the day.
- Minimize sugar and salt intake near bedtime as it may cause increased trips to the bathroom.
- Learn strategies to reduce daily stress so it does not result in poor quality and quantity of sleep.
- Minimize a tense or stressful lifestyle since this may carry over into sleep.
- Embrace mindfulness before bedtime
- Consider meditating close to bedtime or using a body scan or progressive muscle relaxation technique.
- Consider tai chi, qigong, or yoga later in the day.
- Establish a bedtime ritual such as:
- One hour before going to sleep, shut down all phone and computer devices. Then you can either read a book or watch a funny television show (drama may be too stimulating).
- Five minutes before you go to sleep, brush your teeth and floss, wash your hands and face with lavender soap, and shut off all the lights before slipping into your cozy bed with gratitude and pleasant thoughts.
Stress Management Patient Education
The following are some simple patient education strategies that may help patients manage stress:6
- Try yoga, tai chi, qigong
- Use aromatherapy (such as lavender)
- Engage in outdoor physical activities such as walking, hiking, and biking
- Engage in outdoor activities such as gardening
- Participate in hobbies such as reading, pottery, painting, and playing music
- Play with pets
- Get a massage
- Get involved in social activities such as volunteering, coaching, and community dancing
- Listen to music
- Smile and laugh more by watching comedy movies or television shows
Social Connectedness Patient Education
The following are some simple patient education strategies that may help patients improve socialization and social connectedness to form nurturing and constructive relationships:7-13
- Attend local sporting events, music performances, or art and museum exhibits.
- Connect with family and friends locally or on Zoom.
- Connect with your physician, therapist, wellness, or fitness professional via telehealth-delivered services.
- Create or join a community garden club.
- Create or join a lunchtime walking, yoga, or tai chi club.
- Engage in conventional group exercises such as softball, volleyball, basketball, pickleball, paddle tennis, or tennis.
- Engage in mind-body exercises such as yoga, tai chi, or Pilates.
- Engage in work-related community activities and fitness programs.
- Engage in small conversations with cashiers and employees at various stores you visit.
- Engage with members at your community place of worship.
- Enroll in art-based community activities, such as art, dance, drama, music, poetry, pottery, or expressive writing classes.
- Enroll at a local or community college to take cooking, history, or astronomy classes.
- Get a library card and participate in book club events.
- Get involved in nature-based activities, such as bird watching, botanical garden and park visits, farmer's market shopping, forest bathing or hiking, gardening, or walks at a lake, river, or beach.
- Join a group, such as a local bicycling club, chess, or table tennis club, or participate in your favorite hobby.
- Join a gym or fitness center.
- Join self-help groups.
- Join social media platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, or TikTok.
- Play with your pets.
- Volunteer at a community center, hospital, school, or library.
- Volunteer to coach sports or mentor students.
- Walk with a mall club or create one in your neighborhood
If you are interested in learning more about these topics and others, please see my course Integrative and Lifestyle Medicine Toolbox for Rehab and Pain Management with Herman & Wallace.
Resources for Clinicians:
Learn how to include integrative and lifestyle medicine into your clinical practice with these resources:
- Academy of Integrative Health & Medicine
- American College of Lifestyle Medicine
- American College of Preventive Medicine
- Institute of Lifestyle Medicine
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
Instructor Bio:
 Ziya "Z" Altug, PT, DPT, MS, OCS is a board-certified doctor of physical therapy with 32 years of clinical experience treating musculoskeletal injuries. Z currently provides outpatient physical therapy in the home setting in Los Angeles, California, and serves as a continuing education instructor.
Ziya "Z" Altug, PT, DPT, MS, OCS is a board-certified doctor of physical therapy with 32 years of clinical experience treating musculoskeletal injuries. Z currently provides outpatient physical therapy in the home setting in Los Angeles, California, and serves as a continuing education instructor.
Z received his Bachelor of Science in Physical Therapy at the University of Pittsburgh in 1989, Master of Science in Sport and Exercise Studies in 1985 and Bachelor of Science in Physical Education in 1983 from West Virginia University, and a Doctor of Physical Therapy from the College of St. Scholastica in 2015. Z is a long-standing member of the American Physical Therapy Association and a member of the American College of Lifestyle Medicine. He has attended workshops in yoga, tai chi, qigong, Pilates, Feldenkrais Method, and the Alexander Technique.
Z is the author of the books Integrative Healing: Developing Wellness in the Mind and Body (2018), The Anti-Aging Fitness Prescription (2006), and Manual of Clinical Exercise Testing, Prescription, and Rehabilitation (1993). In 2020, he published the chapter Exercise, Dance, Tai Chi, Pilates, and Alexander Technique in The Handbook of Wellness Medicine. In 2021, he published the article Lifestyle Medicine for Chronic Lower Back Pain: An Evidence-Based Approach in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.
References:
- Frates, B., Bonnet, J.P., Joseph, R., & Peterson, J.A. (2019). Lifestyle Medicine Handbook: An Introduction to the Power of Healthy Habits. Monterey, CA: Healthy Learning.
- Altug Z. Integrative Healing: Developing Wellness in the Mind and Body. Springville, UT: Cedar Fort, Inc.; 2018.
- Kryger MH, Roth T, Goldstein CA. Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine (2 Volume set), 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021
- Matsuo T, Miyata Y, Sakai H. Effect of salt intake reduction on nocturia in patients with excessive salt intake. Neurourol Urodyn. 2019;38(3):927-933.
- Vitale KC, Owens R, Hopkins SR, Malhotra A. Sleep hygiene for optimizing recovery in athletes: review and recommendations. Int J Sports Med. 2019;40(8):535-543.
- American College of Lifestyle Medicine. Handout: Lifestyle stress reduction. American College of Lifestyle Medicine; 2019.
- Leavell MA, Leiferman JA, Gascon M, Braddick F, Gonzalez JC, Litt JS. Nature-based social prescribing in urban settings to improve social connectedness and mental well-being: a review. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2019;6(4):297-308.
- National Institutes of Health. Social Wellness Toolkit. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health. Accessed on June 2022.
- Roland M, Everington S, Marshall M. Social prescribing - transforming the relationship between physicians and their patients. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(2):97-99.
- Choi NG, Pepin R, Marti CN, Stevens CJ, Bruce ML. Improving social connectedness for homebound older adults: randomized controlled trial of tele-delivered behavioral activation versus tele-delivered friendly visits. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2020;28(7):698-708.
- Davidson KW, Krist AH, Tseng CW, et al. Incorporation of social risk in US Preventive Services Task Force recommendations and identification of key challenges for primary care. JAMA. 2021;326(14):1410-1415.
- Eder M, Henninger M, Durbin S, et al. Screening and interventions for social risk factors: technical brief to support the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2021;326(14):1416-1428.
- Steinman L, Parrish A, Mayotte C, et al. Increasing social connectedness for underserved older adults living with depression: a pre-post evaluation of PEARLS. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2021;29(8):828-842.
Integrative and Lifestyle Medicine Toolbox for Rehab and Pain Management

Course Dates:
January 21, 2023
Price: $125
Experience Level: Beginner
Contact Hours: 4.5
Description: This course was written and developed by Ziya “Z” Altug, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, a board-certified doctor of physical therapy with 32 years of experience in treating musculoskeletal conditions, Brief lectures on the research and resources and labs will cover a toolbox approach for creating clinically relevant pain, anxiety, depression, and stress management strategies using lifestyle medicine, integrative medicine, expressive and art-based therapies, and the impact of nature on health. Participants will be able to practice Tai Chi/Qigong, expressive and art-based therapies including Music, Dance, and Drama Therapy, nature and aromatic therapies, self-hypnosis, and self-massage.

Rachna Mehta PT, DPT, CIMT, OCS, PRPC, RYT 200 is Board certified in Orthopedics, a Certified Integrated Manual Therapist, and a Herman & Wallace certified Pelvic Rehab Practitioner. Rachna has a personal interest in various eastern holistic healing traditions and she noticed that many of her chronic pain patients were using complementary health care approaches including acupuncture and yoga. Her course Acupressure for Optimal Pelvic Health brings a unique evidence-based approach and explores complementary medicine as a powerful tool for holistic management of the individual as a whole focusing on the physical, emotional, and energy body.
A patient walks into the clinic 30 minutes late for their appointment with me, brimming with anxiety and apologizing profusely. “I’m so sorry,” they say, “I kept driving around in circles and could not find a single parking spot.” Another patient, a teacher, reports that her anxiety and pelvic pain progressively worsens as her day progresses and peaks when she gets home with her own two young children at the end of a long day. A third patient with a 15-year history of pelvic pain with unexplained infertility who has failed every conventional ART treatment suddenly conceives her miracle child naturally with acupuncture. She shares, “My anxiety was always so high, I could never relax. They stimulated acupuncture points all over my body, and it worked. My anxiety was so much under control this time.”
Here are the things running through my mind as I work with these patients:
- What could be the most effective hands-on clinical intervention I could use to calm them down?
- Could I teach them daily acupressure self-care and wellness regimens to alleviate anxiety?
- Could I foster a feeling of self-control in them to manage anxiety in stressful situations?
- How does acupuncture really work for infertility, and why does it use points all over the body?
- Can acupressure be used to stimulate key potent acupoints for anxiety?
- Is there a physical practice of yoga that is calm and meditative and is complementary to acupressure?
These questions led to researching the currently available evidence, and I found that there has been a rising clinical interest in complementary holistic practices over the last several decades for anxiety & chronic stress management. Current research supports both acupressure and yin yoga as powerful tools in the realm of energy medicine.
Acupressure is based on 3000 years of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that believes in Meridian Theory and energy channels which are connected to the function of the visceral organs. There is emerging scientific evidence of acupoints transmitting Qi energy through the vast network of interstitial connective tissue connecting the peripheral nervous system to the central viscera with potentially powerful integrative applications across multiple systems. This network is also continuous with more specialized connective tissues such as the periosteum, perimysium, perineurium, pleura, peritoneum, and meninges (1). Fascia and connective tissue literally pervade every anatomic dimension in the body.
Helene Langevin (2) and colleagues proposed an anatomical/ physiological parallel to explain some of the key concepts of TCM.
- Qi: Sum of all body energetic phenomena (e.g. metabolism, movement, signaling, information exchange)
- Meridian Qi: Connective tissue biochemical/bioelectrical signaling
- Blockage of Qi: Changed connective tissue matrix composition leading to a change in signal transduction
- Restoration of the flow of Qi: Cellular activation/gene expression leading to restored connective tissue matrix composition and signal transduction
Modern acupressure charts map the principal 12 meridians connected to the physiological functions of key organs. The key meridians to focus on in pelvic health patients would be the bladder, kidney, spleen, and stomach meridians. Acupressure is systemically effective for a host of conditions including anxiety, insomnia, chronic pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, infertility, constipation, digestive disturbances, and urinary dysfunctions. Each acupressure point has many internal connections to the visceral organs. Stimulating these points by using acupressure assists the body’s self-regulating mechanisms and facilitate healing and neurophysiological quieting.

A recent study by Elizabeth Monson (3) and colleagues retrospectively analyzed 519 acupressure treatments on hospitalized patients, nurses, and the general public across six US states. They followed a specific acupressure protocol and looked at pre- and post-treatment in conjunction with self-rated pain and anxiety scores, where 0 represented no pain or anxiety, and 10 represented the worst pain and anxiety. They found that:
- Hospitalized patients demonstrated a 4 point ↓ in pain scores and 5 point ↓ in anxiety scores
- Nurses demonstrated a 3 point ↓ in pain scores and 4 point ↓ in anxiety scores
This study concluded that acupressure is a highly satisfactory complementary therapy that can demonstrate a clinically significant decrease in self-rated pain and anxiety scores (2).
A robust body of research also attests to yoga being a powerful integrative health practice for alleviating daily anxiety and stress. Yoga is an umbrella term for various physical, mental, and spiritual practices originating in ancient India. Hath Yoga is the most popular form of Yoga in western society. Yin Yoga, a derivative of Hath Yoga, is a much calmer meditative practice that uses seated and supine postures, held three to five minutes while maintaining deep breathing. Its focus on calmness and mindfulness makes Yin Yoga a tool for relaxation and stress coping, thereby improving psychological health (4).
Yin Yoga is also a wonderful complimentary practice that can be combined with Acupressure. Yin Yoga engages the physical, emotional, and energy body. Yin postures supportively align the body to stress connective tissues along specific meridian lines that activate potent acupressure points along those meridians. The Acupressure for Optimal Pelvic Health remote course explores Yin postures within key meridians and integrates acupressure and Yin Yoga with modifications into rehabilitation interventions. Anxiety and daily wellness self-care program is also a key part of the course.
As pelvic health therapists and medical providers, we can empower our patients to recognize the mind-body-energy interconnections and how they affect multiple systems, giving them the tools and self-care regimens to live healthier anxiety and pain-free lives. Combining our orthopedic skills with mindfulness-based holistic interventions also complements our best evidence-based practices.
The course Acupressure for Optimal Pelvic Health is an evidence-based journey of holistic healing and empowerment curated and taught by Rachna Mehta. To learn how to integrate acupressure and Yin Yoga into your practice, join the next scheduled remote course on October 23-24, 2021.
- Kaptchuk TJ. 2000. The web that has no weaver. Understanding Chinese medicine. Chicago: Contemporary Publishing Group, Inc.2.
- Langevin HM, Yandow JA. Relationship of acupuncture points and meridians to connective tissue planes. Anat Rec. 2002;269(6):257-265. doi:10.1002/ar.10185
- Monson E, Arney D, Benham B, et al. Beyond Pills: Acupressure Impact on Self-Rated Pain and Anxiety Scores. J Altern Complement Med. 2019;25(5):517-521. doi:10.1089/acm.2018.0422
- Daukantaitė D, Tellhed U, Maddux RE, Svensson T, Melander O. Five-week Yin Yoga-based interventions decreased plasma adrenomedullin and increased psychological health in stressed adults: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2018;13(7)
- Hmwe NTT, Browne G, Mollart L, Allanson V, Chan SW. An Integrative review of Acupressure interventions for older people: A focus on sleep quality, depression, anxiety, and agitation. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2019;34(3):381-396. doi:10.1002/gps.5031
- Au DW, Tsang HW, Ling PP, Leung CH, Ip PK, Cheung WM. Effects of Acupressure on Anxiety: A Systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupunct Med. 2015;33(5):353-359. doi:10.1136/acupmed-2014-010720

Aparna Rajagopal, co-author of the Breathing and the Diaphragm: Orthopedic Therapists remote course, shares "I have used breathing and evaluation of the diaphragm as a part of pelvic care for several years now...Through my interactions, I have come to realize that although many of the therapists are aware that the diaphragm and breathing are important, they are unsure of how to assess for dysfunctions and address those dysfunctions."
Pelvic floor patients who may benefit from diaphragmatic breathing exercises include those who present with pelvic pain, incontinence, prolapse, and cervical/thoracic/scapular/lumbar pain. The Breathing and the Diaphragm: Orthopedic Therapists remote course will expand the participant's knowledge of the diaphragm and breathing mechanics. This course offers a different perspective on back pain and alignment, along with the ability to assess and connect breathing and the diaphragm to core stability, continence issues, and the autonomic nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is in charge of those bodily processes that do not require conscious thought. These include digestion, temperature, blood pressure, and breathing. The autonomic nervous system can be hacked or manipulated with deep breathing exercises such as diaphragmatic breathing.
Diaphragmatic breathing involves fully engaging the abdominal muscles and diaphragm when breathing by actively pulling the diaphragm down with each inward breath, allowing the lungs to fill more efficiently. The benefits of diaphragmatic breathing can include lowered heart rate and blood pressure regulation. Patients may also see a decrease in cortisol (a stress hormone), allowing them to relax better (1).
The effects of stress can show as emotional, cognitive, behavioral, or physical symptoms in different people. Pelvic pain can be connected to stress through the pelvic floor stress reflex response. This response is a reaction where the pelvic floor muscles actively contract from a stress trigger, either mental or physical. In such cases, increased muscle contractions can lead to tightness and weakness in the affected muscles. Visualize an agitated, tightened muscle to understand how stress can lead to hypertonic muscles, diarrhea, bladder, and sexual issues
Now let's back up to tie in the stress hormone cortisol. Normal cortisol levels rise and fall in a rhythmic pattern throughout the day, allowing for circadian rhythms. Cortisol also helps immune functions and cell repair. When the body is under stress, cortisol is produced in abnormal levels, leading to compromised immune function, pain, exhaustion, and many other issues. Pelvic conditions connected to abnormal cortisol levels include endometriosis(2), interstitial cystitis (3), vulvovaginal candidiasis, and vulvodynia. If a patient has a high cortisol-related diagnosis, intervention can include diaphragmatic breathing for stress management.
The course Breathing and the Diaphragm: Orthopedic Therapists is curated and taught by Aparna Rajagopal and Leeann Taptich. To learn how to incorporate breathing and the diaphragm into your practice, join the next scheduled remote course on October 23-24, 2021.
- Hopper S, Murray S, Ferrara L, Singleton J. Effectiveness of diaphragmatic breathing for reducing physiological and psychological stress in adults: a quantitative systematic review. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019 Sep;17(9):1855-1876. doi:10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003848.
- Friggi Sebe Petrelluzzi K, Garcia M, Petta C et al. Physical therapy and psychological intervention normalize cortisol levels and improve vitality in women with endometriosis. Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2012;33(4):191-198. doi:10.3109/0167482x.2012.729625.
- Schrepf A, O’Donnell M, Luo Y, Bradley C, Kreder K, Lutgendorf S. Inflammation and Symptom Change in Interstitial Cystitis or Bladder Pain Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary Approach to the Study of Chronic Pelvic Pain Research Network Study. Urology. 2016;90:56-61. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2015.12.040.