Everyday we as pelvic rehab providers get to help patients achieve their goals by meeting them where they are and guiding them along.
A couple of months ago I had a new patient come in to see me who was seven months status post c-section delivery of her first child. She was referred to physical therapy because she could not tolerate anything touching her lower abdomen and she was also unsure of how to start exercising again including returning to her yoga practice. I remember reading her referral and thinking that this should be a simple evaluation and treatment session. What actually happened was a little different.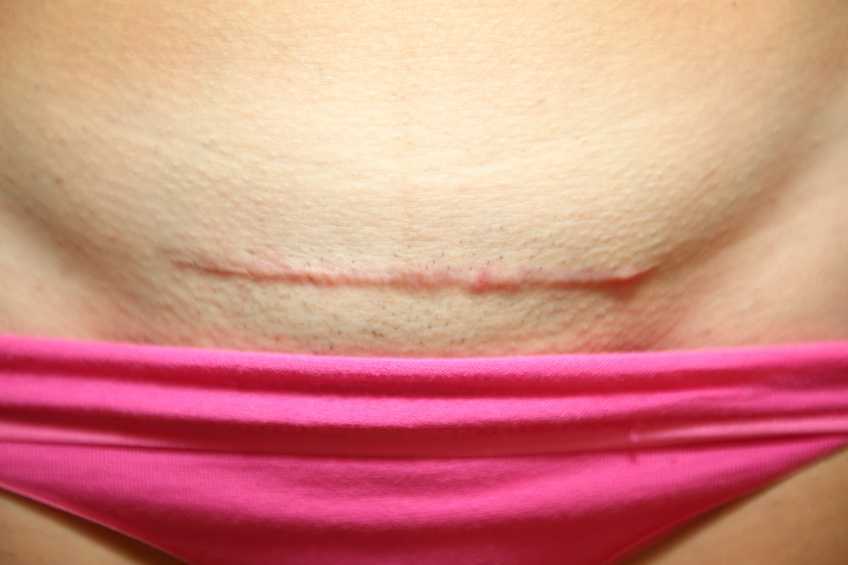
Her delivery hadn’t gone the way she planned, and she was not comfortable discussing it at our first session. This patient had not looked at or touched her c-section incision besides drying it off after her shower for the seven months since delivery. Her physician had made a referral to PT and to a counselor within three months of delivery to help support the patients’ recovery. The patient had not followed through with the PT referral until she had significant encouragement from her counselor and physician.
Initially the patient declined any observation or palpation of her abdomen so at our first session we focused on thoracic range of motion, general posture, and encouraged her to start touching her abdomen through her clothes, even if avoiding direct touch to the incisional region. The patient was agreeable with this starting point. At the second session the patient was willing to have me look at her abdomen and touch the abdomen but she declined direct palpation of the scar region. With simple observation I could see a scar that was closed and healing but also that was pulled inferior towards her pubic bone. She was not comfortable laying flat on the treatment table and had to be supported in a semi-recline throughout the session. She also described buzzing symptoms at the scar region when she reached her arms overhead.
We started some gentle desensitization techniques as would be used with a person that had Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) after an injury. I focused those treatments to the abdominal region but avoided the scar region. We focused her home program on breathing into her abdomen allowing some stretch and expansion of the abdominal region. Her home program also included laying flat for five minutes per day. I asked her to notice any general tension throughout her body during the day and attempt to change it and release it if able.
By the fourth session we where able to begin direct palpation and manual therapy techniques to the c-section scar and the whole abdominal region. The patient was apprehensive but agreed to proceeding with utilizing techniques as described by Wasserman et al2018 including superficial skin rolling, direct scar mobilization and general petrissage/effleurage of the abdomen and lumbothoracic region.
Over the next five sessions the patient was able to start wearing undergarments and pants that touched her lower abdomen. She was able to perform her own self massage to the region and began an exercise program including prone press ups, progressive generalized trunk strengthening, and return to her prior-to-pregnancy yoga practice.
Drawing on the techniques we learn from multiple sources, applying them to the lumbopelvic region, and helping our patients wherever the client is in their journey to wellness, is what inspires me to keep learning.
Techniques like this are taught in my 2-day Manual Therapy Techniques for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist course. I specifically wrote this course so that pelvic rehab therapists that are looking for more techniques and/or more confidence in their palpation skills would have a weekend to hone those skills. We spend time learning anatomy, learning palpation skills, manual techniques, problem solving home programs and discussing cases. Check out Manual Therapy Techniques for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist - Raleigh, NC - June 22-23, 2019 for more information and I hope to see you there.
Wasserman, J. B., Abraham, K., Massery, M., Chu, J., Farrow, A., & Marcoux, B. C. (2018). Soft Tissue Mobilization Techniques Are Effective in Treating Chronic Pain Following Cesarean Section: A Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial. Journal of Women’s Health Physical Therapy, 42(3), 111-119.
The following is a guest submission from Alysson Striner, PT, DPT, PRPC. Dr. Striner became a Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner (PRPC) in May of 2018. She specializes in pelvic rehabilitation, general outpatient orthopedics, and aquatics and treats at Carondelet St Joesph’s Hospital in the Speciality Rehab Clinic located in Tucson, Arizona.
Recently, I had a patient present with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) on his right foot. He stated that the pain had started about 10 days after his prostatectomy when someone had fallen onto his right foot. He reported a bunionectomy on that foot 7 years prior and noted an episode of plantar facilities before his prostatectomy. CRPS is defined as “chronic neurologic condition involving the limbs characterized by severe pain along with sensory, autonomic, motor, and trophic impairments” in a 2017 article "Complex regional pain syndrome; a recent update" by Goh, En Lin. The article goes on to discuss how CRPS can set off a cascade of problems including altered cutaneous innervation, central and peripheral sensitization, altered sympathetic nervous system function, circulating catecholamines, changes in autoimmunity, and neuroplasticity.
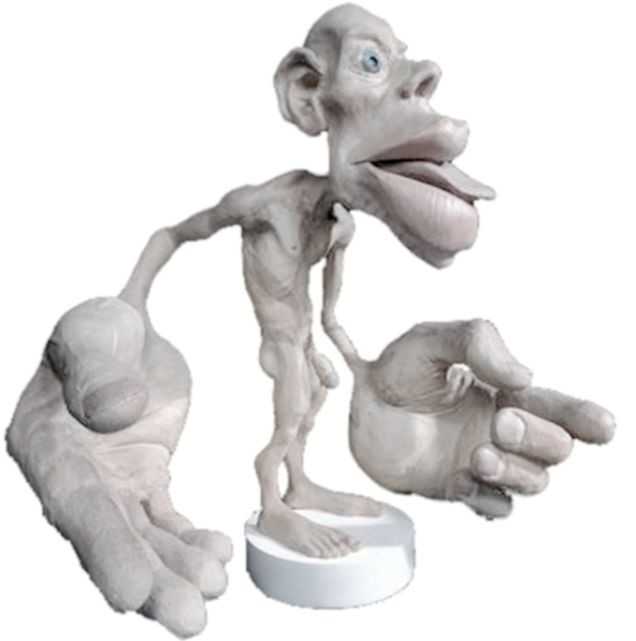 A recent persistent pain theory to explain the relationship between pelvic floor and his foot could be overflow or ‘smudging’ in his homunculus. The homunculus is the map of our physical body in our brain where the feet are located next to the genitals. Possibly when one has pain, there can be ‘smudging’ of our mental body map from one area into another. I have heard this explained as though a chalk or charcoal drawing has been swipes their hand through the picture. A recent study by Schrabrun, SM et al “Smudging of the Motor Cortex is Related to the Severity of Low Back Pain” found that people with chronic low back pain had a loss of cortical organization which and that this loss was associated with the severity and location of LBP.
A recent persistent pain theory to explain the relationship between pelvic floor and his foot could be overflow or ‘smudging’ in his homunculus. The homunculus is the map of our physical body in our brain where the feet are located next to the genitals. Possibly when one has pain, there can be ‘smudging’ of our mental body map from one area into another. I have heard this explained as though a chalk or charcoal drawing has been swipes their hand through the picture. A recent study by Schrabrun, SM et al “Smudging of the Motor Cortex is Related to the Severity of Low Back Pain” found that people with chronic low back pain had a loss of cortical organization which and that this loss was associated with the severity and location of LBP.
There are many ways to improve the organization of the homunculus and create neuroplasticity. One such way was suggested is with Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) to the bottom of the foot to affect bladder spasms and pain. In recent study, “Transcutaneous electrical stimulation of somatic afferent nerves of the foot relieved symptoms related to postoperative bladder spasms,". Zhang, C et al. 2017 found that participates that had either a bladder surgery or a prostate surgery had improvement in bladder spasm symptoms and VAS scores on day two and three. Their protocol was to use two electrodes over the bottom of the foot at 5 Hz with 0.2 millisecond pulse width until a muscle twitch was achieved and was increased, but still comfortable for an hour (there is a picture of electrode placement in the article). The authors note that this neuromodulation of the foot sensory nerves may inhibit interactions between the somatic peripheral neuropathway and autonomic micturition reflex to calm the bladder and pain.
No matter what we do to help calm nervous systems from the top down; pain neuroscience education, mindful based relaxation, graded motor imagery, or from the bottom up; de-sensitization, biofeedback, or good old-fashioned TENS. The result is the same; a cortical organization and happier patients.
En Lin Goh†, Swathikan Chidambaram† and Daqing Ma. "Complex regional pain syndrome: a recent update". Burns & Trauma 2017 5:2.https://doi.org/10.1186/s41038-016-0066-4"
Schabrun SM, Elgueta-Cancino EL, Hodges PW. "Smudging of the Motor Cortex Is Related to the Severity of Low Back Pain." Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017 Aug 1;42(15):1172-1178. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000938
Chanjuan Zhang, et al. "Transcutaneous electrical stimulation of somatic afferent nerves in the foot relieved symptoms related to postoperative bladder spasms". BMC Urol. 2017; 17: 58. doi: 10.1186/s12894-017-0248-9