Vaginal wall thinning associated with menopausal changes can cause vaginal burning and pain, limitations in sexual function, and vaginal redness or even changes in discharge. Because these symptoms can mimic many other conditions such as pelvic floor muscle dysfunction or an infection, it is necessary for the pelvic rehabilitation therapist to be alert to identifying vaginal atrophy as an issue to rule out so that patients can access appropriate medical care when needed.
 Atrophic vaginitis (AV) is a condition of the vaginal walls associated with tissue thinning, discomfort, and inflammation. The tissue changes often extend into the vulvar area as well. Atrophic vaginitis may also be called vaginal atrophy, vulvovaginal atrophy, urogenital atrophy, or genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Although we tend to associate menopause with women who are in their 40’s or 50’s, any woman who has stopped having her menstrual cycles or who has had a significant reduction in her cycles may be at risk for vaginal atrophy. Any woman who has had a hysterectomy may also be at risk of this thinning of the vaginal walls. Common symptoms of vaginal wall thinning include vaginal dryness, tissue irritation, redness, itching, and a “burning” pain. Interruption in sleep, limitations in activities of daily living, and changes in mood and temperament have also been reported.
Atrophic vaginitis (AV) is a condition of the vaginal walls associated with tissue thinning, discomfort, and inflammation. The tissue changes often extend into the vulvar area as well. Atrophic vaginitis may also be called vaginal atrophy, vulvovaginal atrophy, urogenital atrophy, or genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Although we tend to associate menopause with women who are in their 40’s or 50’s, any woman who has stopped having her menstrual cycles or who has had a significant reduction in her cycles may be at risk for vaginal atrophy. Any woman who has had a hysterectomy may also be at risk of this thinning of the vaginal walls. Common symptoms of vaginal wall thinning include vaginal dryness, tissue irritation, redness, itching, and a “burning” pain. Interruption in sleep, limitations in activities of daily living, and changes in mood and temperament have also been reported.
One common pharmacological intervention for vaginal and vulvar atrophy is the topical application of hormone creams such as estrogen. A recent study examined the effects of low dose estrogen therapy on bacteria that populates the vaginal walls.Shen et al., 2016 This bacteria may be causal or correlated to vaginal health, and also appears related to estrogen levels. Sixty women diagnosed with atrophic vaginitis were treated with low dose estrogen therapy and followed for four weeks to assess the vaginal microbiotia via mid-vaginal swabs. Following are highlights from the linked study’s findings,
- Prior to treatment, in symptomatic postmenopausal women the Lactobacilli species were less abundant and made up 11.2% of the community, while in asymptomatic women, the communities were more than 50% lactobacilli
- Gardnerella was more abundant than Lactobacillus in women with atrophic vaginitis
- Overall diversity of bacterial communities between healthy women and those with atrophic vaginitis was not significantly different
- In response to treatment with estrogen, women with AV reported improved symptoms and decreased vaginal pH
- Serum estradiol improved on average from approximately 42 pmol/L to 168 pmol/L by week 2, with little change from week 2 to week 4
- Lactobacillus count was negatively correlated with symptoms (i.e., more Lactobacillis = less symptoms) and Gardnerella and Atopobium counts were positively correlated with symptoms
- There were variations noted in how each woman’s vaginal bacterial communities responded to the estrogen therapy in that some women had a dominance of other bacteria after 4 weeks even though their symptoms decreased
In conclusion, the authors stated that “…a Lactobacillus-dominated vaginal community may be considered as one of the signs of AV treatment success…” along with reduced symptoms and increased serum estradiol levels. Prior studies have recognized barriers to treatment that include lack of patient knowledge of vulvar and vaginal atrophy, failure to discuss associated symptoms with physicians, concerns about safety of treatments or poor symptom relief with prescribed interventions.Kingsburg et al., 2013 This leaves the pelvic rehabilitation provider in a excellent role of educating women in the signs and symptoms of atrophic vaginitis, observing the tissues for changes, and communicating with referring providers and prescribers if a concern is noted. Furthermore, failure to recognize the potential for vaginal atrophy and treating these tissues with manual therapy or exercise may injure or exacerbate the problem.
Interested in learning more? Keep an eye out for a Menopause Rehabilitation and Symptom Management course with Michelle Lyons!
Changes in the Vagina and Vulva. Retrieved June 27, 2016 from http://www.menopause.org/for-women/sexual-health-menopause-online/changes-at-midlife/changes-in-the-vagina-and-vulva
Kingsberg, S. A., Wysocki, S., Magnus, L., & Krychman, M. L. (2013). Vulvar and vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women: findings from the REVIVE (REal Women's VIews of Treatment Options for Menopausal Vaginal ChangEs) survey. The journal of sexual medicine, 10(7), 1790-1799.
Shen, J., Song, N., Williams, C. J., Brown, C. J., Yan, Z., Xu, C., & Forney, L. J. (2016). Effects of low dose estrogen therapy on the vaginal microbiomes of women with atrophic vaginitis. Scientific reports, 6.
Vaginal Atrophy. Retrieved June 27, 2016 from http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vaginal-atrophy/home/ovc-20200167
The following comes to us from Felicia Mohr, DPT, a guest contributor to the Pelvic Rehab Report.
Vaginal mesh kits were used frequently early in the millennium as they led to high initial anatomic success rates with peak use between 2008 and 2010. Objectively they seemed to help elevate women’s pelvic organs to appropriate anatomical locations. Unfortunately there has been a high rate (10% according to a review of current literature on PubMedBarski 2015) of mesh erosion causing recurrent prolapse and/or stress urinary incontinence. Also there are cases when the mesh product perforates surrounding organs causing numerous dangerous complications. The rate of mesh-related complications according to current research is 15-25%. As a result, the FDA has reclassified the risk of synthetic mesh into a higher risk category so that the public has an increased awareness of the risk involved in these types of surgeries.
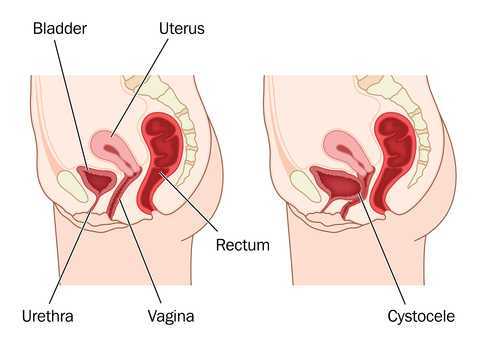 A systematic review and meta-analysis, published in 2015, reviewed the risk factors for mesh erosion following female pelvic floor reconstructive surgery (Deng, et al). They concluded the following factors increase risk of mesh erosion: younger age, more childbirths, premenopausal states, diabetes, smoking, concomitant hysterectomy, and surgery performed by a junior surgeon. Moreover, concomitant POP surgery and preservation of the uterus may be the potential protective factors for mesh erosion.
A systematic review and meta-analysis, published in 2015, reviewed the risk factors for mesh erosion following female pelvic floor reconstructive surgery (Deng, et al). They concluded the following factors increase risk of mesh erosion: younger age, more childbirths, premenopausal states, diabetes, smoking, concomitant hysterectomy, and surgery performed by a junior surgeon. Moreover, concomitant POP surgery and preservation of the uterus may be the potential protective factors for mesh erosion.
It is a common practice to perform a hysterectomy with a POP surgery. Reason being that the oversized uterus from childbearing adds extra weight on pelvic organs. However, the latter study as well as two other recent studies published in 2015 (Huang, Farthmann) also provide evidence that there is no benefit to a concomitant hysterectomy at the 2.5 year follow up and can lead to less satisfaction with surgery according to patient surveys respectively.
Keep in mind that all pelvic floor surgeries do not use the same amount of mesh material and different procedures have different risks associated with them. One retrospective study (Cohen, 2015) addressing incidence of mesh extrusion categorized 576 subjects into three categories: pubo-vaginal sling (PVS) (a small string of mesh around the urethra specifically addressing stress urinary incontinence only); PVS and anterior repair (also referred to as cystocele or bladder prolapse); and PVS with anterior and/or posterior repairs (also referred to as rectocele or rectal prolapse). Mesh extrusion for these types of procedures occurred at the follow rates: approximately 6% for PVS subjects, 15% for PVS + anterior repair, and 11% for PVS + anterior and/or posterior repair. This study did not account for any other types of mesh-related complications.
Pelvic organ prolapse and stress urinary incontinence make up some of the most common conditions for which patients seek Pelvic Floor physical therapy and perhaps this will allow us to better speak to current research on surgical options.
1. Barski D, Deng EY. Management of Mesh Complications after stress urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolaps repair: review and analysis of the current literature. Biomed Research International; 2015Article ID 831285.
2. Deng T. et al. Risk factor for mesh erosion after female pelvic floor reconstructive surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJU International. Doi:10.1111/bju.13158.
3. Huang LY, et al. Medium-term comparison of uterus preservation versus hysterectomy in pelvic organ prolapse treatment with prolift mesh. International Urogynecology Journal. 2015;26(7):1013-20.
4. Farthmann J, et al. Functional outcome after pelvic floor reconstructive surgery with or without concomitant hysterectomy. Archives of Gynec and Obstet. 2015; 291(3):573-7.
5. Cohen S, Kaveler E. The incidence of mesh extrusion after vaginal incontinence and pelvic floor prolapse surgery. J of Hospital Admin. 2014; 3(4): www.sciedu.ca/jha.
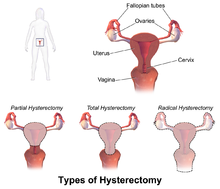 ACOG (American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology) describes hysterectomy as a treatment of last resort, but studies show that anywhere from 10 to 90% of hysterectomies performed in the United States are not medically necessary, evidenced by the fact that today, approximately 90 percent of hysterectomies are performed electively. Corona et al stated: ‘…that alternatives to hysterectomy are underutilized in women undergoing hysterectomy for AUB, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, or pelvic pain. The rate of unsupportive pathology when hysterectomies were done for these indications was 18%.’
ACOG (American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology) describes hysterectomy as a treatment of last resort, but studies show that anywhere from 10 to 90% of hysterectomies performed in the United States are not medically necessary, evidenced by the fact that today, approximately 90 percent of hysterectomies are performed electively. Corona et al stated: ‘…that alternatives to hysterectomy are underutilized in women undergoing hysterectomy for AUB, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, or pelvic pain. The rate of unsupportive pathology when hysterectomies were done for these indications was 18%.’
The US has the highest rate of hysterectomy in the industrialized world; it is the second most common surgical procedure carried out on women. 1 in 3 American women have their uterus removed by the age of 60, with the highest rates in women aged 30-54 (according to Corona et al in 2014, one in five women may not need it).
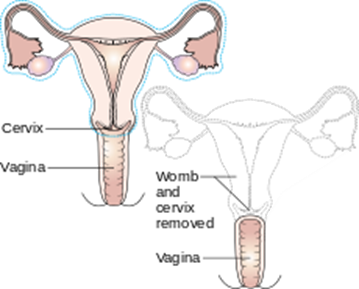 Reasons for hysterectomy include cancer, bleeding with childbirth and severe infection with uterine damage, all of which make up about 10% of cases. The other 90% are made up of medical, non-surgical and other surgical reasons, such as for menstrual cramps, heavy bleeding and fibroids. Unfortunately, too many women are also having hysterectomies as a treatment option for endometriosis (instead of laparoscopic excision, histological confirmation and pelvic rehab follow up)
Reasons for hysterectomy include cancer, bleeding with childbirth and severe infection with uterine damage, all of which make up about 10% of cases. The other 90% are made up of medical, non-surgical and other surgical reasons, such as for menstrual cramps, heavy bleeding and fibroids. Unfortunately, too many women are also having hysterectomies as a treatment option for endometriosis (instead of laparoscopic excision, histological confirmation and pelvic rehab follow up)
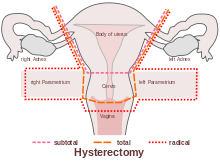
Numerous women who undergo hysterectomy remain unclear about the details of their surgical procedures or indeed the implication for short and long term recovery. Clinically, I have seen many women who assume that as they have had a ‘Total’ Hysterectomy, that includes removal of their ovaries (Total vs Partial Hysterectomy generally refers to cervical preservation). I have also see many women confused as to why their recovery from what has been a laparoscopic surgery, with small incisions, is taking so long. A surgical colleague described it well in my opinion: ‘A laparoscopic hysterectomy is major abdominal/pelvic surgery with tiny incisions’.
 In Part Two of this blog, I will discuss the sequelae of hysterectomy and the key role of pelvic rehab. Interested in learning more about Endometriosis, Fertility and Hysterectomy? Join me in Denver in January!
In Part Two of this blog, I will discuss the sequelae of hysterectomy and the key role of pelvic rehab. Interested in learning more about Endometriosis, Fertility and Hysterectomy? Join me in Denver in January!
The Boston Women's Health Book Collective. Our Bodies, Ourselves: A New Edition For A New Era. New York: Touchstone, 2005., Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Online. "Hysterectomy Surveillance" --- United States, 1994,1999, 2002. http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/ss5105a1.htm
‘Use of other treatments before hysterectomy for benign conditions in a statewide hospital collaborative’ Corona et al (Presented in oral and poster format at the 4oth Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, Scottsdale March 24-26 2014)








































