The journey to and through motherhood is, no doubt, filled with an array of emotional, mental, and physical changes. It can and should be, one of the most empowering times in a person’s life, but it can start to feel overwhelming when there is any degree of uncertainty or when there are obstacles that present themselves throughout the journey. The body is expected to change and grow in ways that are both magical and daunting for the birthing person and the clinicians in the pelvic health arena should be providing the education to help the pendulum swing towards the magic. Unfortunately, access to this education is sparse, recommendations can be conflicting (pending who you're talking to), and an understanding of the services that we can, and should be, providing in the perinatal period are not well defined nor understood by the majority of the healthcare continuum of providers.
During pregnancy, the body transforms with such beautiful intent. The overarching intention is to support adaptation to nurture and accommodate the developing fetus. During this transformation, the body will inevitably undergo physiologic changes in every system of the body, including the neuromusculoskeletal system. These changes in the neuromusculoskeletal system can contribute to the common ailments and complaints of our clients who are pregnant. Pregnancy-related low back pain, pelvic girdle pain, pubic symphysis dysfunction, and neuropathy are amongst some of those ailments whose symptom drivers are the nerves and muscles. As pelvic health clinicians, what is our best effort to treat these tissues during the gestational period?
How does dry needling fit in during pregnancy?
The way we approach tissue dysfunction during the gestational period is no different than at other times in a person’s life. We do, however, have to consider things like the stage of gestation, appropriate zones of treatment, dosage, and patient positioning for certain interventions, one of those being dry needling. In regards to dry needling intervention, we avoid implementing this in the first trimester secondary to the higher risk of spontaneous miscarriage.
There is no evidence to suggest that dry needling intervention would contribute to spontaneous miscarriage. However, as a clinician, we want to protect ourselves so as not to be associated with this unfortunate adverse event. We also withhold implementing dry needling in the zones of the thoracolumbar junction, the pelvic floor musculature, and the anterior abdominal musculature throughout the entire gestational period; this is due to avoiding the region of innervation to the uterus to mitigate association with a possible spontaneous pre-term labor and to abstain placing a needle within geographic proximity to the developing fetus. Otherwise, dry needling is an appropriate intervention for the management of neuromusculoskeletal conditions in this patient population, especially when other clinical approaches for pain mitigation (i.e.: pharmaceutical use) are contraindicated or simply not offered by other healthcare providers. A properly trained clinician can safely implement dry needling as a powerful intervention for pain relief and neuromuscular reset to allow for better activity and load tolerance during the gestational period. Improving activity and load tolerance for the expecting mother has a multitude of benefits for both physical and mental wellness.
Amazing!! What about in the postpartum period?
In the postpartum period, the body will inevitably go through a massive shift in the overall performance of the neuromuscular system. Birth-related neuromuscular dysfunction is common following both vaginal and cesarian delivery due to the mechanical and biochemical stressors placed on the involved tissues, a concept that shouldn’t be surprising for the rehabilitative clinician. Consider your postoperative patient following a total knee replacement; there is a certain degree of expectation surrounding neuromuscular shutdown following the procedure secondary to the inflammatory cascade that follows. Performance for daily activities such as ambulation, transitional movements, and ability to participate in recreational tasks is limited during the acute and subacute recovery period. It takes time to regain mobility of the involved joints and the neuromuscular coordination and strength of the impacted tissues. We progress the patient through our plan of care to reset the dysfunctional tissues, reinforce good movement strategies, and reload the tissues back to function. The neuromuscular performance following a vaginal or cesarean delivery is no different. The muscle groups impacted following birth are typically those of the core canister including the diaphragm, abdominal wall, pelvic floor, and lumbopelvic posterior stabilizers.
One of the best reset tools we have as rehabilitative clinicians is dry needling. We are able to specify treatment to the tissue targets that are unique to each client’s symptom presentation while utilizing electrical stimulation to influence the nervous system for both tissue recovery and performance. Being a bioelectric system, our bodies respond beautifully to this type of input, especially when followed with appropriate interventions to reinforce neuromotor coordination and functional loading. This sequence of interventions optimizes the overall function of the nervous system which ultimately dictates the behavior and performance of the rest of the body. As it relates to our postpartum clientele this should be something we are considering in the immediate postpartum period to optimize birth recovery, especially for the heavily impacted tissues like the abdominal wall, lumbopelvic stabilizers and pelvic floor.
We have a continuously developing body of evidence that supports the utilization of dry needling for tissue health and performance. The mechanisms behind this are biomechanical, biochemical, vascular, and neural in nature. There is also emerging evidence that is exploring the utilization of dry needling with electrical stimulation (aka neuromodulation) for wound healing. The possible impact that we can have on the healing of episiotomy incisions, cesarean incisions, or perineal tears in the acute and subacute postpartum stage is encouraging given the evidence, and has also been seen to be very powerful anecdotally.
If you want to learn more about the implementation of dry needling into your practice as it relates to the perinatal period, join us on an upcoming Dry Needling and Pelvic Health: Pregnancy and Postpartum Considerations! There are two more courses scheduled this year. One this summer in Arlington VA on June 22-23, and the other this fall in Seattle WA on October 18-20.
AUTHOR BIO
Kelly Sammis, PT, DPT, OCS, PCES, AFDN-S, CLT
 Kelly Sammis is a physical therapist, educator of dry needling and all things pelvic, Pilates instructor, wife, and mama living and working in Parker, Colorado. Her passion for treatment in physical therapy is in sports performance, pelvic health, and overall wellness. She specializes in the treatment of male and female pelvic floor dysfunction, athletic injury/return to sport, sports performance, and persistent pain. Her formal education took place at Ohio University (2007) and The University of St Augustine for Health Sciences (2010).
Kelly Sammis is a physical therapist, educator of dry needling and all things pelvic, Pilates instructor, wife, and mama living and working in Parker, Colorado. Her passion for treatment in physical therapy is in sports performance, pelvic health, and overall wellness. She specializes in the treatment of male and female pelvic floor dysfunction, athletic injury/return to sport, sports performance, and persistent pain. Her formal education took place at Ohio University (2007) and The University of St Augustine for Health Sciences (2010).
She is a Midwest native with a strong history of treating persistent pain, pelvic floor, and return to sport dysfunctions. Kelly serves as lead faculty developing and teaching dry needling and pelvic health courses nationwide. When she is not treating clients or teaching you can find her spending time with her husband, two children, and labradoodle, Dexter, exploring our landscapes and the beautiful mountains of Colorado!

It is important that the PRPC remains current and reflects the knowledge and skills of the pelvic rehab practitioner working in the field today. The best practice for professional certification examinations like the PRPC is for them to be evaluated every 7-10 years to ensure that they continue to reflect the most current knowledge and evidence in the field.
As the PRPC will become 10 years old in 2024, HW is excited to announce that we have gathered a dedicated team of Subject Matter Experts, to analyze and update the PRPC items (multiple choice questions and answers) where needed. The Subject Matter Experts have been chosen from HW Senior Faculty and have been teaching for the Institute for over a decade. They live and work all around the United States, come from diverse backgrounds, and treat different regional patient populations all of which are important for an exam that is administered worldwide. They will be deciding which items need to be thrown out, reworked, or kept. Expected changes to the exam include updated terminology and case studies to be more inclusive of patients across the gender spectrum. The result of this process will be an exam that does not change significantly - items will still cover knowledge and skills for treating pelvic rehab patients throughout the life cycle - but that keeps up with the newest research in that field.
By going through this process, HW ensures that the PRPC remains a valid and legally defensible distinction of competence in the field.
Questions About PRPC Eligibility & Benefits

@sir_duke_samoyed I be good boy helping my mom study for her PRPC 📚.
TIP: #PRPC to share photos of your PRPC Certificate and study sessions on social media!
Do I need to take any particular courses to be eligible for this certification?
There is no required coursework one must complete in order to sit for the PRPC exam. Those therapists who possess the required clinical experience who apply for and successfully pass the exam will be awarded PRPC. Most therapists complete pelvic rehab coursework and then use those skills in the clinic for years prior to pursuing certification. HW recommends that therapists considering applying for the PRPC review the List of Knowledge and Skill Statements covered on the exam and assess their comfort level with those topics. Advanced coursework may be useful in filling any knowledge gaps that exist.

Thank you to Ayesha Bhonsle and Heather Coulter for sharing their PRPC certificates with H&W.
What are the eligibility requirements to apply for PRPC?
To be eligible to sit for the exam, all applicants must have completed 2000 hours of direct pelvic patient care in the past 8 years, 500 of which must have been completed in the last 2 years. Patient care hours can only be earned by a licensed clinician, and hours spent with patients prior to licensure do not satisfy this requirement.
Definition of Direct Pelvic Patient Care
For purposes of this application, pelvic patient care includes hours spent on direct patient care related to conditions of pelvic pain, pelvic girdle dysfunction, conditions of bowel, bladder, and sexual dysfunction that relate, in whole or in part, to the health and function of pelvic structures and the pelvic floor. Other conditions that qualify as direct pelvic patient care may include dysfunctions of the abdomen, thoracolumbar spine, or the lumbo-pelvic-hip complex. These hours can include care for pediatric, adolescent, adult, and aged patients of any gender.
There is no comprehensive list of activities that encompass direct patient care. A general guideline is that direct patient care includes any time spent by a clinician that has a direct influence on the care of a specific individual patient. This time may be paid, or provided at no cost. While time spent on the examination, evaluation, diagnosis, prognosis, or intervention of an individual absolutely qualifies as direct patient care, there are other activities that applicants may apply toward this requirement.
Approved Professions
All clinicians holding a license as a: Physical Therapist (PT), Physical Therapist Assistant (PTA), Physician (MD), Registered Nurse (RN), Occupational Therapist (OT), Certified Occupational Therapy Assistant (COTA), Doctor of Osteopathy (DO), Advanced Registered Nurse Practitioner (ARNP), or Physician’s Assistant (PA-C) are automatically approved to apply for PRPC.
Thank you to Ayesha Bhonsle for sharing her practitioner listings with H&W for this article.
What are the benefits of becoming a PRPC-certified practitioner?
Clinicians who earn their PRPC certification may amend their professional title and all accompanying documentation (CV, business cards, resume) with the letters "PRPC" to distinguish themselves as an expert in the field of pelvic rehabilitation. These practitioners will also receive the following HW benefits:
- Lifetime Course Discount - H&W extends a $50 discount on all courses for the duration of your certification.
- PRPC Directory Listing - H&W maintains a directory dedicated to Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioners
- PelvicRehab.com Gold Listing - Your PelvicRehab.com practitioner listing is updated to gold and shows at the top of local search.
Click Here to Learn More About Becoming Certified!
Is your certification expiring soon?
The PRPC Certification is valid for 10 years from the date you passed the exam. That means that if you became certified in 2014 you will need to retake the PRPC exam in 2024 to maintain your credential.
As a PRPC Certified Practitioner wanting to renew your credentials you will need to go through the PRPC application process online. The difference is that you will need to reach out to HW to receive a practitioner-specific renewal code so that your application fee will be waived. You are responsible for paying the exam fee - and will need to pass the exam to maintain your credential for another 10 years.

Herman & Wallace offers a number of downloadable products on our website for your clinical practice, and we want to put you in charge of deciding which new products we create and offer!
What is a Prefund?
The HW philosophy is that we should only be making products that are useful to our practitioners. In our efforts to create the most valuable products and keep the price as low as possible, we have launched a new Prefund product development program.
Need more information? Check out the Prefund FAQs.
Here is how it works:
- Herman & Wallace creates a product concept, a description of the product and its contents, without fully creating the product.
- The product concept can be found on the HW Product Page as a “Prefund” product for a limited period of 7 days. In this case, the products will be available from May 22, 2024 until midnight on May 28, 2024.
- All product concepts include:
- A description of the product
- Product content list: patient forms, PowerPoint files, handouts, mapping tools, etc
- Standard retail price of the product once it is launched
- Prefund retail price of the product - which is 40% lower than the retail price
- All product concepts include:
- Practitioners who would like to buy the product can prefund the product concept at a 40% discount on the standard retail price in exchange for receiving the product upon Herman & Wallace completing its development.
- If you see a product you'd like to purchase, then prefund it! If the product gets enough pre-funders, then HW will develop the product.
- Once the product is developed, we'll email your product to you.
There is NO RISK!
Prefunding a product carries NO RISK. If the product does not receive enough prefunding by the end of the trial period, Herman & Wallace will refund 100% of the amount contributed by each prefunder.
Product concepts to choose from:
Prefund and Downloadable Products are available on the HW Product Page.
- Inclusivity for Beginners
- Pricing: Prefund $45, Standard $75
- This product includes tips and pearls of wisdom to enhance your understanding of diversity, equality, and inclusivity as well as tools like up-to-date terminology and definitions to help practitioners create a safe and welcoming environment for clients.
- Birth Prep for Pelvic Health Clients
- Pricing: Prefund $90, Standard $150
- This product will make it incredibly easy for you to host a Birth Prep class for any audience.
- Trauma Informed Care Checklist
- Pricing: Prefund $45, Standard $75
- This product will help you review the concepts of trauma-informed care and check in with yourself and the practices of your workplace. It will then provide guidelines and tips to provide the best possible trauma-informed care to your clients.
- Hosting a Pelvic Floor Student
- Pricing: Prefund $60, Standard $100
- This is the perfect document to help prepare any clinician for a pelvic health student.
- Quick Reference Treatment Checklists
- Pricing: Prefund $45, Standard $75
- These quick informative checklists include topics like constipation, stress incontinence, urge incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, hemorrhoid management, and painful insertion.
Carpe Diem
By prefunding a product, you are helping guide what resources HW creates. This keeps prices lower on all products by assuring we don’t spend resources creating products that our audience does not value. If a prefund concept does not get funded, you get a 100% refund. If it does meet the minimum, you will receive the product concept you prefunded at a significant discount!

Vestibulodynia is defined as pain at the vestibule, which is the area around the opening of the vagina (introitus). Being diagnosed with vestibulodynia can leave patients feeling frustrated because it doesn’t explain WHY they have pain at the vestibule. There are several types of vestibulodynia including infection, inflammation, neoplastic, neurologic, trauma, and hormonal deficiencies.
The most common type of vestibulodynia is caused by hormonal deficiencies known as Hormonally-Mediated Vestibulodynia. This type is caused by hormonal changes including taking birth control, breast feeding, postpartum, estrogen blockers, and peri or post menopause.
The most common cause of Hormonally-Mediated vestibulodynia in younger women (under the age of 25) is systemic birth control (i.e. oral contraceptive pills (OCPs), depo-shot, NuvaRing). Side effects of birth control (BC) such as breakthrough bleeding, nausea, headaches, increased risk of stroke, and abdominal cramping are more commonly discussed among doctors and patients.
However, what is NOT often discussed with patients prior to starting birth control, especially OCPs, is that systemic BC use causes vestibulodynia, decrease vaginal lubrication, decrease thickness of labia minora, and decreased vaginal introitus size, all leading to dyspareunia (painful sex). These changes can occur as early as 90 days after starting OCPs or with long-term use.
Unfortunately, if the onset of birth control was before the age of 17, there’s even a higher risk of developing hormonally associated vestibulodynia.1
So, WHY and HOW, does this happen?
 Systemic birth control gets processed through the liver which INCREASES a protein called the Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG). SHBG binds to the free testosterone in the blood, so even if your body is making testosterone, high levels of SHBG (from the BC) DECREASE the testosterone in your body. This inhibits testosterone from getting to the tissue that needs it to be healthy—–the vestibule. The vestibule is rich with androgen receptors! If those receptors aren’t getting the testosterone (and estrogen) they need because of the increased SHBG then the vestibular tissue can become painful (vestibulodynia)!
Systemic birth control gets processed through the liver which INCREASES a protein called the Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG). SHBG binds to the free testosterone in the blood, so even if your body is making testosterone, high levels of SHBG (from the BC) DECREASE the testosterone in your body. This inhibits testosterone from getting to the tissue that needs it to be healthy—–the vestibule. The vestibule is rich with androgen receptors! If those receptors aren’t getting the testosterone (and estrogen) they need because of the increased SHBG then the vestibular tissue can become painful (vestibulodynia)!
Most commonly patients will complain about pain at the opening upon entry, dryness, friction, feeling of tearing, and actual tissue tearing resulting in bleeding, or inability to tolerate penetration at all.
Vestibulodynia can also lead to pelvic floor muscle overactivity which contributes to even more pain! Join the Sexual Medicine in Pelvic Rehab class on the weekend of June 15th-16th to learn how to identify, treat, and differentially diagnose different causes of sexual dysfunctions to get your patients better faster!
Reference:
- Goldstein, A, Burrows L, and Goldstein I. Can oral contraceptives cause vestibulodynia? J Sex Med 2010; 7: 1585-1587
AUTHOR BIO
Tara Sullivan, PT, PRPC, WCS, IF

Dr. Tara Sullivan, PT, PRPC, WCS, IF started in the healthcare field as a massage therapist practicing for over ten years, including three years of teaching massage and anatomy & physiology. During that time, she attended college at Oregon State University earning her Bachelor of Science degree in Exercise and Sport Science, and she continued to earn her Masters of Science in Human Movement and Doctorate in Physical Therapy from A.T. Still University. Dr. Tara has specialized in Pelvic Floor Dysfunction (PFD) treating bowel, bladder, sexual dysfunctions, and pelvic pain exclusively since 2012. She has earned her Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner Certification (PRPC) deeming her an expert in the field of pelvic rehabilitation, treating men, women, and children. Dr. Sullivan is also a board-certified clinical specialist in women’s health (WCS) through the APTA and a Fellow of the International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health (IF).
Dr. Tara established the pelvic health program at HonorHealth in Scottsdale and expanded the practice to 12 locations across the valley. She continues treating patients with her hands-on individualized approach, taking the time to listen and educate them, empowering them to return to a healthy and improved quality of life. Dr. Tara has developed and taught several pelvic health courses and lectures at local universities in Arizona including Northern Arizona University, Franklin Pierce University, and Midwestern University. In 2019, she joined the faculty team at Herman and Wallace teaching continuing education courses for rehab therapists and other health care providers interested in the pelvic health specialty, including a course she authored-Sexual Medicine in Pelvic Rehab, and co-author of Pain Science for the Chronic Pelvic Pain Population. Dr. Tara is very passionate about creating awareness of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction and launched her website pelvicfloorspecialist.com to continue educating the public and other healthcare professionals.
In March 2024, Dr. Tara left HonorHealth and founded her company Mind to Body Healing (M2B) to continue spreading awareness on pelvic health, mentor other healthcare providers, and incorporate sexual counseling into her pelvic floor physical therapy practice. She has partnered with Co-Owner, Dr. Kylee Austin, PT.

We are preparing for a busy second half of the year, and are seeking hosts for our satellite and in-person course offerings. If you'd like to cut down on travel and earn a free course registration, consider hosting a course with us this year! Satellites require a minimum space for 16 attendees, and in-person courses need to be able to accommodate 30+.
We always want to hear from those interested in hosting our courses. We work with healthcare organizations of all types, sizes, and locations. Please, Contact us about hosting Pelvic Function Level 1 or any other course!
There are two formats of course which you can host, and they are described below.
Satellite Lab Courses (such as those in the Pelvic Function Series)
This is when the instructor presents lectures remotely via Zoom to several satellites at once for a scheduled course date while on-site teaching assistants guide participants at each given location with questions and labs.
Satellite lab events can be great for clinics that have space for 16+ participants, and the following equipment:
- One lab table for every two participants (minimum eight)
- One chair for each participant to use during the lectures
- Either an LCD projector and projection screen OR a large television (minimum of 52" screen)
- Laptop with Zoom downloaded and up-to-date, and any necessary cables to connect the laptop to the projector/TV
- Speakers that are loud enough for the full room to clearly hear the instructor. We DO NOT recommend Bluetooth speakers.
In-Person Courses (such as Modalities and Pelvic Function)
At in-person courses, registrants, teaching assistants, and instructors gather at a single location for lectures and labs. In-person hosts who are located in densely populated areas are prioritized and who have a demonstrated history of successfully hosting courses.
In-person courses can be great for clinics that have space for 30+ participants, including one instructor and 2-3 teaching assistants, and the following equipment:
- One lab table for every two participants (minimum eight)
- One chair for each participant to use during the lectures
- A lapel microphone for the instructor to use during lecture
- Speakers that are loud enough for the full room to clearly hear the instructor. We DO NOT recommend Bluetooth speakers.
Remote Courses
Remote courses take place entirely on Zoom and do not gather in lab groups. However, if there is enough interest in taking a course, it is possible to host one of these courses as an in-person course.
Find out more and submit your hosting interest form today at https://www.hermanwallace.com/host-a-course.

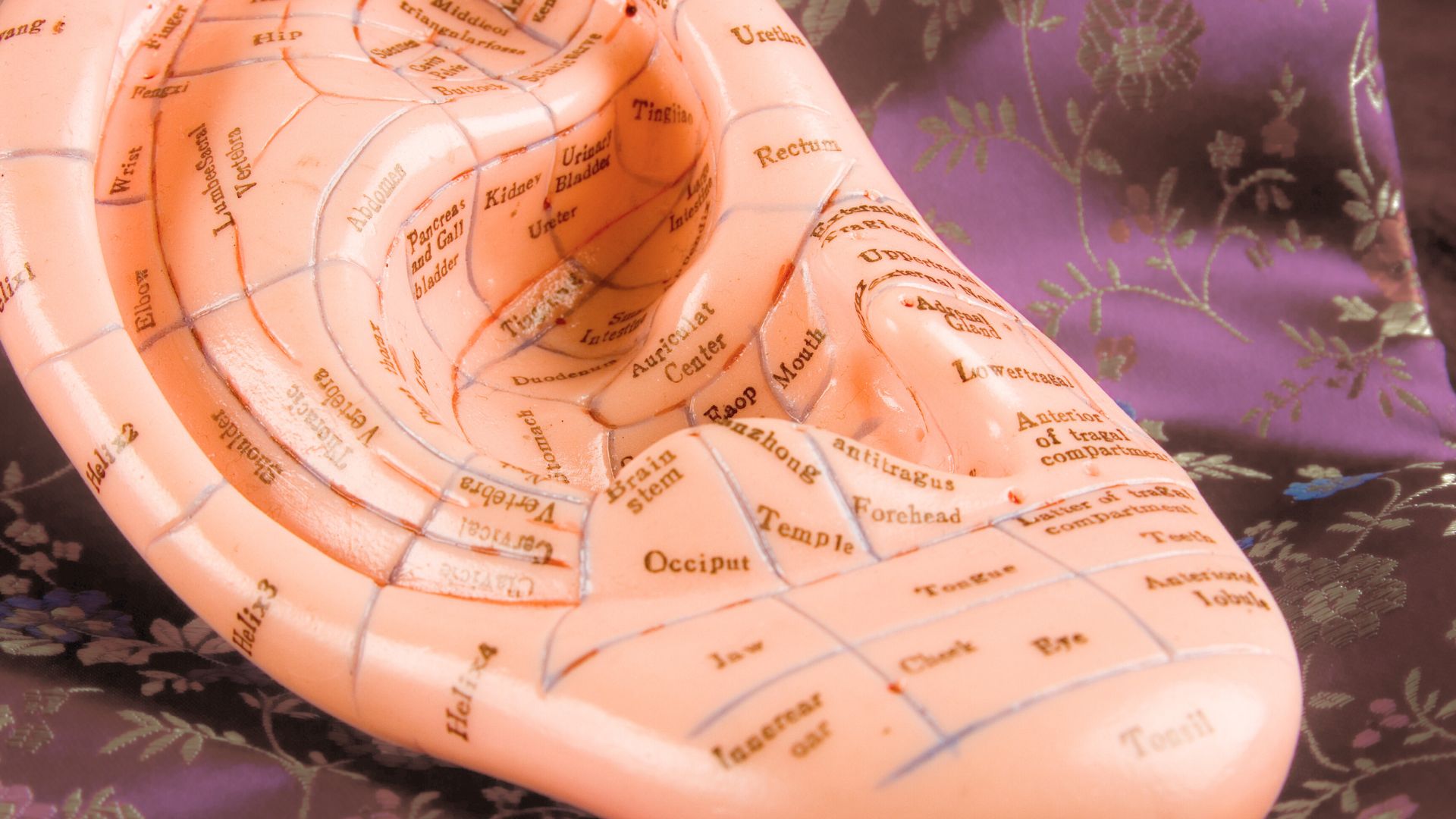
Did you know that you could access and regulate the Vagus nerve through Acupressure points in the ear?
 At HWConnect last year, I had the pleasure of meeting the amazing Ramona Horton. Ramona introduced us to Acupressure points in the outer ear that can directly stimulate the Auricular branch of the Vagus nerve and here you can see us both practicing Auricular Acupressure.
At HWConnect last year, I had the pleasure of meeting the amazing Ramona Horton. Ramona introduced us to Acupressure points in the outer ear that can directly stimulate the Auricular branch of the Vagus nerve and here you can see us both practicing Auricular Acupressure.
Auricular therapy includes Acupuncture and Acupressure in the auricle. The ear is innervated by cranial and spinal nerves, which are separated into motor and sensory areas. The motor area includes the facial nerve, which controls the outer ear muscles. The sensory area is composed of Auricular branches of the Vagus nerve1.
The Auricular branch of the Vagus nerve innervates multiple areas of the ear. The three main areas are the Concha, Cymba Concha, and the Inner Tragus. The miraculous Vagus nerve plays an important role in maintaining physiological homeostasis and autonomic self-regulation across multiple systems in the body. Stimulation of the Vagus nerve through auricular Acupressure can provide Vagal regulation impacting both the autonomic and central nervous systems. The measurement of vagal tone in humans has become one index of stress vulnerability2.
In addition to the acupressure points in the ear, there are several Acupressure points like Central Vessel 17 ( CV 17 ), Yintang ( EX HN3 ), Heart 7, and Pericardium 6 that can be used for calming and self-regulation. Key potent points in the Kidney, Bladder, Spleen, Stomach, Pericardium, and Heart meridians play a vital role in emotional regulation as well as addressing a host of bowel and bladder dysfunctions.
Acupressure is widely considered to be a powerful Complementary & Alternative Medicine (CAM) therapy and is gaining acceptance within the medical community as part of an Integrative medicine approach. It draws its roots from Acupuncture which is part of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) believed to be over 3000 years old. Acupressure involves the application of pressure to points located along the energy meridians of the body which are connected to the visceral functions of vital organ systems.
 Emerging research shows that these Acupoints are embedded in a three-dimensional fascial network throughout the body and have a high electrical conductivity on the surface of the skin. Histological studies show a high density of A and C afferent fibers at these points. Through a vast network of interstitial connective tissue, these Acupoints connect the peripheral nervous system to the central viscera.
Emerging research shows that these Acupoints are embedded in a three-dimensional fascial network throughout the body and have a high electrical conductivity on the surface of the skin. Histological studies show a high density of A and C afferent fibers at these points. Through a vast network of interstitial connective tissue, these Acupoints connect the peripheral nervous system to the central viscera.
Acupressure is a non-invasive, low-cost, and efficient CAM therapy approach and can be used as an adjunct to traditional rehabilitation interventions. Research shows that tapping on Acupressure points has been used as part of Emotional Freedom Techniques (EFT) as well as for the treatment of urinary incontinence, dysmenorrhea, menstrual issues, constipation, anxiety, and a host of other conditions.
The course Acupressure for Optimal Pelvic Health is next offered on June 1st -2nd and explores Acupressure as an evidence-based modality for the management of a host of pelvic health conditions and as a self-regulation modality for the management of anxiety, stress, pain, and symptom management. The course covers two patient home exercise programs with specific potent points for Anxiety and for Daily Wellness and introduces Yin Yoga as a complementary practice to Acupressure.
This course is curated and taught by Rachna Mehta PT, DPT, CIMT, PRPC, RYT 200. Rachna has integrated Acupressure as part of her rehabilitation toolbox for several years now bringing holistic healing and wellness to her patients.
References
- Hou PW, Hsu HC, Lin YW, Tang NY, Cheng CY, Hsieh CL. The History, Mechanism, and Clinical Application of Auricular Therapy in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:495684. doi:10.1155/2015/495684
- Oleson T. Application of Polyvagal Theory to Auricular Acupuncture. Med Acupunct. 2018;30(3):123-125. doi:10.1089/acu.2018.29085.tol
- Monson E, Arney D, Benham B, et al. Beyond Pills: Acupressure Impact on Self-Rated Pain and Anxiety Scores. J Altern Complement Med. 2019;25(5):517-521.
- Au DW, Tsang HW, Ling PP, Leung CH, Ip PK, Cheung WM. Effects of acupressure on anxiety: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupunct Med. 2015;33(5):353-359. doi:10.1136/acupmed-2014-010720
- Son CG. Clinical application of single acupoint (HT7). Integr Med Res. 2019;8(4):227-228.
- Kwon CY, Lee B. Acupuncture or Acupressure on Yintang (EX-HN 3) for Anxiety: A Preliminary Review. Med Acupunct. 2018;30(2):73-79.
AUTHOR BIO:
Rachna Mehta PT, DPT, CIMT, PRPC, RYT 200
 Rachna Mehta PT, DPT, CIMT, OCS, PRPC, RYT 200 graduated from Columbia University, New York with a Doctor of Physical Therapy degree. Rachna has been working in outpatient hospital and private practice settings for over 15 years with a dual focus on Orthopedics and Pelvic Health. She was instrumental in starting one of the first Women’s Health Programs in an outpatient orthopedic clinic setting in Mercer County, New Jersey in 2009. She has authored articles on pelvic health for many publications. She is a Certified Integrated Manual Therapist through Great Lakes Seminars, is Board-certified in Orthopedics, is a certified Pelvic Rehab Practitioner, and is also a registered yoga teacher through Yoga Alliance. Rachna has trained in both Hatha Yoga and Yin Yoga traditions and brings the essence of Yoga to her clinical practice.
Rachna Mehta PT, DPT, CIMT, OCS, PRPC, RYT 200 graduated from Columbia University, New York with a Doctor of Physical Therapy degree. Rachna has been working in outpatient hospital and private practice settings for over 15 years with a dual focus on Orthopedics and Pelvic Health. She was instrumental in starting one of the first Women’s Health Programs in an outpatient orthopedic clinic setting in Mercer County, New Jersey in 2009. She has authored articles on pelvic health for many publications. She is a Certified Integrated Manual Therapist through Great Lakes Seminars, is Board-certified in Orthopedics, is a certified Pelvic Rehab Practitioner, and is also a registered yoga teacher through Yoga Alliance. Rachna has trained in both Hatha Yoga and Yin Yoga traditions and brings the essence of Yoga to her clinical practice.
Rachna currently practices in an outpatient setting. The majority of her clinical orthopedic practice has focused on treating musculoskeletal, neurological, pre- and post-operative surgical conditions to name a few. She specializes in working with pelvic health patients who have bowel & bladder issues with high pelvic pain which sparked her interest in Eastern holistic healing traditions and complementary medicine. She has spent many hours training in holistic healing workshops with teachers based worldwide. She is a member of the American Physical Therapy Association and a member of APTA’s Academy of Orthopaedic Physical Therapy and the Academy of Pelvic Health Physical Therapy.
Rachna also owns TeachPhysio, a PT education and management consulting company. Her course Acupressure for Optimal Pelvic Health brings a unique evidence-based approach and explores complementary medicine as a powerful tool for holistic management of the individual as a whole focusing on the physical, emotional, and energy body.

Do you listen to any podcasts? What about podcasts that are focused on pelvic issues and aimed toward the pelvic health practitioner? Here at Herman & Wallace, many of us listen to these and we all have our favorites. Recently HW was lucky enough to work with The Pelvic Service Announcement when Callie and Rachel interviewed Holly Tanner for the episode “Stay Curious and Stay Open” which is available on streaming platforms today.
Who are Callie Teel and Rachel Fritz?
 Callie and Rachel are two physical therapists whose passion for women’s health and commitment to education are changing the way people think about this important field.
Callie and Rachel are two physical therapists whose passion for women’s health and commitment to education are changing the way people think about this important field.
Callie and Rachel first crossed paths at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, where they both graduated from physical therapy school in 2021. Following their graduation, the duo began their careers at Optimal Physical Therapy in Amarillo, Texas. It didn't take long for them to realize that there was a significant gap in the public's understanding of pelvic health and the role of pelvic floor physical therapy.
As Callie and Rachel embarked on their new careers, they frequently encountered patients who were unaware of the benefits and importance of pelvic health. Many of these patients were women dealing with postpartum recovery, incontinence, pelvic pain, and other issues that affect quality of life. Callie and Rachel saw an opportunity to make a difference—not just in their clinic but also in the wider community.
Pelvic Service Announcement Podcast
 Determined to bridge the gap in knowledge, Callie and Rachel decided to share their expertise with the public in a way that was both accessible and engaging. This led to the creation of the "Pelvic Service Announcement Podcast," or PSA for short. Through their podcast, they aim to demystify pelvic health, answer common questions, and offer practical advice for anyone interested in learning more about the subject.
Determined to bridge the gap in knowledge, Callie and Rachel decided to share their expertise with the public in a way that was both accessible and engaging. This led to the creation of the "Pelvic Service Announcement Podcast," or PSA for short. Through their podcast, they aim to demystify pelvic health, answer common questions, and offer practical advice for anyone interested in learning more about the subject.
Since launching the PSA podcast, Callie and Rachel have gained a devoted following, with listeners appreciating their down-to-earth approach and willingness to tackle topics that are often considered taboo. They cover a wide range of issues, from pregnancy and childbirth to pelvic pain and sexual health, always with a focus on empowering their audience with knowledge and resources.
For those interested in learning more, the PSA podcast is available on all major streaming platforms. Tune in to hear Callie and Rachel discuss the latest in pelvic health and share valuable insights that you won't want to miss.
Stay Curious and Stay Open Episode Description
Get ready for one of the most exciting guests ever to be featured on The Pelvic Service Announcement. This week, the PSA girls were honored to host Holly Tanner, PT, DPT, MA, OCS, WCS, PRPC, LMP, BCB-PMD, CCI for the first-ever Herman & Wallace podcast collaboration. Holly is the Director of Education for the Herman & Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute and shared some valuable insights into the world of pelvic health education, managing complicated cases, and navigating interpersonal relationships in the clinic. Whether you're a patient, clinician, or just someone with a love for pelvic health, this is an episode you don't want to miss.

Yoga is a common term in our current society. We can find it in a variety of settings from dedicated studios, gyms, inside corporations, online, on Zoom, at home, and on retreat. The basic structure of a typical yoga class is a series of flowing or non-flowing postures, some requiring balance, some requiring going upside down, and many requiring significant mobility to achieve a certain shape. At the end of these classes is a pose called savasana, corpse pose (or sometimes translated for comfort as final resting pose). In this pose, which is often a treat for students after working through class, students lie on the ground, eyes closed, possibly supported by props and rest. It is perhaps the only other time in the day that that person is instructed to lie on the floor in between sleep cycles.
Savasana is one of many restorative yoga postures. In the work created, and popularized by Judith Hanson Lasater, PT, PhD1, restorative yoga has taken a turn away from the active physical postures, breath manipulations, and meditations that are commonplace in how we think of yoga. She has focused on rest and the need for rest in our current climate of productivity, poor self-care, and difficulty managing stress and pain.
In a dedicated restorative yoga class (not a fusion of exercise then rest, or stretch then rest…which are really lovely and have their own benefits), a student comes to class, gathers a number of props, and is instructed through 3 to 5 postures, all held for long durations to complete an hour or longer class. Consider what it would look like to do 3 things over 1 hour with the intent of resting. It is quite a counterculture. Students have various experiences with this type of practice, but over time many begin to feel the need for rest (or restorative practice) in an equivalent way that one feels thirsty or hungry.
We know the benefits of rest: being able to access the ventral vagal aspect of the parasympathetic nervous system is what Dr. Stephen Porges2 suggests supports health, growth, and restoration. There is an impact on the ventral vagal complex in the brainstem that regulates the heart, the muscles of the face and head, as well as the tone of the airway. To heal, we need access to this pathway. To manage stress, we need to access this pathway. To be able to choose our actions rather than be reactionary, we need to access this pathway. Restorative yoga is an accessible method that may be a new tool in a patient’s toolbox to help manage their nervous systems.
Learn how to incorporate restorative yoga in your daily practice and clinic - join Kate Bailey in Restorative Yoga for Physical Therapists on June 15th. You don't have to be a PT to join, all clinicians are welcome!
References:
- Relax and Renew: Restful Yoga for Stressful Times by Judith Hanson Lasater PT, PhD
- Polyvagal Theory by Stephen W Porges PhD
AUTHOR BIO:
Kate Bailey, PT, DPT, MS

Kate Bailey received her Doctorate in Physical Therapy and Master of Science in Anatomy from the University of Delaware. Her physical therapy practice is focused on pelvic health for all genders and ages. Kate brings over 15 years of teaching movement experience to her physical therapy practice with specialties in Pilates and yoga with a focus on alignment and embodiment. Kate’s Pilates background was unusual as it followed a multi-lineage price apprenticeship model that included the study of complementary movement methodologies such as the Franklin Method, Feldenkrais, and Gyrotonics®. Building on her Pilates teaching experience, Kate began an in-depth study of yoga, training with renowned teachers of the vinyasa and Iyengar traditions. She held a private practice teaching

Have you ever heard the phrase “In one ear and out the other?” I sure have, I have vivid memories of my grandmother scolding me for just that. She could never understand how when she said things to me, particularly a list of tasks to do, I could never seem to remember. Funnily enough, my grandfather’s nickname for me was “rabbit ears” because he swore I could pick up on a conversation from anywhere in close proximity so it wasn’t my hearing. Pretty conflicting and confusing, right? I had trouble processing things I heard or remembering them long enough to do them. Years of Catholic school helped to give me structure and tools to keep myself and my fun little brain organized and on task, and I ended up being able to keep up with the rest of my class.
The older and more self-aware I got, the more I realized my brain doesn’t work the way everyone else’s does. The more I worked with kiddos with autism and ADHD, the more I realized my brain worked similarly to theirs. When I first heard the term “neurodivergent” I felt immediately like I had found the answer to a question I didn’t even know existed for myself. This was why I wasn’t the same as other people in processing all things! This is why I had to touch everything to learn about it. This is why I had to rewrite all my notes from professors instead of just being able to absorb what they said. This is why I needed mnemonics, stories, acronyms, and other little “hacks” to learn things.
There are many different ways people can learn. The most common forms of learning consider if a person learns best through visual, aural/ auditory, reading/writing, or kinesthetic movement. Individuals can be any combination of these, which can vary as they grow through life. Someone may start out learning better kinesthetically and learn to process information better visually as they age. In our COVID era, a new format of teaching became more prevalent, bringing “at distance” learning in to save the day in many instances.

The prevalence of distance learning via forums such as Google Meet or Zoom brought up some questions about how well students could learn. Did students learn as well virtually? Did different types of learners have different results? Did how students felt they learned correlate with the outcome measures of learning? Distance education provides the ability for some populations to get education they would not be able to attain otherwise. In a study by Wakahiu & Kangethe, 2014, “participants described learning experiences with profound statements that endorsed online learning as an excellent strategy for fulfilling their dreams to acquire an education.”
Distance learning has many benefits including the ability to learn new materials and achieve new intellectual goals in most locations on a flexible time schedule. Another benefit is the access to visual resources and the potential to be able to rewatch. The decreased cost of transport and the safety (and hopefully less stress) of staying home were also huge benefits. Some disadvantages include not being able to guarantee effective learning, the ability to stay attentive, or be successful with materials. There can be connection and technological problems as well as some students not having the best learning environment in their home (Masalimova et al, 2022). When I think of learning and pelvic health, I think not having face-to-face interaction, accountability, and reinforcement of practicing the skills can hinder some student’s learning ability.
A report by the U.S. Department of Education compared the exam grades for online and face-to-face versions of the same course from 1996 to 2008 and concluded that “online learning could produce learning outcomes equivalent to or better than face-to-face learning (Zheng, 2021).” Cacault et al., 2021 also assessed the effects of online lectures finding that having access to a live-streamed lecture in addition to an in-person option “improves the achievement of high-ability students, but lowers the achievement of low-ability students.”
How does this apply to Herman and Wallace? The pelvic institute has a variety of ways to learn including online courses, self-hosted options, satellite in-person classes with TAs, and in-person classes with instructors. They have made sure to account for different scenarios in order to make pelvic health learning accessible for all they can. The newest addition to the categories of “in person” and “with instructors” is Modalities and Pelvic Function. I had the pleasure of being on the curriculum team for this class and also being one of the instructors for the first run.

I thought people would like the stuff. I thought they would be excited to try biofeedback and electrical stimulation. I thought they would be pleasantly surprised by prizes and goodie bags full of awesome takeaways. I knew it would be a novel learning experience.
What I did not expect was the overwhelming feedback from participants stating things like“this course was one of the best I have met for my learning style.” The curious part is that when they were asked what their preferred learning style was, they were all different! Some liked to see, some needed to hear it, and some just were there to touch and feel and touch again. Varied practitioners, varied experience levels, varied treatment settings and population and one very consistent point of feedback…”This class just gets me.”
If you’re on the hunt for a class that “puts it all together” when it comes to the tools and toys that can be used for the pelvic floor, check out Modalities and Pelvic Function. Not only are there SO MANY samples (think three shipping crates full - sorry UPS) BUT this class shows you how much is out there to treat pelvic health patients, the pros/cons, the indications, contraindications, and relative precautions as well as the language on how to educate your patient on the use of these items in the clinic or as part of their home self-care routine. Join me this summer either in Raleigh NC on July 13-14 or in Manchester NH on August 24-25!

Don’t believe me…here are two testimonials from our inaugural class!
“Of all of the pelvic floor courses I have taken up to date, this is by far the most enjoyable one! not only did it include how to efficiently treat patients, but it was well organized, exciting content, and everyone was lovely! the instructors were so personable and taught in a way to benefit any learning style. I will be recommending this to all of my fellow PF PTs!” - Rachel Biek, PT, DPT
“I loved the in-person portion of this class! The instructors (Mora and Jenna) were perfect in their roles, we were relaxed and had so much fun exploring the variety of tools to use. The feel of the class was supportive and intimate, and we had adequate time to explore everything. Mora and Jenna did an excellent job, hard to believe this was their first time teaching this class!” - Allison M. Gannon, PT, DPT
REFERENCES:
- Cacault, Christian Hildebrand, Jérémy Laurent-Lucchetti, Michele Pellizzari, Distance Learning in Higher Education: Evidence from a Randomized Experiment, Journal of the European Economic Association, Volume 19, Issue 4, August 2021, Pages 2322–2372, https://doi.org/10.1093/jeea/jvaa060
- Masalimova, A. R., Khvatova, M. A., Chikileva, L. S., Zvyagintseva, E. P., Stepanova, V. V., & Melnik, M. V. (2022, March). Distance learning in higher education during COVID-19. In Frontiers in Education (Vol. 7, p. 822958). Frontiers Media SA.
- Wakahiu, J., & Kangethe, S. (2014). Efficacy of online distance learning: Lessons from the Higher Education for Sisters in Africa Program. European Journal of Research and Reflection in Educational Sciences, 2(1), 1-25.
- Zheng, M., Bender, D. & Lyon, C. Online learning during COVID-19 produced equivalent or better student course performance as compared with pre-pandemic: empirical evidence from a school-wide comparative study. BMC Med Educ 21, 495 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02909-z
AUTHOR BIO:
Mora Pluchino, PT, DPT, PRPC

I am a graduate from Stockton University with my BS in Biology (2007) and Doctorate of Physical Therapy (2009). I have experience in a variety of areas and settings, working with children and adults, including orthopedics, bracing, neuromuscular issues, vestibular issues, and robotics training. I began treating Pelvic Health patients in 2016 and now have experience treating women, men, and children with a variety of Pelvic Health dysfunction. There is not much I have not treated since beginning this journey and I am always happy to further my education to better help my patients meet their goals.
I strive to help all of my patients return to a quality of life and activity that they are happy with for the best bladder, bowel, and sexual functioning they are capable of at the present time. In 2020, I opened my own practice called Practically Perfect Physical Therapy Consulting to help meet the needs of more clients. I have been a guest lecturer for Rutgers University Blackwood Campus and Stockton University for their Pediatric and Pelvic Floor modules since 2016. I have also been a TA with Herman and Wallace since 2020 and have over 150 hours of lab instruction experience.

Did you know that the Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner Certification (PRPC) is celebrating its 10th anniversary? That's right, the first PRPC examination was administered in 2014 and since then, over 700 practitioners from all over the world have earned their certification.
Are you ready to join the ranks of these proficient professionals? Becoming PRPC certified allows you to proudly display the designation "PRPC" after your name, establishing you as an expert in pelvic rehabilitation.
Not sure if you qualify to sit for the PRPC examination? Don't worry, here are some frequently asked questions that may help clarify your eligibility.
What is the PRPC?
The certification available through the Institute is called the Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner Certification (PRPC). Earning the PRPC Certification is a professional achievement that demonstrates your dedication and expertise in the field. Through a specialized exam, you'll validate your knowledge and join an exclusive community of respected practitioners.
The PRPC was the first-ever certification exam for therapists seeking distinction for treating pelvic dysfunction in all genders throughout the life cycle.
Who can sit for the exam? Do I have to be a physical therapist?
While a license to practice skills in pelvic rehabilitation is required for the PRPC exam, you don't have to be a physical therapist to apply. In fact, HW welcomes a diverse group of professionals including Physical Therapists (PTs), Physical Therapist Assistants (PTAs), Physicians (MDs), Registered Nurses (RNs), Occupational Therapists (OTs), Occupational Therapist Assistants (OTAs), Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (DOs), Doctors of Chiropractic Medicine (DCs), Advanced Registered Nurse Practitioners (ARNPs), Nurse Midwives (CNMs), Doctors of Naturopathic Medicine (NDs), and Physician Assistants (PA-Cs) with an active state-board license.
Do I have to take certain Herman & Wallace courses?
There are no course prerequisites for taking the PRPC exam. A valid certification exam tests demonstrable knowledge and skills, which can be gained from a combination of coursework, clinical experience, professional mentorship, etc.
Therapists considering applying should have a comprehensive skill set, which is often gained through several beginner, intermediate, and advanced courses in pelvic function and dysfunction. These can include the Pelvic Function Series, from Level 1 to Capstone, as well as specialized courses for bowel, bladder, sexual, and pelvic pain dysfunctions, depending on your interests and patient demographics.
Pricing for PRPC is discounted for those who have completed at least one course through Herman & Wallace.
How much pelvic rehabilitation experience do I need?
To be eligible to sit for the exam, all applicants must have completed a minimum of 2000 hours of direct pelvic patient care within the past 8 years, with at least 500 of those hours completed in the last 2 years. It's important to note that these patient care hours must come from a licensed clinician and cannot include any hours spent before becoming licensed.
A general guideline for what qualifies as direct pelvic patient care is any time spent directly impacting the care of a specific patient. These activities include (but are not limited to) examination, evaluation, diagnoses, treatment plans, and intervention for conditions related in whole or in part, to the health and function of pelvic structures and the pelvic floor. This includes seeing patients for pelvic pain, pelvic girdle dysfunction, and conditions of bowel, bladder, and sexual dysfunction and includes the care for pediatric, adolescent, adult, and aged patients of any gender.
Where can I find more information?
All the details of the PRPC can be found on our website through the Certification Tab. You can find sample questions, pricing information, and even some study resources!
Are you ready to take your clinical practice to the next level?
Don’t miss this opportunity to become PRPC Certified! Remember - this is the only certification that encompasses pelvic rehabilitation for ALL people across the lifespan. The next testing administration is November 1-15, 2024. The registration cut-off date is October 1st, and the sooner you get your application approved, the faster you can be connected to like-minded practitioners who want to study with you for the exam!
While the exam itself may not be "fun" (let's be honest), the studying process is where you truly elevate your expertise. Immerse yourself in a wealth of knowledge, expand your skills, and refine your techniques - all while preparing for the exam. Good luck on your journey to becoming a certified expert in pelvic rehabilitation!
A testimonial from Erika Darbro, PT, DPT, PRPC
"As a perpetual learner, I recognize the importance of staying up to date with the latest advancements in the field. Each year, I actively participate in numerous continuing education courses, a practice that reflects my dedication to providing the highest quality of care. It was a natural next step to take my commitment a step further by pursuing the Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner Certification (PRPC) in 2020.
"Choosing to become certified was not a decision made lightly. The PRPC certification stood out as the perfect fit for my clinical ethos – to treat all genders. Unlike some certifications that focus solely on women's health, the PRPC encompasses pelvic health topics for all populations. This alignment with my values was a driving force behind my choice, emphasizing my dedication to being an inclusive pelvic health practitioner.
"Obtaining the PRPC certification was not just about acquiring a credential; it was a statement of my commitment to being an expert in the pelvic health field. It serves as a recognition of my passion for treating the pelvic health population and reinforces the idea that I don't merely dabble in pelvic health.
"The pursuit of certification was also a personal challenge. It pushed me to elevate my skills, deepen my knowledge, and continually evolve as a practitioner. By challenging myself, I hope to inspire other healthcare professionals to embrace continuous learning and strive for excellence in their field."