So often, we think of vulvodynia as a condition of the skin. And it is….kind of. Vulvodynia is a long-term pain (or burning, discomfort, or itching) that is present in the outer genitals, also known as the vulva. This condition is defined as a discomfort that has lasted longer than 3 months. The symptoms of vulvodynia can vary. In some patients, it is provoked (brought on by touch or stimulation), and in some cases, it is unprovoked (present without stimulation). Some patients have pain just in the outer vulva, while others also present with pelvic floor muscle tension or urethra, bladder, or vaginal canal irritation.
The definition of vulvodynia itself states there is no known reason. This means it is not because of a skin disruption, hormonal disorder, herpes or other skin conditions, or active infection, such as yeast. This means we really don’t know just why a person has symptoms once they have been medically ruled out.
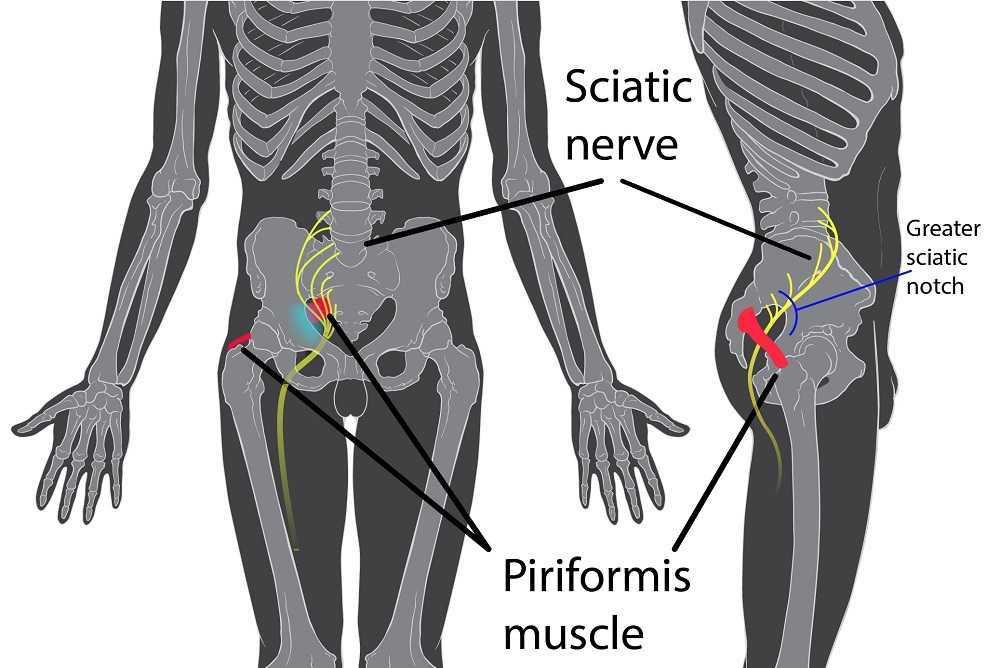
When we look at the symptoms of neuralgia (an irritated or overly talkative nerve), we find symptoms listed such as pain, hypersensitivity, burning, tingling, itching, or trigger points. Certainly, there is a lot of overlap between neuralgia symptoms and vulvodynia symptoms.
When there is compression of a nerve, it can create neuralgia of the affected dermatome. In fact, in studies, we find neural proliferation of the peripheral nerve with vulvodynia in cell biopsy in women or in animal models (1, 2). Often, neural compression is part of the problem, and this is why we see treatment models proving effective at times with nerve blocks or nerve decompression (3, 4).
Of course, when treating such patients, we can and should still employ proven topical agents to make the treatments comfortable and effective, such as lidocaine solutions (5). Vulvodynia is best treated and managed as a team, with manual therapy and patient education from pelvic health providers being a very important limb of treatment.
By treating fascial tunnels that nerves run through, treating the fascia around the clitoris, and treating the deep fascia and tissues of the labia majora and mons, we can have an effect on the pudendal nerve branches, as well as the genitofemoral and ilioinguinal nerves supplying this region. In Lumbar Nerve Manual Assessment and Treatment scheduled for May 17-18, and Sacral Nerve Manual Assessment and Treatment scheduled for May 31-June 1, both heavy manual therapy classes, we learn to decompress the neurovascular bundle from proximal to distal and to treat distal soft tissue structures that may be compressing nerves.
Resources:
1. Goetsch MF, Morgan TK, Korcheva VB, Li H, Peters D, Leclair CM. Histologic and receptor analysis of primary and secondary vestibulodynia and controls: a prospective study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;202:614.e1–614.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.01.028.
2. Bornstein J. Vulvar disease. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2019. Vulvar pain and vulvodynia; pp. 343–367.
3. Vulvodynia treatments, National Vulvodynia Association (nva.org)
4. Possover M, Forman A. Pelvic Neuralgias by Neuro-Vascular Entrapment: Anatomical Findings in a Series of 97 Consecutive Patients Treated by Laparoscopic Nerve Decompression. Pain Physician. 2015 Nov;18(6):E1139-43. PMID: 26606029.
5. Loflin BJ, Westmoreland K, Williams NT. Vulvodynia: A Review of the Literature. J Pharm Technol. 2019 Feb;35(1):11-24. doi: 10.1177/8755122518793256. Epub 2018 Aug 20. PMID: 34861006; PMCID: PMC6313270.
AUTHOR BIO:
Nari Clemons, PT, PRPC
 Nari Clemons, PT, PRPC (she/her) has been teaching with the institute since 2004. She has written the following courses: Lumbar Nerve Manual Assessment /Treatment and Sacral Nerve Manual Assessment/Treatment. She has co-authored the PF Series Capstone course with Allison Ariail and Jenna Ross, and the Boundaries, Self Care, and Meditation Course (the burnout course) with Jenna Ross. In addition to teaching the classes she has authored, Nari also teaches all the other classes in the PF series: PF1, PF2A, PF2B, and Capstone. She was one of the question authors for the PRPC, and she has presented at many conferences, including CSM.
Nari Clemons, PT, PRPC (she/her) has been teaching with the institute since 2004. She has written the following courses: Lumbar Nerve Manual Assessment /Treatment and Sacral Nerve Manual Assessment/Treatment. She has co-authored the PF Series Capstone course with Allison Ariail and Jenna Ross, and the Boundaries, Self Care, and Meditation Course (the burnout course) with Jenna Ross. In addition to teaching the classes she has authored, Nari also teaches all the other classes in the PF series: PF1, PF2A, PF2B, and Capstone. She was one of the question authors for the PRPC, and she has presented at many conferences, including CSM.
Nari’s passions include teaching students how to use their hands more receptively and precisely for advanced manual therapy skills while keeping it simple enough to feel successful. She also is an advocate for therapists learning how to feel well and thrive as they care for others, which is a skill that can be developed. “Basically, I love helping therapists learn to help themselves and others more while having a lot of fun doing it.” Nari lives in Portland Oregon, where she runs a local study/mentoring group and has a private practice, Portland Pelvic Therapy. Her interests include meditation, working out, nature, and being constantly humbled from raising her three amazing teenagers!
The lumbar sacral nerve plexus can be divided into the direction the nerves travel, either anterior or posterior. This post will focus on anterior hip nerves. I remember writing about the brachial plexus over and over in physical therapy school, but only a few times for the lumbosacral plexus. Patients frequently report anterior hip and pubic pain and can often have signs and symptoms of nerve entrapment. This article orients the reader to links between signs and symptoms and examination to help appropriately diagnosis specific nerves in the athletic population.
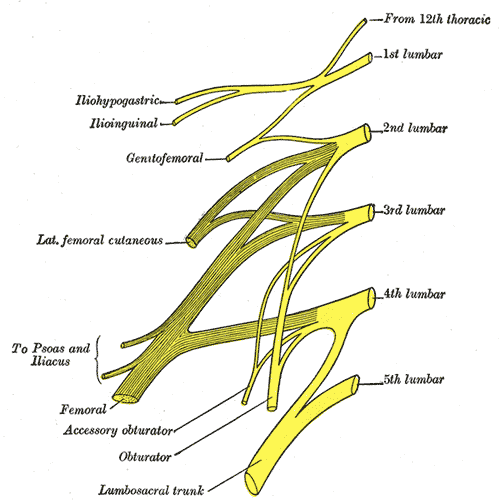 The obturator, femoral and lateral femoral cutaneous are more commonly entrapped in sports injuries. Although the three nerves that travel together through the inguinal canal (ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric, and genitofemoral) are less common, however surgery can create nerve entrapment sequelae.
The obturator, femoral and lateral femoral cutaneous are more commonly entrapped in sports injuries. Although the three nerves that travel together through the inguinal canal (ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric, and genitofemoral) are less common, however surgery can create nerve entrapment sequelae.
There are a few places where the obturator nerve can become squished. Typically, as it leaves the obturator canal which presents at medial thigh pain, and then again in the fascia of the adductors which presents as pain with abduction. The challenge is to differentiate between the nerve and adductor strain. Obturator nerve entrapment will test positive with passive hip abduction and extension, but negative resisted hip adduction.
The femoral nerve can become entrapped in a kind of compartment syndrome as it goes between the psoas and iliacus. This can lead to compression to the neurovascular bundle with resultant swelling, edema, and ischemia. Signs of femoral nerve compression include anterior thigh numbness and paresthesias. Occasionally, this can also include the saphenous nerve with symptoms continuing along medial knee to foot. Femoral nerve entrapment can create quadricep muscle weakness and atrophy, with diminished or absent patella tendon reflexes. Symptoms are reproduced with hip extension and knee flexion thereby elongating the femoral nerve.
The lateral femoral cutaneous (LFC) nerve is sensory. Diagnosed as meralgia paresthetica, the LFC nerve is typically entrapped where it penetrates under the inguinal ligament just medial to the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS). Symptoms include numbness, tingling, hypersensitivity to touch, burning along outer thigh along the iliotibial band. The LFC nerve can often be compressed by wearing heavy belts (scuba divers, construction belts, etc). Special tests that indicate LFC are pelvic compression in side lying with involved side up to slack the inguinal ligament and Tinels sign.
Anterior hip pain is fairly common in pelvic floor patients. Differential diagnosis and treatment of these anterior nerves can allow patients to return to full daily function. To learn manual assessment and treatment techhniques for the lumbar nerves, consider attending Lumbar Nerve Manual Assessment and Treatment.
Martin R, Martin HD, Kivlan BR. Nerve Entrapment In The Hip Region: Current Concepts Review. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2017 Dec;12(7):1163-1173.
Birthing can be an unpredictable process for mothers and babies. With cases of fetal distress, the baby can require rapid delivery. Alternatively, in cases with cephalo-pelvic disproportion, the baby has a larger head, or the mother has a decreased capacity within the pelvis to allow the fetus to travel through the birthing canal. Additionally, the baby may have posterior presentation, colloquially known as “sunny side up” in which the baby’s occipital bone is toward the sacrum. With any of these situations, it is good to know c-sections are an option to safely deliver the child.
 Women may also be inclined to try to get a c-section to avoid pelvic complication or tears or because of a history of a severe prior tear. As pelvic therapists, we know that the number of vaginal births and history of vaginal tears increase the risk of urinary incontinence and prolapse. Yet, many therapists are unfamiliar with the effects of c-section and the impact of rehab for diastasis.
Women may also be inclined to try to get a c-section to avoid pelvic complication or tears or because of a history of a severe prior tear. As pelvic therapists, we know that the number of vaginal births and history of vaginal tears increase the risk of urinary incontinence and prolapse. Yet, many therapists are unfamiliar with the effects of c-section and the impact of rehab for diastasis.
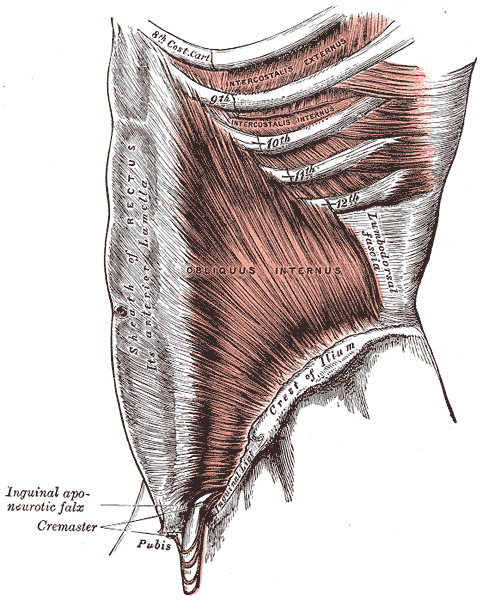
A 2008 dissection study of 37 cadavers studied the path of the ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerves. The course of the nerves was compared with standard abdominal surgical incisions, including appendectomy, inguinal, pfannestiel incisions (the latter used in cesarean sections). The study concluded that surgical incisions performed below the level of the anterior superior iliac spines (ASIS) carry the risk of injury to the ilioinguinal and iloiohypogastric nerves 1. Another 2005 study reported low transverse fascial incision risk injury to the ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerves, and the pain of entrapment of these nerves may benefit from neurectomy in recalcitrant cases.2
Why does injury to the nerves matter? After pregnancy, patients may need rehab and retraining of their abdominal recruitment patterns for diastasis and stability. The ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerves are the innervation for both the transverse abdominus and the obliques below the umbilicus. When we are working to retrain the muscles, certainly neural entrapment or poor firing can greatly impact the success of our intervention as rehab professionals. Interestingly, a study from Turkey showed patients had a significant increase in diastasis recti abdominis (DRA) with a history of 2 cesarean sections and increased parity and recurrent abdominal surgery increase the risk of DRA.2
A fourth study looked at 23 patients with ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerve entrapment syndrome following transverse lower abdominal incision (such as a c-section). In this study, the diagnostic triad of ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerve entrapment after operation was defined as 1) typical burning or lancinating pain near the incision that radiates to the area supplied by the nerve, 2). Clear evidence of impaired sensory perception of that nerve, and 3) pain relieved by local anaesthetic.4
One of the other symptoms we may see in an area of nerve damage is a small outpouching in the area of decreased innervation on the front lower abdominal wall.
So, what can we do with this information? The good news is that as rehab professionals, we can treat along the fascial pathway of the nerve to release in key areas of entrapment. We can mobilize the nerve directly. Neural tension testing can help us differentiate the nerve in question and we can use neural glides and slides after having freed up the nerve from the area of compression. Then, we can increase the communication of the nerve with the muscles by using specific, localized strengthening and stretch in areas of prior compression. All of these techniques are taught in in our course, Lumbar Nerve Manual Treatment and Assessment. Come join us in San Diego May 3-5, 2019 to learn how to differentially diagnose and treat entrapment of all of the nerves of the lumbar plexus.
Okiemy, G., Ele, N., Odzebe, A. S., Chocolat, R., & Massengo, R. (2008). The ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves. The anatomic bases in preventing postoperative neuropathies after appendectomy, inguinal herniorraphy, caesareans. Le Mali medical, 23(4), 1-4.
Whiteside, J. L., & Barber, M. D. (2005). Ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric neurectomy for management of intractable right lower quadrant pain after cesarean section: a case report. The Journal of reproductive medicine, 50(11), 857-859.
Turan, V., Colluoglu, C., Turkuilmaz, E., & Korucuoglu, U. (2011). Prevalence of diastasis recti abdominis in the population of young multiparous adults in Turkey. Ginekologia polska, 82(11).
Stulz, P., & Pfeiffer, K. M. (1982). Peripheral nerve injuries resulting from common surgical procedures in the lower portion of the abdomen. Archives of Surgery, 117(3), 324-327.
Most people are told that inguinal hernia repair is a low risk surgery. While death or severe injury is rare, penile or testes pain after hernia repair is not a novel or recent finding. In 1943, Magee first discussed patients having genitofemoral neuralgia after appendix surgery. By 1945, both Magee and Lyons stated that surgical neurolysis gave relief of genital pain following surgical injury (neurolysis is a surgical cutting of the nerve to stop all function). However, it should be noted that with neurolysis, sensory loss will also occur, which is an undesired symptom for sexual function and pleasure. In 1978 Sunderland stated genitofemoral neuralgia was a well-documented chronic condition after inguinal hernia repair.
 Let’s do a quick anatomy review. The inguinal canal is located at the lower abdomen and is actually an extension of the external oblique muscles. Is travels along the line from the ASIS to the pubic tubercle, occupying grossly the medial third of this segment. It has a lateral ring where contents from the abdomen exit and a medial ring where the contents of the canal exit superficially. This ring contains the spermatic cord (male), round ligament (female), as well as the ilioinguinal and genitofemoral nerves. For males, in early life, the testes descend from the abdominal cavity to the exterior scrotal sac through the inguinal canal, bringing a layer of the obliques, transverse abdominus, and transversalis fascia with them within the first year of life. Just as a female can experience prolapse from prolonged increased intra-abdominal pressure, a male can have a herniation through the anterior abdominal wall and inguinal canal with increased abdominal pressure. Such pressure inducing activities can be lifting, coughing, and sports activities. When this occurs, an inguinal hernia repair is generally indicated. Because the genitofemoral nerve is within the contents of the inguinal canal, it can be susceptible to surgery in this area. The genitofemoral nerve has sensory innervation to the penis and testes and is responsible for the cremasteric reflex. Symptoms of genitofemoral neuralgia in men can be penis or testes pain, numbness, hypersensitivity, and decreased sexual satisfaction or function.
Let’s do a quick anatomy review. The inguinal canal is located at the lower abdomen and is actually an extension of the external oblique muscles. Is travels along the line from the ASIS to the pubic tubercle, occupying grossly the medial third of this segment. It has a lateral ring where contents from the abdomen exit and a medial ring where the contents of the canal exit superficially. This ring contains the spermatic cord (male), round ligament (female), as well as the ilioinguinal and genitofemoral nerves. For males, in early life, the testes descend from the abdominal cavity to the exterior scrotal sac through the inguinal canal, bringing a layer of the obliques, transverse abdominus, and transversalis fascia with them within the first year of life. Just as a female can experience prolapse from prolonged increased intra-abdominal pressure, a male can have a herniation through the anterior abdominal wall and inguinal canal with increased abdominal pressure. Such pressure inducing activities can be lifting, coughing, and sports activities. When this occurs, an inguinal hernia repair is generally indicated. Because the genitofemoral nerve is within the contents of the inguinal canal, it can be susceptible to surgery in this area. The genitofemoral nerve has sensory innervation to the penis and testes and is responsible for the cremasteric reflex. Symptoms of genitofemoral neuralgia in men can be penis or testes pain, numbness, hypersensitivity, and decreased sexual satisfaction or function.
In 1999 Stark et al noted pain reports as high as 63% post hernia repair. The highest rates of genitofemoral neuralgia are reported with laparoscopic or open hernia repair (Pencina, 2001). The mechanism for GF neural entrapment is entrapment within scar or fibrous adhesions and parasthesia along the genitofemoral nerve (Harms 1984, Starling and Harms 1989, Murovic 2005, and Ducic 2008). It is well known that scar and adhesion densify and visceral adhesions increase for years after surgery. Thus, symptoms can increase long after the surgery or may take years to develop. In 2006, Brara postulated that mesh in the region can contribute to subsequent genitofemoral nerve tethering which can be exacerbated by mesh in the inguinal or the retroperitoneal space. With an anterior mesh placement, there is no fascial protection left for the genitofemoral nerve.
Genitofemoral neuralgia is predominately reported as a result of iatrogenic nerve damage during surgery or trauma to the inguinal and femoral regions (Murovic et al, 2005). However, genitofemoral neuropathy can be difficulty and elusive to diagnose due to overlap with other inguinal nerves (Harms, 1984 and Chen 2011).
In my clinical experience, I have seen such symptoms after hernia repair, but also after procedures near the inguinal region such as femoral catheters for heart procedures, appendectomies, and occasionally after vasectomy.
As a pelvic PT, what are we to do with this information? First off, we can realize that all pelvic neuropathy is not necessarily due to the pudendal nerve. In the anterior pelvis, there is dual innervation from the inguinal nerves off the lumbar plexus as well as the dorsal branch of the pudendal nerve. When patients have a history of inguinal hernia repair, we can consider the genitofemoral nerve as a source of pain. Medicinally, the only research validated options for treatment are meds such as Lyrica or Gabapentin that come with drowsiness, dizziness and a score of side effects. Surgically neurectomy or neural ablation are options with numbness resulting, however, many patients do not want repeated surgery or numbness of the genitals. As pelvic therapists, we can manually fascially clear the path of the nerve from L1/L2, through the psoas, into and out of the canal and into the genitals. We can also manually directly mobilize the nerve at key points of contact as well as doing pain free sliders and gliders and then give the patient a home program to maintain mobility. Pelvic manual therapy can offer a low risk, side-effect free option to ameliorate the sequella of inguinal hernia repair. Come join us at Lumbar Nerve Manual Assessment and Treatment in Chicago this Spring to learn how to effectively treat all the nerves of the lumbar plexus.
Cesmebasi, A., Yadav, A., Gielecki, J., Tubbs, R. S., & Loukas, M. (2015). Genitofemoral neuralgia: a review. Clinical Anatomy, 28(1), 128-135.
Lyon, E. K. (1945). Genitofemoral causalgia. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 53(3), 213.
Magee, R. K. (1943). Genitofemoral Causalgia: New Syndrome. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 98(3), 311.
Sunderland S. Nerves and nerve injuries. 2nd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1978
Recently, I had a patient present to my practice with unretractable vaginal pain that was causing her quite a bit of suffering. Peyton (name changed) had been referred by a local osteopathic physician. For around a year, she had increasing severe vaginal pain. There was no history of assault, trauma, fall, or injury around the time of onset of symptoms. However, she had a kidney infection that caused back pain in the month prior to her pain onset.
 Peyton is home schooled, but she was unable to attend outings that required longer sitting, such as field trips or church. She also was having some urinary retention with start and stop stream and resultant urinary frequency. Peyton’s mother said the pain was distressing to Peyton and would cause her to cry. She had an unremarkable medical history. However, under further questioning, we discovered she did have a history of bed wetting later than usual (until age 7) and she had persistent leg pain. With standing longer than 15 minutes, her legs would hurt and feel weak, which prevented her from performing sports or being physically active. She also had experienced some achy low back sensations since the kidney infection. Peyton had been screened by urology, her primary care, an osteopath, as well as a vulvar pains specialist who diagnosed her with nerve pain, but said there is no good viable treatment.
Peyton is home schooled, but she was unable to attend outings that required longer sitting, such as field trips or church. She also was having some urinary retention with start and stop stream and resultant urinary frequency. Peyton’s mother said the pain was distressing to Peyton and would cause her to cry. She had an unremarkable medical history. However, under further questioning, we discovered she did have a history of bed wetting later than usual (until age 7) and she had persistent leg pain. With standing longer than 15 minutes, her legs would hurt and feel weak, which prevented her from performing sports or being physically active. She also had experienced some achy low back sensations since the kidney infection. Peyton had been screened by urology, her primary care, an osteopath, as well as a vulvar pains specialist who diagnosed her with nerve pain, but said there is no good viable treatment.
Objective findings revealed normal range of motion in her spine with the exception of limited forward flexion (feeling of back tightness at end range). Hip screening was negative for FABERS, labral screening or capsular pain patterns. General dural tension screening was positive for increased lower extremity and sensation of back tightness with slump c sit. Neural tension test was positive bilaterally for sciatic, R genitofemoral, L Iliohypogastric and Ilioinguinal nerves, and bilateral femoral nerves. Patient had a mild, barely perceptible lumbar scoliosis, and development of bilateral lower extremities and feet was symmetric and normal.
Because of the child’s age, we did not perform internal vaginal exam or treatment. This required treating the nerves that supply the vaginal area. All treatments were done with the patient’s mother present with both consent of the child and the mother.
For treatment, we started with the three inguinal nerves (Ilioinguinal, Iliohypogastric and genitofemoral) because of their relationship with the kidney (symptoms came on after kidney infection) as well as the correlation with the patient’s most limiting symptoms (genital pain). We cleared the fascia along the lumbar nerve roots, the lateral trunk fascia, the psoas, the inguinal region, the entrapments along the kidney and psoas, the inguinal rings and canal, and worked on neural rhythm (these techniques can be learned at the Pelvic Nerve Manual Assessment and Treatment class that I will be teaching later this month).
Over the next weeks, we used similar treatments for the sciatic nerve, femoral nerve, pudendal, and coccygeal nerves. We noted that the patient had an area of restricted tissue along her coccyx that was adhered, and her symptoms had some correlation with tethered cord. We did lots of soft tissue work along the coccyx and working along the coccyx roots, including some internal rectal work. We also did fascial and visceral work in the bladder region, as well as in the lumbar and sacro-coccygeal region.
Peyton’s referring physician and mother were notified of findings and possible tethered cord symptoms (leg weakness and pain, bladder symptoms, delayed nocturnal continence). The patient’s family felt she was getting better and was not interested in any kind of surgical intervention, and her physician also felt that with our progress, he was not interested in exploring that referral, unless the family was interested.
After just 4 treatments Peyton was no longer having any vaginal symptoms and was emptying the bladder normally. After 8 treatments Peyton was reporting no more lumbar pain or lower extremity symptoms, and follow up treatments were reduced to once a month. The patient was given a home program of neural flossing in a small yoga program we recorded on her mother’s phone. We had her mother work on the small area that remained adhered along patient’s tailbone. The area is much smaller, but it reproduces some pelvic pain for the patient, so we are carefully and slowly working along this area because of some of the global neural sx it produces.
The patient’s mother reports she is more active, no longer complaining of leg or vaginal pain. The patient has less generalized anxiety and she is able to void fully. When the pt grows in height, there is a return in some symptoms, likely due to increased neural tension. So, we have the family on standby and when the patient grows, they come back in for 2 visits, which is usually enough to get the patient back to her new baseline.