The following post was contributed by Herman & Wallace faculty member Ramona Horton. Ramona teaches three courses for the Institute; "Myofascial Release for Pelvic Dysfunction", "Mobilization of Visceral Fascia for the Treatment of Pelvic Dysfunction - Level 1: The Urologic System", and "Mobilization of Visceral Fascia for the Treatment of Pelvic Dysfunction - Level 2: The Reproductive System". Join her at Visceral Mobilization of the Urologic System - Madison, WI on June 5-7!
My physical therapy training and initial experience were in the US Army, so I had a strong bias toward utilization of manual therapy techniques based on a structural evaluation. When the birth of my 10 pound baby boy threw me head-long into the desire to become a pelvic dysfunction practitioner, I became plagued by the question: how do you treat the bowel and bladder, without treating the bowel and bladder? That, along with a mild obsession for the study of anatomy was the genesis of my desire to explore the technique of visceral mobilization.
The field of pelvic physical therapy has moved far beyond the rehabilitation of the pelvic floor muscles for the purpose of gaining continence, which was its origin. Now pelvic rehabilitation is a comprehensive specialty within the PT profession, treating a variety of populations and conditions (Haslam & Laycock 2015). Research has provided a greater understanding of the abdomino-pelvic canister as a functional and anatomical construct based on the somatic structures of the abdominal cavity and pelvic basin that work synergistically to support the midline of the body. The canister is bounded by the respiratory diaphragm and crura, along with the psoas muscle whose fascia intimately blends with the pelvic floor and the obturator internus and lastly the transversus abdominis muscle (Lee et al. 2008). The walls of this canister are occupied by and intimately connected to the visceral structures found within. These midline contents carry a significant mass within the body. In order for the canister to move, the viscera must be able to move as well, not only in relationship to one another, but with respect to their surrounding container. There are three primary mechanisms by which disruption of these sliding surfaces could contribute to pain and dysfunction: visceral referred pain, central sensitization and changes in local tissue dynamics.
Since the inception of physical therapy, manual manipulation of tissues has been a foundational practice within the profession. Manual therapy is a generic therapeutic category for hands-on treatment of a structural anomaly; it encompasses a variety of techniques which can be subdivided into either soft tissue based or joint based. Although the majority of manual therapy research has been on the musculoskeletal system, its effects are not exclusive to any particular region of the anatomy. The Orthopaedic Section of the American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) defines the technique of mobilization as "the act of imparting movement, actively or passively, to a joint or soft tissue" (Farrell & Jensen 1992). Visceral mobilization is a treatment approach focusing on mobilizing the fascial layer of the visceral system with respect to the somatic frame; it therefore falls under the classification of soft tissue based manual therapies. Soft tissue and or fascial based manual therapies have higher-levels of evidence to support their use for treating musculoskeletal pain and dysfunction (Ajimsha & Al-Mudahka 2014; Gay et al. 2013). Although many models have been proposed, the specific mechanisms behind the response of the musculoskeletal system to manual interventions are still not fully understood (Bialosky et al. 2009; Clark & Thomas 2012).
The previous model of manual therapy directly relieving local tissue provocation has given way to a recognition that the observed clinical improvement is not simply a result of the practitioner directly altering the structure beneath their hands through mechanical means. Rather this improvement is a combination of afferent input influencing the neurophysiologic output, changes in the endogenous cannabinoid system, and even a placebo responses simply because of touch (Bialosky et al. 2009; McParland 2008; Gay et al. 2014).
There is significant clinical evidence that issues of somatic pelvic pain, bowel, bladder and reproductive system dysfunction may be the result of visceral referred pain, central sensitization and restrictions in visceral tissue mobility which may further contribute to dysfunction within the canister of core muscles. The musculoskeletal framework is a mysterious, perplexing and complicated system. It is unique in that it offers us a variety of tissues and techniques from which to choose in order to help our patients from a manual therapy perspective. Science has acknowledged that the visceral structures and their connective tissue attachments indeed have an influence on the function of the somatic frame, the question is can we manually manipulate these structures and bring about an effect with a reasonable degree of specificity while producing a therapeutic outcome.
Part 2 of this report will discuss the evidence to support visceral mobilization.
Ajimsha M.S., Al-Mudahka N.R. & Al-Madzhar J.A. (2015) Effectiveness of myofascial release: Systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies 19, 102-112.
Clark B.C., Thomas, J.S., Walkowski S., Howell J.N. (2012) The biology of manual therapies. The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association 112 (9), 617-29.
Bialosky J., Bishop M. & Price D. (2009) The mechanisms of manual therapy in the treatment of musculoskeletal pain: a comprehensive model. Manual Therapy 14 (5), 531-538.
Gay C.W., Robinson M.E., George S.Z., Perlstein W.M. & Bishop M.D. (2014) Immediate changes after manual therapy in resting-state functional connectivity as measured by functional magnetic resonance imaging in participants with induced low back pain. Journal of Manipulative and Physiologic Therapeutics 37 (6), 614-627.
Haslam J. & Laycock J. (2015) How did we get here? The development of women’s health physiotherapy special interest groups in the UK. Journal of Pelvic Obstetric and Gynecological Physiotherapy 116 (Spring), 15-24.
Farrell J.P. & Jensen G.M. (1992) Manual therapy: a critical assessment of role in the profession of physical therapy. Physical Therapy 72, 843-852.
Lee D.G., Lee L.J. & McLaughlin L. (2008) Stability, continence and breathing: The role of fascia following pregnancy and delivery. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies 12 (4), 333-348.
McPartland J M (2008) Expression of the endocannabinoid system in fibroblasts and myofascial tissues. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies 12(2), 169-182.
The following is a contribution from Elisa Marchand, PTA, PRPC. Elisa is the first PTA to become a Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner! Elisa started a Pelvic Floor program with a locally-owned rehab company where she mentored 3 different PT's through the years. In that time, Elisa also taught as an adjunct with the local PTA program. Elisa works at McKenna Physical Therapy in Peoria, IL.
 As a physical therapist assistant, the following should cause me to rethink my passion for and practice within women's health PT. "The SOWH is opposed to the teaching of internal pelvic assessment and treatment to all supportive personnel including physical therapist assistants." (Position Statement on Internal Pelvic Floor Assessment and Treatment: Section on Women's Health, APTA; Feb 2014) It should have stopped me from sitting for and becoming the first-ever PTA certified as a PRPC. Fortunately, this is not the case.
As a physical therapist assistant, the following should cause me to rethink my passion for and practice within women's health PT. "The SOWH is opposed to the teaching of internal pelvic assessment and treatment to all supportive personnel including physical therapist assistants." (Position Statement on Internal Pelvic Floor Assessment and Treatment: Section on Women's Health, APTA; Feb 2014) It should have stopped me from sitting for and becoming the first-ever PTA certified as a PRPC. Fortunately, this is not the case.
I want to be clear from the start; I understand the need for clear boundaries with regards to the scope of practice of PTAs. However, the interpretation of these rules can get quite muddy. In the APTA's "Guide for Conduct of the PTA", the following clarifications are made, including their interpretations:
3C. Physical therapist assistants shall make decisions based upon their level of competence and consistent with patient/client values. Interpretation: To fulfill 3C, the physical therapist assistant must be knowledgeable about his or her legal scope of work as well as level of competence. As a physical therapist assistant gains experience and additional knowledge, there may be areas of physical therapy interventions in which he or she displays advanced skills...To make sound decisions, the physical therapist assistant must be able to self-reflect on his or her current level of competence.
3E. [PTA's] shall provide physical therapy services under the direction and supervision of a physical therapist and shall communicate with the physical therapist when patient/client status requires modifications to the established plan of care. Interpretation: Standard 3E goes beyond simply stating that the physical therapist assistant operates under the supervision of the physical therapist. Although a physical therapist retains responsibility for the patient/client throughout the episode of care, this standard requires the physical therapist assistant to take action by communicating with the supervising physical therapist when changes in the patient/client status indicate that modifications to the plan of care may be needed.
Through the years of working as a PTA, I have practiced in a variety of settings. Some of these settings have allowed for a high level of autonomy (such as in my current workplace), and some have operated in quite the opposite-- where my treatments were dictated step-by-step by the PT. No matter the state in which one lives, physical therapy clinics will vary in their method of treatment and utilization of PTAs. In Illinois, where I practice, the following is the detailed description of a PTA per the Illinois Practice Act:
"'Physical therapist assistant' means a person licensed to assist a physical therapist and who has met all requirements as provided in this Act and who works under the supervision of a licensed physical therapist to assist in implementing the physical therapy treatment program as established by the licensed physical therapist. The patient care activities provided by the physical therapist assistant shall not include the interpretation of referrals, evaluation procedures, or the planning or major modification of patient programs." (http://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs3.asp?ActID=1319&ChapterID=24)
Additionally, per the APTA's Standards of Ethical Conduct for the Physical Therapist Assistant: "6B. Physical therapist assistants shall engage in lifelong learning consistent with changes in their roles and responsibilities and advances in the practice of physical therapy." (http://www.apta.org/uploadedFiles/APTAorg/About_Us/Policies/Ethics/StandardsEthicalConductPTA.pdf) Personally, I take this as a green light for PTA's to immerse themselves in whatever their niche or passion may be. Thus, if a PTA is following this standard, and the advances in PT call for more trained therapists with an understanding of the pelvic floor, and the appropriate oversight provided-- as in my case; what is the hold-up?
Counter to the above expectations, the Section on Women's Health's Position Statement on Internal Pelvic Floor Assessment and Treatment states:
"Any internal pelvic (vaginal or rectal) myofascial release or soft tissue mobilization techniques that would require a continuous ongoing re-evaluation and reassessment should be performed by the physical therapist and not delegated to supportive personnel including physical therapist assistants. The SOWH recognizes that therapeutic exercise, neuromuscular reeducation and behavioral retraining techniques for pelvic floor dysfunction at times requires ongoing critical decision making while at other times are relatively routine. In the routine circumstances, those techniques may be delegated. When the higher level of critical decision making is necessary those techniques should be performed by the physical therapist and not delegated to support personnel including the physical therapist assistant."
In this above set-up, PTA's are made to sound as if incapable of using any critical thinking skills. Or, at the least, able to operate with very limited critical reasoning. Furthermore, in the typical treatment of pelvic floor conditions, how is the decision-making process required for individualized treatment any different than that to the external pelvis, or the low back, or the foot for that matter?! The skill and awareness that was required in transferring a patient in the ICU when I was a new grad was in some ways more complex with more of a direct impact on a person's survival and well-being, than what I do now. Yet, how am I not qualified to do something in which I have extensive training? This seems inconsistent.
In my opinion, the PTA is more than just "supportive personnel". On the other hand, I also believe that new PTA grads may not have a place in pelvic floor PT. There are complexities within, and knowledge required of anatomy and physiology of the pelvis, which the PTA does not get from his or her program. Though doctorate students entering the PT world today also do not have much exposure to the pelvic floor, they at least have gone through a more thorough coverage of anatomy, physiology, and disease processes. Despite the differences in schooling, MANY physical therapists see their assistants as vital assets to their clinics.
One incredibly positive aspect of being a PTA is the follow-through I have with my clients. I LOVE getting to know my patients, and feel that I am allowed this luxury more frequently than PT's whose schedules may need to stay open for new evaluations. I frequently have clients say to me, "I would never have dreamed that I'd be talking about (fill in the blank) with ANYBODY!" Usually, this is after a few sessions of working together. I cherish seeing the freedom and healing that comes when people feel comfortable enough to open up their physical, emotional, and spiritual selves.
Yes, as a PTA we are limited by the scope of practice placed before us. However, I do not see that as a set of limitations that binds us to a very narrow existence. With the training one receives through continuing education such as with Herman & Wallace, the PTA can gain the necessary skills for treatment. And from this, the possibilities are endless!
Today's post is written by faculty member Martina Hauptmann, who instructs the Pilates for Pelvic Dysfunction, Osteoporosis, and Peripartum course. Come learn how to apply Pilates in your practice this September 19-20 in Chicago, IL!
Treating the incompetent pelvic floor (urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse) is a staple of therapists who have specialized in this complex area.
Ever since Dr. Arnold Kegel published his research “A Non-surgical Method of Increasing the Tone of the Sphincters and Their Supporting Structures” back in 1942 women have been strengthening their pelvic floor by conscious contraction of their perineum by either squeezing or lifting.
Another method to strengthen the pelvic floor is through the muscles that are extrinsic synergists to the pelvic floor musculature. The hip abductors, adductors, extensors and lateral rotators are extrinsically linked to the pelvic floor musculature. Except for one of the hip lateral rotators, the obturator internus, which by its anatomical attachments is actually an intrinsic synergist of the pelvic floor.
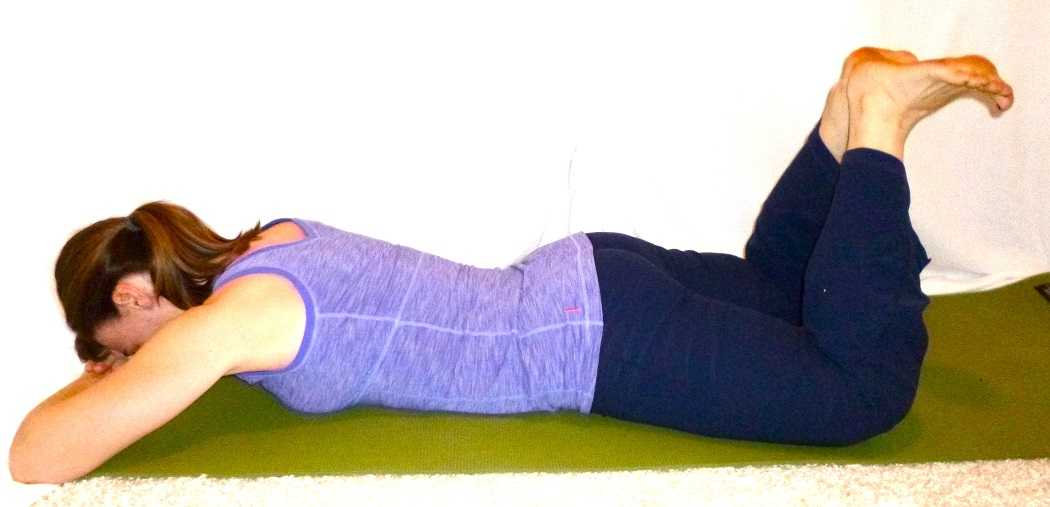
Pilates is an exercise method that seeks to increase a client’s strength, posture, control, and body awareness through precise exercises. The Heel Squeeze exercise is an excellent exercise to indirectly strengthen the pelvic floor via isometric contraction of the hip lateral rotators and hip extensors.
To perform the Heel Squeeze exercise, have the client lie prone with their legs hip distance apart, knees bent. The heels are touching and the toes pointing away from center. Draw the client’s awareness to their abdominals and have them slightly lift their stomach away from the mat. Instruct the client that she should continue with this contraction of her abdominals. Then as she exhales, the client squeezes her heels together and presses her pubic bone down into the mat. The client should hold this contraction for 5 seconds and do 8-12 repetitions.
This post was written by Jennafer Vande Vegte, MSPT, BCB-PMD, PRPC. You can catch Jennafer teaching the Pelvic Floor Level 2B course this weekend in Columbus.

"I hate my vagina and my vagina hates me. We have a hate- hate relationship'" said my patient Sandy (name has been changed) to me after treatment. Sandy's harsh words settled between us. I understood perfectly why she might feel this way. I have been treating Sandy on and off for four years. She has had over fifteen pelvic surgeries. Her journey started with a hysterectomy and mesh implantation to treat her prolapsed bladder. She did well for several months and then her pain began. Her physician refused to believe that her pain was coming from the mesh. This pattern was repeated for several years as Sandy tried in vain to explain her pain to her medical providers. She was told her pain was all in her head and put on psych meds. Finally, five years later, Sandy found her way to an experienced urogynecologist who recognized that Sandy was having a reaction to the mesh from her prolapse surgery. It turns out that Sandy's body rejected the mesh like an allergen. Her tissues had built up fibrotic nodules to protect itself from exposure to the mesh. It has taken years and multiple operations to remove all the mesh and all the nodules. Of course then Sandy's prolapse recurred as well as her stress incontinence and she recently had surgery to try to give her some support. In PT we attempted to manage her pain, normalize her pelvic floor function, strengthen her supportive muscles and fascia. Due to years of chronic pain, her pelvic floor would spasm so completely internal work was not possible. Sandy began to also get Botox injections to her pelvic floor and pudendal nerve blocks. She uses Flexeril, Lidocaine and Valium vaginally three times a day to manage her chronic pelvic pain. She is on disability because she cannot work. Later this month Sandy will have her 16th surgery to remove a hematoma caused by her previous surgery and another nodule that we found in her left vulva. Sandy is the most complicated case of mesh complication that I have seen in my practice, however I regularly see women who have had problems with mesh that we manage through PT and also women that have had mesh removal. No one expects to have complications with their surgery and when they do it can be life altering.
In a recent review of the literature surrounding mesh complications Barski and Deng cite that over 300,000 women in the US will undergo surgical correction for stress incontinence (SUI) or pelvic organ prolapse (POP). Mesh related complications have been reported at rates of 15-25%. Mesh removal occurs at a rate of 1-2%. Mesh erosion will occur in 10% of women. There are over 30,000 cases in US courts today related to pain and disability due to mesh complications. The authors looked at mesh complication statistics from studies concerning three surgical procedures: mid urethral slings, transvaginal mesh and abdominal colposacropexy .
The authors note there are sometimes reasons why mesh goes wrong: it is used for the wrong indication, there could be faulty surgical technique, and the material properties of mesh are inherently problematic for some women. Risk factors in patient selection are previous pelvic surgery, obesity and estrogen status. There are several types of complications described: trauma of insertion, inflammation from a foreign body reaction, infection, rejection, and compromised stability of the prosthesis over time. With mid urethral slings there were also several other complications listed such as over active bladder (52%), urinary obstruction (45%), SUI (26%) mesh exposure (18%) chronic pelvic pain (18%). For transvaginal mesh, reported rate of erosion was 21%, dysparunia 11%, mesh shrinkage, abscess and fistula totaled less than 10%. Transvaginal obturator tape was noted to be traumatic for the pelvic floor. Infections that might occur in the obturator fossa require careful and through treatment. Of women who have complications 60% will end up requiring surgical removal. It is imperative to find a surgeon who is experienced and skilled with this procedure as complete excision can be difficult and there are risks of bleeding, fistula, neuropathy and recurrence of prolapse and SUI. After recovery, 10-50% of women who have had excision will have another surgery to correct POP or SUI.
As pelvic health physical therapists we are strategically poised to both help women manage SUI and POP conservatively. We also have the skills needed to help rehabilitate women dealing with complications from mesh, either to avoid removal or after removal. Our job goes beyond the physical too, often helping women cope with the emotional toll that can parallel her medical journey. At PF2B we will discuss conservative prolape management and give you tools to help patients cope with chronic pain. Would love to see you there.
This post was written by Elizabeth Hampton PT, WCS, BCIA-PMB, who teaches the course Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain: Musculoskeletal Factors in Pelvic Floor Dysfunction. You can catch Elizabeth teaching this course in April in Milwaukee.
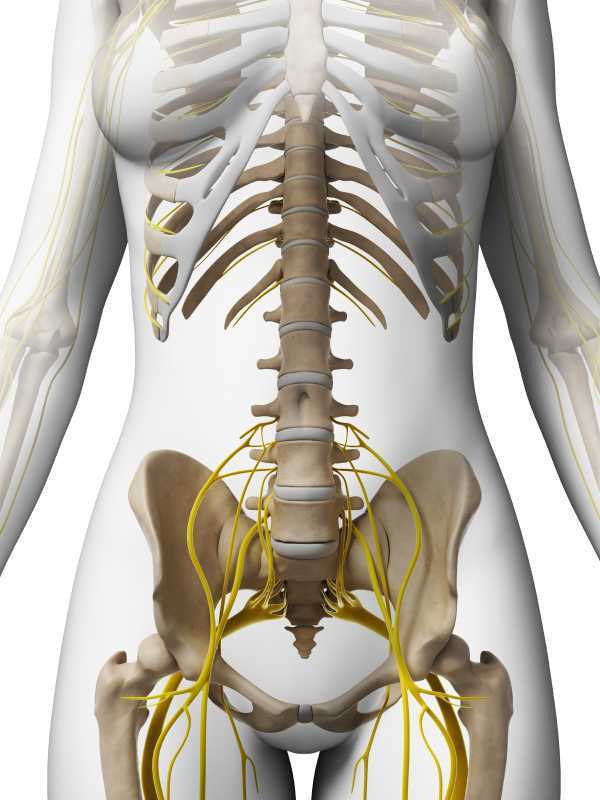
Chronic pelvic pain has multifactorial etiology, which may include urogynecologic, colorectal, gastrointestinal, sexual, neuropsychiatric, neurological and musculoskeletal disorders. (Biasi et al 2014) Herman and Wallace faculty member, Elizabeth Hampton PT, WCS, BCB-PMD has developed an evidence based systematic screen for pelvic pain that she presents in her course “Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain”. One possible origin of pelvic pain as well as chronic psoas pain and hypertonus may arise from genitofemoral, ilioinguinal or iliohypogastric neuralgia, the screening of which is addressed in the “Finding the Driver” extrapelvic exam.
The iliohypogastric nerve arises from the anterior ramus of the L1 spinal nerve and is contributed to by the subcostal nerve arising from T12. This sensory nerve travels laterally through the psoas major and quadratus lumborum deep to the kidneys, piercing the transverse abdominis and dividing into the lateral and anterior cutaneous branches between the TVA and internal oblique. The anterior cutaneous branch provides suprapubic sensation and the lateral cutaneous branch provides sensation to the superiolateral gluteal area, lateral to the area innervated by the superior cluneal nerve. (10)
The ilioinguinal nerve arises from the L1 spinal levels, passes through the psoas major inferior to the iliohypogastric nerve, across the quadratus lumborum and iliacus and lastly through the transversus abdominis along with the iliohypogastric nerve between the transverse abdominis and the internal oblique muscle. (7) The ilioinguinal nerve supplies the skin of the medial thigh, upper part of the scrotum/labia as well as penile root (5).
The genitofemoral nerve arises from the L1 and L2 spinal levels and splits into the genital and femoral branches after passing through the psoas muscle. (1). The genital branch (motor and sensory) passes through the inguinal canal and innervates the upper area of the scrotum of men. In women it runs alongside the round ligament and innervates the area of the skin of the mons pubis and labia majora. The motor function of the genital branch is associated with the cremasteric reflex. The femoral (sensory) branch runs alongside the external iliac artery, through the inguinal canal and innervates the skin of the upper anterior thigh. (8)
Differential diagnosis of entrapment of one of the three nerves can be challenging due to their overlapping sensory innervations and anatomic variability. Rab et al found up to 4 different patterns of anatomical variability in these nerve pathways. (9)
Transient or lasting genitofemoral, ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric neuralgia results from compression or irritation of these nerves anywhere along their pathway: from their spinal origin to distal pathways. Cesmebasi at al report that “neuropathy can result in paresthesias, burning pain, and hypoalgesia associated with the nerve distributions. “ (11) These entrapments may be associated with surgery, T12-L2 segmental dysfunction or HNP, constipation and is commonly observed clinically alongside psoas overactivity and pain. Lichtenstein found that up groin pain after hernia surgery ranged from 6-29% with Bischoff et al (2012) (6) denoting the post-operative neuralgia ranging from 5-10%.
Differential diagnosis of nerve entrapments are key skills in the screening of musculoskeletal contributing factors to pelvic pain and physical therapists are uniquely skilled to put all of the puzzle pieces together in these complex clients. Finding the Driver is being offered twice in 2015: April 23-25, 2015 at Marquette University and again in the fall. Check Herman & Wallace's webite for further details.
http://www.gotpaindocs.com/gentfmrl_nurlga.htm
Tubbs et al.Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine. March 2005 / Vol. 2 / No. 3 / Pages 335-338. Anatomical landmarks for the lumbar plexus on the posterior abdominal wall. http://thejns.org/doi/abs/10.3171/spi.2005.2.3.0335
Phillips EH. Surgical Endoscopy. January 1995, Volume 9, Issue 1, pp 16-21. Incidence of complications following laparoscopic hernioplasty
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00268-012-1657-2
Tsu W et al. World Journal of Surgery. October 2012, Volume 36, Issue 10, pp 2311-2319. Preservation Versus Division of Ilioinguinal Nerve on Open Mesh Repair of Inguinal Hernia: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Bischoff JM. Hernia. October 2012, Volume 16, Issue 5, pp 573-577. Does nerve identification during open inguinal herniorrhaphy reduce the risk of nerve damage and persistent pain?
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ilioinguinal_nerve
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genitofemoral_nerve
Rab M, Ebmer And J, Dellon AL.. Anatomic variability of the ilioinguinal and genitofemoral nerve: implications for the treatment of groin pain.
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery [2001, 108(6):1618-1623].
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cutaneous_innervation_of_the_lower_limbs
Cesmebasi et al (2014) Genitofemoral neuralgia: A review. Clinical Anatomy. Volume 28, Issue 1, pages 128–135, January 2015. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ca.22481/abstract

The following is contributed by faculty member Ginger Garner, who teaches the Hib Labrum Injury course. You can read more about that course on the Herman & Wallace course page.
Hip labral injury (HLI) is a relatively new diagnosis in the last 10 years of orthopaedic and rehabilitative care. However, just because HLI is a new diagnosis doesn’t mean the injury is new. In fact, HLI is posited to be responsible for the premature aging and osteoarthritis of the hip joint and pelvis that leads to hip replacements. HLI is also a major source of hip pain, with groin pain being the most common subjective complaint.However, groin pain is not the only complaint that is associated with HLI. Pelvic pain commonly goes hand-in-hand with hip pain.
What does this mean for patients? If you have hip or pelvic pain you should be evaluated by an HLI specialist, which can be a PT, surgeon, or osteopath who has received additional training on managing HLI. It is critical that you see someone who specializes in HLI. If HLI or other hip or pelvic injury is suspected, it is important that you follow up with a physical therapist who has had advanced training in HLI rehab for the best chance of recovery.
I find the premenstrual cycle pain (usually 1-5 days before the cycle begins) is a common phenomenon with many women with HLI (operative and non-operative), which is an area that needs more attention in research. Some women say it feels like they have retorn their labrum, and as a result, they get fearful – which affects not just their physical functioning but their psychoemotional and social well-being.
They limit activity which can exacerbate faulty neuromuscular patterning and deconditioning and result in increased pain from faulty structural support. Their realm of social activity and self-efficacy can suffer, which is also not good for long-term well-being.
Additionally, sleep can be interrupted with HLI and pelvic pain, which can dysregulate the HPA (hypothalamic pituitary adrenal) Axis and cause further problems with issues like pain centralization, cortisol dysregulation, and digestion. A recent study correlated vulvodynia and FAI (femoracetabular impingement), a type of hip impingement commonly found with HLI. The study found that those women who received early surgical intervention received the most relief from vulvodynia, while those who had a longer duration of pain did not experience the same level of improvement.
The take-home message is that early intervention for HLI is absolutely critical for the best long-term prognosis, and that pelvic pain, which can include anything from vulvodynia, dyspareunia, interstitial cystitis, non-relaxing pelvic floor/myalgia, pudendal neuralgia or entrapment, athletic pubalgia, and/or continence issues, although a common occurrence with HLI, is not normal and should be addressed by a trained pelvic rehab professional.
Want more? Read my post about Hip Labrum Tear Risk: Why Early Care is Critical, is absolutely necessary for the best long-term prognosis.
Today's post on the Pelvic Rehab Report comes from faculty member Allison Ariail, PT, DPT, CLT-LANA, BCB-PMD, PRPC. Allison instructs the ultrasound imaging courses, the next of which will be Rehabilitative Ultra Sound Imaging: Women's Health and Orthopedic Topics in Baltimore, MD on Jun 12, 2015 - Jun 14, 2015.

In the past several decades there has been quite a bit of research regarding stabilization of the low back and pelvic ring. We as therapists have changed our focus from working more of the global stabilization muscles to the local stabilizing muscles; the transverse abdominis, the lumbar multifidus, and the pelvic floor. Both research studies and clinical experience has shown us what a positive difference working on these muscles can makes for back pain and pelvic ring pain, as well as for the risk of injury in the back and pelvic ring. However, what does it do for risk of injury for the lower limb? In 2014, Hides and Stanton published a study looking at the effects of motor control training on lower extremity injury in Australian professional football players. A pre- and post-intervention trial was used during the playing season of the Australian football league as a panel design. Assessment included magnetic resonance imaging and measurements of the cross-sectional area of the multifidus, psoas, and quadratus lumborum, as well as the change in trunk cross-sectional area due to voluntary contraction of the transverse abdominis muscle. A motor control program included training of the multifidus, transversus abdominis, and the pelvic floor muscles using ultrasound imaging for feedback that then progressed into a functional rehabilitation program was used with some of the players. Injury data was collected throughout the study. Results showed that a smaller multifidus or quadratus lumborum was predictive of lower limb injury during the playing season. Additionally, the risk of sustaining a severe injury was lower for players who received the motor control intervention.
This is interesting and intriguing information. Yes, there are many factors that are involved in sustaining an injury during a sport. However, it would be a good idea to do a quick screen of the local stabilizing muscles before a playing season, whether it is a professional player or an adolescent player. Do adolescents really have issues with weakness in their local stabilizing muscles? Yes! Clinically I have seen adolescent players who display back pain and other issues related to weakness in their core muscles. Usually this occurs after they have gone through a growth spurt, but some of these adolescent athletes did not recover, even several years after the large growth spurt.
What a nice community service it would be to screen a local sports team for strength of the local stabilizing muscles in order to decrease injuries! It would also be nice to see additional research regarding this topic! To learn more about recent research and how to use ultrasound imaging to accurately assess and treat the local stabilizing muscles, join me at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore this June for the Rehabilitative Ultrasound Imaging for the Pelvic Girdle and Pelvic Floor course.
Hides JA, Stanton WR. Can motor control training lower the risk of injury for professional football players? Med Sci Sports Exec. 2014; 46(4): 762-8.
Today's post is written by faculty member Allison Ariail, PT, DPT, CLT-LANA, BCB-PMD, PRPC. You can join Allison in her Rehabilitative Ultrasound Imaging: Women's Health and Orthopedic Topics course, which takes place in Baltimore this year, June 12-14.
Since the mid 1990’s the POP-Q has been used to quantify, describe and stage pelvic organ prolapse. A series of 6 points are measured in the vagina in relation to the hymen. In a recent years, translabial ultrasound imaging has been used to look at the pelvic organs and the pelvic floor. A skilled practitioner can view pelvic floor muscle contractions, as well as Valsalva maneuvers and the effects each of these have on the pelvic organs. For example funneling of the urethral meatus, rotation of the urethra, opening of the retrovesical angle, and dropping of the bladder neck and uterus can be viewed using ultrasound imaging of the anterior compartment during Valsalva maneuvers. Pelvic organ descent seen on ultrasound imaging has been associated with symptoms of prolapse.

Until now the relationship between ultrasound and clinical findings has not been examined. A recent study by Dietz set out to see if there is an association between clinical prolapse findings and pelvic descent seen on ultrasound. Data was obtained on 825 women seeking treatment at a urogynecological center for symptoms of lower urinary tract or pelvic floor muscle dysfunction. Five coordinates of the POP-Q scale were measured and compared to ultrasound measures of descent. All data was blinded against other data obtained. Clinically, 78% of the women were found to have a POP-Q stage of 2 or greater. It was found that all coordinates were strongly associated with ultrasound measures of descent. The association was almost linear, particularly for the anterior compartment. This means that ultrasound measures can be used to quantify prolapse and be comparable to the POP-Q. Proposed cutoffs have been made for the bladder, uterus, and rectum in relation to the pubic symphysis.
It is exciting to see ultrasound use in the quantification and identification of more gynecological disorders. The use of translabial ultrasound imaging is growing and continuing to be researched. It is an exciting field to be a part of and I look forward to seeing where this research goes. I believe it will be used to help improve surgical procedures as well candidate selection for surgery. Join more for more discussion regarding translabial ultrasound imaging and learn how to view these images in Rehabilitative Ultrasound Imaging for the Pelvic Girdle and Pelvic Floor in Baltimore this June!
Dietz HP, Kamisan Atan I, Salita A. The association between ICS POPQ coordinates and translabial ultrasound findings: implications for the definition of ‘normal pelvic organ support’. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2015; April.
Today’s contribution to the Pelvic Rehab Report comes from Allison Ariail, the instructor for Herman & Wallace’s Rehabilitative Ultrasound Imaging courses. Join Allison and others this June 12-14 at Rehabilitative Ultra Sound Imaging: Women's Health and Orthopedic Topics - Baltimore, MD!
Is an Ultrasound that provides images of the pelvic floor and other deep musculature a cool gadget to have in the office or something that is truly essential? That depends on who you are asking! If you know how to use Ultrasound imaging properly and market yourself and your practice accordingly, it can become a tool that is not only fun to have and handy to use clinically, but also essential to providing your most efficient and thorough care!
Using an ultrasound (US) machine allows you to view the deeper musculature to assess how the muscles are functioning. The most common muscles assessed with US imaging are the transverse abdominis, the multifidus, and the pelvic floor. The patient then can use what is seen on the US screen as biofeedback to retrain their strategy and timing of recruitment. The therapist can also assess the patient’s ability to activate and maintain a contraction in various positions and even during motor tasks as well. This type of biofeedback is not only useful for pelvic floor patients, but is also important for patients with back and sacroiliac joint pain. Research is showing that using this type of stabilization program is making a difference in athletes. Julie Hides has published two articles recently showing that this type of stabilization program has helped with low back pain in professional cricket players, as well as to decrease the rate of lower extremity injury in Australian professional football players. (1,2) (see my post on The Local Stabilizing Muscles and Lower Extremity Injury.
You may be saying to yourself that you can save a lot of money and just palpate the transverse abdominis (TA), and the multifidus. However I would ask you… are you really feeling a transverse abdominis contraction, or some of the internal obliques? I have had 2 patients referred to me from very capable therapists that I respect and look up to. They were referred to me due to a lack of progress in their treatment. The therapist was addressing a local stabilization program, but their back pain was not getting better. To their credit, the therapist was able to train both patients to perform a proper TA contraction in supine, however one patient was unable to hold a contraction beyond 1 second, and another one was not able to activate it in sitting, or standing. This would explain why they were not progressing with respect to their pain. After treating each patient for 1 or 2 visits using US imaging, and sending them back to their referring therapist, they made rapid progress. Both therapists were so convinced on the usefulness of US imaging that they both went out and bought a machine to use in their clinic. Additionally, you would be surprised how many physical therapists (I can’t count the number on two hands anymore) I have seen that think they are properly performing a TA contraction and want to see how they are doing on the US. However, once we used the US imaging to assess their TA contraction, they realized they were overcompensating with their internal obliques. This is with physical therapists who have more knowledge than the general public regarding the importance of these muscles and how to activate them!
If you are knowledgeable in using ultrasound imaging, you open your doors to a number of possible patients you may not be currently accessing as referrals. There are numerous women and men who would like to receive treatment for pelvic floor weakness issues, but do not want to have to disrobe each treatment. Using ultrasound imaging is a wonderful option for these patients. It also is a way to treat younger patients that you have not been able to treat in the past as well (I would recommend taking the Pediatric Incontinence and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction course prior to treating pediatric patients). By using ultrasound imaging you not only gain an edge over your competing clinics that specialize in pelvic floor therapy, but you can gain an edge for back patients and sacroiliac joint patients as well. For the reasons I stated above when discussing a stabilization program centered on the use of US imaging, you could become very busy with referrals from spine surgeons, and ortho docs. In my office we have six therapists trained in using ultrasound imaging and two ultrasound machines. One of our most limiting factors is not the lack of patients to use ultrasound on, but that we only have two US units available to use! We have several spine physicians that send all of their patients to us because they have seen the difference using ultrasound imaging and the stabilization program can make in patients’ lives. We are eagerly awaiting a third machine and know it will be immediately used and allow us to further grow our clinic.
Now you may be saying, “Yes this would be handy but the pricing makes it impossible!” I would say think outside of the box! Some machines are going down in price making them more affordable. Plus, the settings we as therapists use are pretty basic, so we do not need to purchase a unit with a lot of bells and whistles that makes it more expensive. However there are other ways to acquire a unit other than purchasing one brand new. You could look into the price of refurbished units or look to your referring physician groups that you have a good relationship with. You may be surprised to find out how much physician’s offices get for machines when they are upgrading; hardly anything! If you work for a hospital system you may be able get the old machine transferred to your department for no cost to you! Or if you work in a private practice, you could offer to match the little amount the office would get from the vendor when upgrading. I guarantee you it would not be as much as a new unit. You also might be able to share a unit with another department, office, or clinic. In the past, I have shared ultrasound units with a surgical department, and a gynecology office. I would use the ultrasound some days of the week, and they would other days of the week. It worked out well! There are a lot of possibilities of ways to acquire an ultrasound unit if you think outside of the box! It may take a little effort coordinating things in order to get an US unit, but with proper knowledge, proper marketing, and word of mouth your business will grow and you will not regret the decision to invest in your practice!
Join me to discuss more ideas of how to use US imaging to grow your practice in both clinical skill as well as business growth this June in Baltimore!
1. Hides, Stanton, Wilson et al. Retraining motor control of abdominal muscles among elite cricketers with low back pain. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010; 20: 834-842.
2. Hides JA, Stanton WR. Can motor control training lower the risk of injury for professional football players? Med Sci Sports Exec. 2014; 46(4): 762-8.
This post was written by H&W instructor Elizabeth Hampton. Elizabeth will be presenting her Finding the Driver course in Milwaukee in April!

One of the most consistent questions that we hear at the Pelvic Floor 2B course is, “How do you choose between a pelvic floor and a musculoskeletal exam during your first visit with a pelvic pain client?” The answer depends on a number of factors, which include your clinical reasoning, toolbox, the client’s presentation, the clinical specialty, and expectations of the referring provider as well as the expectations of the client. It can be stressful to imagine gathering a detailed history, testing, client education and a home program within the first visit! Now that we have less time and total visits to evaluate and treat these complex issues, it can be overwhelming to know where to start.
Chronic pelvic pain has multifactorial etiology, which may include urogynecologic, colorectal, gastrointestinal, sexual, neuropsychiatric, neurological and musculoskeletal disorders. (Biasi et al 2014) Herman and Wallace faculty member, Elizabeth Hampton PT, WCS, BCB-PMD has developed an evidence based systematic screen for pelvic pain that she presents in her course “Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain”. “There are a number of extraordinary models that exist for treatment of pelvic pain including Diane Lee’s Integrated System of Function, Postural Restoration Institute, Institute of Physical Art and more,” states Hampton. “However, regardless of the treatment style and expertise of the clinician, each clinician should be able to perform fundamental tissue specific screening. If a client has L45 discogenic LBP with segmental hypermobility into extension, femoral acetabular impingement, urinary frequency > 12/day as well as constipation contributed to by puborectalis functional and structural shortness, all clinicians should be able to arrive at the same fundamental findings during their screening exam. The driver of the PFM overactivity(3) needs to be explored further as local treatment alone (biofeedback and downtraining) will not resolve until the condition causing the hypertonus is found and treated.” Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain is a course that models a comprehensive intrapelvic and extrapelvic screening exam with evidence based validated testing to rule out red flags, understand key factors in the client’s case as well as develop clinical reasoning for prioritizing treatment and plan of care. The screening exam complements any treatment model as it identifies tissue specific pain generators and structural condition, which will lead the clinician to follow their clinical reasoning and treatment model. Once the fundamentals are established, the clinician can move beyond screening and drill down into treatment of key factors which may include specific muscle gripping patterns, arthokinematic assessment and respiratory evaluation and retraining, among others.
Co-morbidities are common in pelvic pain are well documented (1, 2) and clinically these multiple factors are the reason pelvic pain is complex to evaluate and treat. Intrapelvic (urogynecologic, colorectal, sexual) as well as extrapelvic (orthopedic, neurologic, psychological and biomechanical clinical expertise) are required for skilled evaluation and treatment of this population. It is precisely this complexity, which makes working with pelvic pain clients challenging and extraordinarily rewarding. Physical therapists are uniquely skilled to put all of the puzzle pieces together in these complex clients. Finding the Driver is being offered twice in 2015: April 23-25, 2015 at Marquette University and again in the fall. Check Herman Wallace.com for further details.
1. Chronic pelvic pain: comorbidity between chronic musculoskeletal pain and vulvodynia. Reumatismo: 2014 6;66(1):87-91. Epub 2014 Jun 6. G Biasi, V Di Sabatino, A Ghizzani, M Galeazzi
2. http://www.jhasim.net/files/articlefiles/pdf/XASIM_Master_5_6_p306_315.pdf
3. IUGA/ICS Terminology for Female Pelvic Floor Dysfunction. http://c.ymcdn.com/sites/www.iuga.org/resource/resmgr/iuga_documents/iugaics_termdysfunction.pdf









































