The pelvis contains several parallel nerve groups. One of which is the lumbar plexus and its sensitive branches. This nerve web arises from the anterior rami of lumbar spinal nerves L1 to L4 and T12 from the thoracic spinal nerve.
Nari Clemons instructs the remote course, Lumbar Nerve Manual Assessment and Treatment, which addresses assessments for the contributory nerves from the lumbar plexus, anatomy, differential diagnosis, and objective findings for specific nerves of the lumbar plexus. This advanced-level course also provides twelve lab techniques for manually treating the nerves of the lumbar plexus.
Peripheral lumbar plexus nerves included in this course are Iliohypogastric, Ilioinguinal, Genitofemoral, Lateral Femoral Cutaneous, Femoral, and Obturator Nerves. These nerves are vital for the functioning of the lower extremities, including maintaining the ability to extend the knee, flex the hip, and adduct the thigh.
When a nerve becomes restricted, it disrupts the nerve signal allowing for symptoms to present as possible pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling. The lumbar plexus is vulnerable to injury when its bony protection, the pelvis, is compromised. Based on research from Anthony Chiodo, retroperitoneal hemorrhage, superior ramus fractures, traction, and penetrating injuries all can cause injury to the lumbar plexus. There are also a variety of conditions such as herniated disc, spinal arthritis, repetitive activities, and even poor posture that can lead to lumbar nerve pain, or a pinched nerve.
Nari explains in the Lumbar Course anatomy lecture that, "Dura matter covers the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerve. If you have tension in the peripheral nerves it can cause tension in the central nervous system and vice versa. When working with the nerves it is important to down-train the nervous system. Because the nerves run continuously it is always important to down-train and practice pain theory." She continues to explain that "The osteopathic approach to the fascial system of the peripheral nerve does not have a grounding in scientific research and is based on clinical experience from individuals using peripheral nerve palpation as a method for the evaluation of the nerve's function."
This means that there is not a singular proven technique that is more helpful than another when addressing nerves. The Lumbar Nerve Manual Assessment and Treatment course is essentially a melting pot that pulls from multiple studies and research. The evidence-based, step-by-step approach to treating the lumbar nerve includes
- Decompression to clear the path of the nerve and potential sites of restriction.
- Fascial techniques, just like those that we use with the other fascia of the body.
- Slacking the nerve towards its origin to create ease.
- Gliding the nerve in a pain-free manner.
- Strengthening the weakened muscles.
Differential diagnosis and treatment of these lumbar plexus nerves can allow patients to return to full daily function. Learn manual assessment and treatment techniques from Nari Clemons in the next Lumbar Nerve Manual Assessment and Treatment remote course, scheduled for September 11-12, 2021.
Holly Tanner, PT, DPT, MA, OCS, WCS, PRPC, LMP, BCB-PMB, CCI is a faculty member and the Director of Education at Herman & Wallace. She owns a private practice that focuses on pelvic rehabilitation and on chronic myofascial pain. Along with H&W faculty member Stacey Futterman, she co-authored the Male Pelvic Floor course.
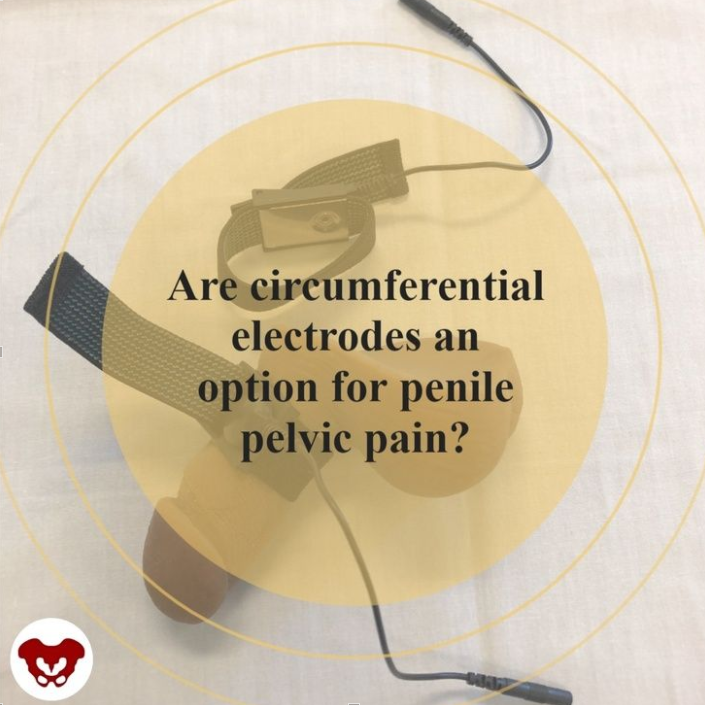
In the article by Schneider and colleagues (2013) “Refractory chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men: can transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation help?” the authors conclude that TENS can be effective and safe as a treatment for pelvic pain. What is interesting about the technique they utilize in the intervention is that the electrodes are circumferential, designed to be worn around the penis itself. While this particular treatment may not be of interest for or applicable to all patients with pelvic pain, it may indeed be a valuable tool to add to the list of a comprehensive treatment approach, particularly for the patients who have penile pain or involvement of nerves such as ilioinguinal or the dorsal branch of the pudendal nerve that supplies the penis.
The patients in the report are defined as having “refractory pain” meaning that they have been treated and failed to improve. (Although the definition of “treated” would likely not include a comprehensive pelvic rehabilitation approach.) Patients treated themselves at home for 30 minutes, twice per day at 80 Hz, 150 µs at the sensory threshold level. Outcomes tools included a pain diary using a visual analog scale (VAS) and NIH-CPSI quality of life item at baseline, at 3 months after TENS use, and at last known follow-up appointment. 60 men aged 21-82 years were
Results included successful treatment after 12 weeks in 48% of subjects, and a positive effect was maintained in 21 patients after a mean follow-up of over 43 months. Success meant a greater than 50% reduction in pain VAS and a VAS less than or equal to 3. Pain visual analog scale decreased from 6.6 to 3.9, and QOL improved significantly as well. Fortunately, no adverse events were reported.
While circumferential electrodes are not the only type of electrodes that can be used in pelvic pain TENS application, these electrodes that have a stretchy band to help increased comfort and approximation of the treating surface can allow easy re-use of the electrode and direct placement over the penile tissues. in the image below, one electrode has been placed around the body of the penis and the other is left off simply for viewing the surface of the treatment surface of the electrode. One of 2 leads and electrodes could be used depending on location and extent of pain, and depending on patient preference. Current Medical Technologies carries circumferential electrodes if you are interested in purchasing them.
Although there is no one best treatment pathway for chronic pelvic pain, we can rely on the fact that most patients need multidisciplinary and multimodal support. For conditions that involve overactive nerves or referred pain into the penis, or even for distal treatment for more proximal discomfort, TENS may serve as one “tool in the toolbox” for chronic pelvic, and in particular, chronic penile pain. Pain in the glans, or end of the penis, can be a debilitating and frustrating aspect of pelvic pain (see prior blog post on Pain in the Glans Penis here (link: https://hermanwallace.com/blog/dysfunction-in-glans-penis), and the annoying, distracting sensation of clothing touching the penis can be a source of near-constant irritation. Neuromodulation can be one pathway to assist in moving beyond pain patterns, and it’s a pathway that can be relatively affordable and portable. Because TENS can be applied independently by many patients, TENS can also be a way to improve self-efficacy and provide one strategy for self-care that can be an adjunct to clinical care.
If you’d like to learn more treatment strategies for pelvic pain, the next Men’s Pelvic Health is taking place November 6-7, 2021. Click here (https://hermanwallace.com/continuing-education-courses/male-pelvic-floor-function-dysfunction-and-treatment-satellite-lab-course) to sign up for this course that will sell out! If you are unable to attend a Satellite location, you can easily sign up on your own by scheduling your own lab partner!
If you would like to purchase electrodes, you can find them on the CMT site here: https://www.cmtmedical.com/
Schneider, M. P., Tellenbach, M., Mordasini, L., Thalmann, G. N., & Kessler, T. M. (2013). Refractory chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men: can transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation help?BJU Internationa

Osteoporosis is known to be a painless, progressive condition that leads to a weakening of the bones and can lead to a higher risk for broken bones. The upcoming remote course, Osteoporosis Management, scheduled for September 18-19, 2021, will discuss the scope of problems, specific tests for evaluating patients, appropriate safe exercises and dosing, and basic nutrition.
H&W faculty member Deb Gulbrandson recommends using the National Osteoporosis Foundation database for a resource and emphasizes the prevalence of osteoporosis is in a past interview for the Pelvic Rehab Report. "Approximately 1 in 2 women over the age of 50 will suffer a fragility fracture in their lifetime...According to the US Census Bureau, there are 72 million baby boomers (age 51-72) in 2019. Currently, over 10 million Americans have osteoporosis and 44 million have low bone mass."
A well-known consequence of osteoporosis is the increased risk of fragility fractures. A fragility fracture is often the first sign of osteoporosis and can be the cause of pain, disability, and quality of life for the patient. Research by Marsha van Oostwaard provided data that suggests about 13 percent of men and 40 percent of women with osteoporosis will experience a fragility fracture in their lifetime. Men also have a higher rate of mortality from fragility fractures relative to women (1).
The International Osteoporosis Foundation reports that patients who have suffered from a fragility fracture are at a high risk of experiencing secondary fractures, especially within two years of the initial fracture. Fragility fractures can result in osteoporotic patients from events that would not elicit an injury in a healthy adult. These events can include falling from a standing position and other low-energy traumas.
Fragility fractures are characterized by low bone mineral density and have an increased incidence with age (2). The risk of a fragility fracture is also influenced by bone geometry and microstructure. The most serious fracture sites are at the hip and vertebrae, but fractures can occur also on the ribs and other locations. Healthcare practitioners can assist patients in adapting lifestyle factors including exercise, sleep positions, and nutrition with the aim of helping prevent falls from occurring.
Deb Gulbrandson shares the goal of the Osteoporosis Management remote course: "This course is based on the Meeks Method created by Sara Meeks, PT, MS, GCS...we have branched out to add information on sleep hygiene, exercise dosing, and basic nutrition for a person with low bone mass. Knowing how to recognize signs, screen for osteoporosis, and design an effective and safe program can be life-changing for these patients."
Join H&W at the Osteoporosis Management remote course, scheduled for September 18-19, 2021, to learn more about treating patients with osteoporosis.
- Fragility Fracture Nursing: Holistic Care and Management of the Orthogeriatric Patient [Internet]. Marsha van Oostwaard. Hertz K, Santy-Tomlinson J. Springer; 2018.
- The burden of osteoporotic fractures: a method for setting intervention thresholds. Kanis, J.A., et al. Osteoporos Int, 2001. 12(5): p. 417-27.

The hip flexor muscles include the Iliopsoas group (Psoas Major, Psoas Minor, and Iliacus), Rectus Femoris, Pectineus, Gracillis, Tensor Fascia Latae, and Sartorius. When the hip flexors are tight it can cause tension on the pelvic floor. This can pull on the lower back and pelvis as well as change the orientation of the hip socket, lead to knee pain, foot pain, bladder leakage, prolapse, and so much more. The ramifications of iliacus and iliopsoas dysfunctions are discussed in Ramona Horton's visceral course series:
- Mobilization of the Visceral Fascia: The Gastrointestinal System
- Mobilization of the Visceral Fascia - The Urinary System
- Mobilization of the Visceral Fascia - The Reproductive System
You can also learn about this in a contemporary and evidence-based model with Steve Dischiavi in his Sacroiliac Joint Current Concepts and Athletes & Pelvic Rehabilitation remote courses.
A common issue with the iliacus and hip flexors is that they can shorten over time due to a lack of stretching or a sedentary lifestyle. When this happens, the muscle adapts by becoming short, dense, and inflexible and can have trouble returning to its previous resting length. A muscle that resides in this chronic contraction can become ischemic, develop trigger points, and distort movement in the body.
If you are treating patients with pain in their lower abdomen, sacroiliac joint, or that wraps around the lower back and buttocks, it could be because the hip flexors are tight. Traditional testing performed by medical practitioners tends to come back negative as many tests do not evaluate soft tissue issues. The best way to diagnose these concerns is through assessment with skilled palpation and structural evaluation.
One assessment test used for the iliopsoas is discussed in the Athletes & Pelvic Rehabilitation course. This is the Thomas Test which measures the flexibility of the hip flexors. In this test, the patient is supine while flexing the unaffected, contralateral leg at the hip until lumbar lordosis disappears. The length of the iliopsoas is determined by the angle of hip flexion displayed by the patient. The test is positive when the patient is unable to keep their lower back and sacrum against the table, the hip has a posterior tilt (or hip extension) greater than 15°, or the knee is unable to meet more than 80° flexion. A positive test indicates a decrease in flexibility iliopsoas muscles.
Treatment plans for the iliacus and hip flexors include stretching. An example includes the hip extension stretch or other active isolated stretches. Manual therapy, including trigger point release, can be used in conjunction with stretching to help muscle adhesion and release muscle tension. As with all treatment, the practitioner should discuss the risks, benefits, and treatment options, and obtain consent with patients. Prior to proceeding with manual therapy treatment make sure to establish a pain scale, assess the patient's range of motion and strength, and (if needed) perform the appropriate neurologic testing.
To learn more about manual therapy options for the visceral fascia, join Ramon Horton in her Mobilization of the Visceral Fascia Satellite Lab Course Series (multiple satellite locations available):
- Mobilization of the Visceral Fascia: The Gastrointestinal System - October 15-17, 2021
- Mobilization of the Visceral Fascia: The Urinary System- September 17-19, 2021
- Mobilization of the Visceral Fascia: The Reproductive System - October 1-3, 2021
To learn more about treatment philosophies for the pelvis and pelvic floor and global considerations of how these structures contribute to human movement you can join Steve Dischiavi:
- Athletes & Pelvic Rehabilitation Remote Course - September 18-19, 2021
- Sacroiliac Joint Current Concepts Remote Course - August 21, 2021

The world needs more clinicians who can treat pelvic pain, pelvic organ prolapse, urinary incontinence, diastasis recti, and the many other conditions that constitute pelvic floor/pelvic girdle dysfunction. Most clinicians who specialize in pelvic rehabilitation are Physical Therapists (PT) or Occupational Therapists (OT), though other licenses also allow you to work with patients who have pelvic floor dysfunction. Many doctors, nurses, and internationally licensed medical professionals are beginning to explore the field of pelvic rehabilitation.
In an interview for the Pelvic Rehab Report, faculty and instructor Tiffany Ellsworth Lee MA, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC, shared that "Occupational therapists wishing to pursue pelvic floor have a few options. The first thing is to find a pelvic floor clinical setting...or check to see if they can start a women's health program with a strong focus on the pelvic floor. OTs quite often do not start out in pelvic health directly after school. Since this is a newer area as compared to other certifications such as the NDT and PNF, it takes a little bit of research, time, and effort to find one’s exact niche. To get started, an OT should seek out courses that teach the basics of bladder and bowel management. It is important to understand the anatomy and physiology of the bladder, bowel, and sexual systems."
Once you have a license to practice, you can start learning to specialize in pelvic rehabilitation. The best place to start is with the H&W Pelvic Floor Level 1 satellite lab course, which offers immediately applicable clinical skills for evaluating and treating urinary incontinence or the musculoskeletal components of urogynecologic pain syndromes. Most practitioners who take Pelvic Floor 1 return to study in the next courses in the series.
You can learn all about the colorectal system, and how to treat conditions such as coccyx pain, pudendal neuralgia, and male pelvic pain in the Pelvic Floor 2A course, and in Pelvic Floor 2B you can expand your knowledge in topics such as movement assessment and re-training, prolapse, and pelvic pain. Then in the Pelvic Floor Capstone course, the final advanced course, you dive deep into topics such as hormones and their influence on conditions, surgeries and recovery, and skilled manual therapy techniques. Once you know your patient demographic, you can check out our growing list of specialty courses that include series topics including yoga, oncology, pregnancy, fascial mobilization, and much more.
Once you have gained experience in the field, you may consider sitting for the Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner Certification (PRPC). This certification recognizes expertise in pelvic rehabilitation for patients of all genders throughout the lifecycle. To be eligible to sit for the exam, applicants must have completed 2000 licensed hours of direct pelvic patient care in the past eight years, 500 of which must have been in the last two years.

The following is our interview with Mahmoud Shalaby, PT, MS, DPT, PRPC. Mahmoud recently passed the Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner Certification (PRPC) exam. He practices at PT of The City in Brooklyn, NY, and is a Teaching Assistant for local New York satellite courses with H&W. Mahmoud was kind enough to share some thoughts about his career with us. Thank you, Mahmoud - and congratulations on receiving your PRPC!
In 2016, I was offered the chance to shadow a senior PT who specialized in pelvic rehab. This specialty was mysterious for me. I didn't think that there was much we could offer to patients with pelvic issues like incontinence, prolapse, IC, and such until I started to treat them. Once I commenced learning more, it never ends.
There is always more to discover and I've always been impressed with the role of physical therapists in assessing and treating pelvic issues. I continue to be very excited to learn more and to develop my experience while further participating in studies to improve my skills and tools in improving people's quality of life.
Herman & Wallace institute has always been my partner in success, they knew how to get me on the track and impressively integrate all resources across body systems to make me confident and skillful to help patients.
When I`ve attended the courses at Herman & Wallace, I have looked at their great Pelvic Rehab certification and immediately I`ve decided to become a certified pelvic rehab specialist for many reasons. To begin with, we must keep high standards to provide such a specific skilled service, in addition to improving my skills, knowledge, and quality to help patients. There are a lot of people suffering from those issues, they either do not know how to address those issues or they do not know where to go.
In particular cultures and religions, the gender of the doctor matters, especially when it comes to sensitive topics, and I am proud to be among the two or three male certified pelvic rehab specialists across the country and I am always happy to get the patients comfortable and confident to be able to address their issues and help them reach their goals.
Working as a teaching assistant at Herman & Wallace is a great opportunity to learn more and explore how newbie therapists think, and help them to see the great skills and tools at this specialty.
As pelvic rehab specialists, we have a great responsibility to raise awareness and educate the community and let them know that we are here for them.

Kate Bailey, PT, DPT, MS, E-RYT 500, YACEP, Y4C, CPI curated and instructs the remote course on Restorative Yoga for Physical Therapists, which is scheduled for September 11-12, 2021. Kate brings over 15 years of teaching movement experience to her physical therapy practice with specialties in Pilates and yoga with a focus on alignment and embodiment. Kate’s pilates background was unusual as it followed a multi-lineage price apprenticeship model that included the study of complementary movement methodologies such as the Franklin Method, Feldenkrais, and Gyrotonics®. Building on her Pilates teaching experience, Kate began an in-depth study of yoga, training with renown teachers of the vinyasa and Iyengar traditions. She held a private practice teaching movement prior to transitioning into physical therapy and relocating to Seattle.
Without a doubt, these past couple of years have been tough with this global pandemic of a virus that caused major shifts in how we work, play, learn and socialize. Wherever you live on this planet, it is nearly impossible not to have been affected by the stress and trauma that the Covid-19 virus has created. Just like with any other stressor, the first step of management is recognition. Check, done.
Step two involves making conscious choices about how we want to live. This is where we have some options, including self-care. “Self-care” is one of my least favorite phrases. Not because at its core, self-care is not important. But because it's another thing on an overflowing to-do list and can create even more of a sense of imbalance, lack of accomplishment, and self-defeat. Yet, learning how to manage stress is a skill we all need: individually and communally.
However, there is a step before stress management that we need to address first. Interoception, defined by Porges, Ph.D., is the process that describes both conscious feelings and unconscious monitoring of bodily processes by the nervous system. As a clinician, this is a key aspect of every single patient care plan. I am a big fan of embodied decision making, and yet our somatic intelligence (or interoceptive skills) is widely underdeveloped.
Just as emotional intelligence is getting some wonderful development, through the work of researchers and educators like Marc Brackett, Ph.D. of Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence, our wellbeing and access to wellness are dependent on our ability to understand the sensations and signals throughout our body and then make a choice. This is important since you can’t make an embodied choice (step 2) before you have the data (step 1 - interoception). An example would be to imagine if you never felt the sensation of hunger, or the ‘hangry’ feeling when it’s been too long since the last boost of nourishment…how would you determine that you are hungry?
So, what to do? Many of us (clinicians and patients alike) live in a world full of overstimulation, productivity requirements, and constant stress. To develop interoception, finding little periods of stillness can be really useful. In yoga, there is a dedicated practice called pratyahara. Translated from Sanskrit to English as ‘withdrawal of the senses.’ The senses, in this case, includes all the sense organs: sight, smell, sound, touch, taste, movement (vestibular), and spatial placement (proprioception). Traditionally this is an aspect of meditation.
In my experience as a yoga teacher and physical therapist, I find this practice more accessible in the restorative yoga practice. It can take some graded exposure, but at the heart of the restorative yoga practice is stillness, darkness, silence, and support from props so that the body doesn’t have to do anything. These are also the essential components described by Herbert Benson, MD in his work on the Relaxation Response. In his work, he showed the relaxation response to be effective in decreasing heart and respiration rate triggering the benefits of the vagal nerve; which we are learning has so much to do with our ability to neuroregulate and participate in individual and communal stress management.
Restorative yoga is a practice of wakefully resting. Immordino-Yang et al, studied the brain in functional MRI when individuals were wakefully resting. The study found that during wakeful rest (without a meditative component where the brain has a task of concentration) the brain goes into a mode of neural processing called default mode. In default mode, the brain supports memory recall, imagining the future, and developing socio-emotional intelligence. In relationship to stress management, this is so important because it re-centers us, and allows for connection for even more neuroregulation.
For my patients, I often joke about lying on the floor. Really, it is not a joke at all. Lying on the floor for 15 minutes is savasana. Savasana is a wakeful resting and a practice of relaxation response. It seems easy: you always have access to a floor. You don’t need anything fancy. Aside from the neuroregulatory benefits of rest, savasana also gives the postural muscles a break. It allows the hip flexors to re-lengthen and the cervicothoracic junction to realign.
It is pretty great, and really accessible for most people. For those who are not comfortable flat, that’s where the props used in restorative yoga come into play. As physical and occupational therapists, we are so well primed to help people learn how to support their bodies in rest to get the benefits of rest.
Burnout, the Secret to unlocking the stress cycle by Emily Nagoski, Ph.D. and Amelia Nagoski, DMA
Polyvagal Theory, Stephen W Porges, PhD
Immordino-Yang et al. - Perspectives on Psychological Science - 2012
The Relaxation Response by Herbert Benson, MD, and Miriam Z Klipper

Mia Fine, MS, LMFT, CST, CIIP is the author and instructor of the Sexual Interviewing for Pelvic Health Therapists remote course scheduled for August 14-15, 2021. Mia’s specialties are sexual health concerns, eroticism, intimacy, alternative sex and relationships (kink/BDSM and non-monogamy), LGBTQIA+ genders/orientations/sexualities, and desire discrepancy. Her course Sexual Interviewing for Pelvic Health Therapists is intended for pelvic rehab therapists who want to learn tools and strategies from a sex therapist’s toolkit. Mia shares the following blog detailing some of the books that have influenced her.
As a science, psychology, somatics, and sexuality education nerd, books are my go-to psychoeducation sources. The books listed below are resources that I offer to my clients, send to family and friends for birthdays and holidays, and inform the work I do as a clinical supervisor, professor, and therapist. I’m excited to share some of my favorites that might help you and the patients with whom you work.
A prerequisite for anyone with a vulva (or who is partnered with someone with a vulva) is the book Come As You Are written by Emily Nagoski. Before a therapeutic intake session, I invite my clients who have vulvas to read this book. It is important to me that my clients and I share the same language that is offered in this fabulous resource. Nagoski illustrates the Dual Control Model for sexual arousal, interest, and desire in ways that are accessible and digestible for all. When clients understand the difference between Spontaneous Arousal and Responsive Arousal, and why these happen, and when, it is a game-changer for them and their partner. This book is a must for anyone who works with pelvic floor pain. And excitingly, these topics will be covered in my upcoming Herman & Wallace course!
The Politics of Trauma written by Staci Haines (also the author of Healing Sex) is a deep dive into, well, the politics of trauma. In this book, she explores the somatic experiences we humans have when we are activated. Her detailed description of fight, flight, freeze, fawn, and dissociate is nothing short of brilliant. This book is a must for those who are interested in exploring the impact that social justice, racial justice, transformative justice, and restorative justice have on our lived experiences of trauma.
The Body is Not An Apology is another brilliant book by Sonya Renee Taylor. It highlights the many effects of the “isms and obias” (such as Sexism, Racism, Fat-phobia, Transphobia) embedded in our everyday life and how identifying these frees us of the barriers they place on our quality of life. The isms and obias she explores impact the way we view ourselves, talk to ourselves, and relate to others. This book is incredibly inspiring, as is the author, Sonya Renee Taylor.
Additional books I love, many of which are written by close friends and colleagues include:
- Trans Sex by Lucie Fielding
- Wild Side Sex: the Book of Kink by Midori
- Gender Trauma by Alex Iantaffi
- Polyvagal Exercises for Safety and Connection by Deb Dana
- Becoming Cliterate by Laurie Mintz
- Better Sex Through Mindfulness by Lori A. Brotto
- The Art of Giving and Receiving: The Wheel of Consentby Betty Martin, Robyn Dalzen
These books have improved, and informed, my therapeutic work with clients and are recommendations I offer on a weekly, if not daily, basis. For additional resources, check out my website:https://miafinetherapy.com/. I look forward to exploring more comprehensive and accessible resources with you at my upcoming course Sexual Interviewing for Pelvic Health Therapists remote course scheduled for August 14-15, 2021!
The majority of practitioners begin their pelvic rehabilitation journey by taking Pelvic Floor Level 1, which is an excellent starting point. This course provides the basics of anatomy, techniques, and knowledge needed to start treating patients.
Another option for your pelvic floor journey is the Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1 remote course. Caring for patients with cancer begins at diagnosis, and as a pelvic rehabilitation practitioner, you are an integral part of the oncology team. This course addresses the issues commonly seen in a patient who has been diagnosed with cancer.
Several cancers can affect the pelvic region and pelvic floor. Such cancers include bladder, colorectal, prostate, and ovarian cancers. Treatments for pelvic cancers include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and pelvic rehabilitation. These treatment options depend on the tumor size, location, or stage and negatively affect pelvic floor function and quality of life.
Cancer patients also often have intimacy issues that stem from their diagnosis and treatment. Holly Tanner shares that "...cancer treatment can change relational roles, finances, work-life, independence, and other factors including hormone levels. Exhaustion (on the part of the patient and the caregiver), role changes, changes in libido, and performance anxiety can create further challenges." A pelvic rehabilitation practitioner can assist the patient in their recovery and reframing of intimacy.
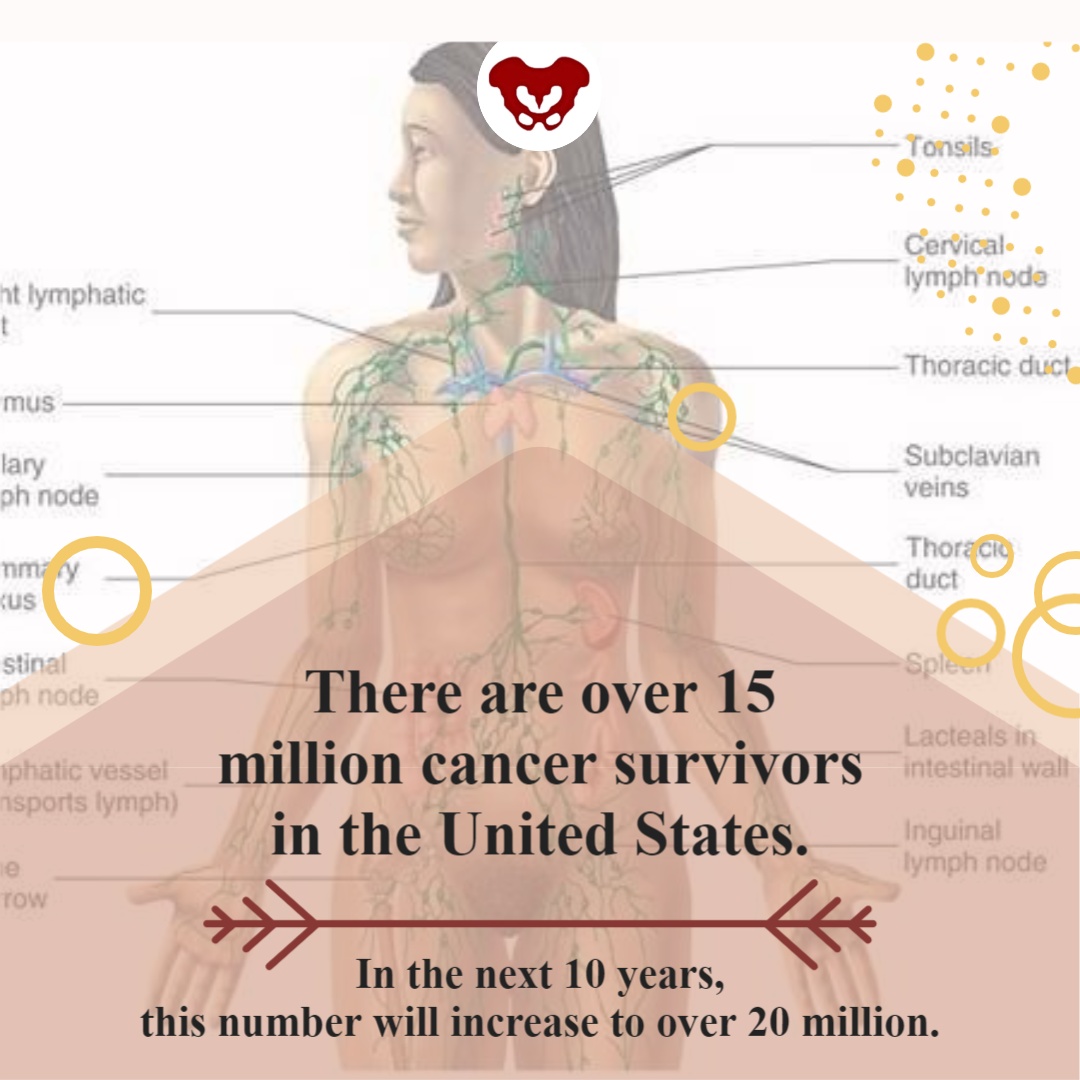
In addition to sexual function, the pelvic floor helps to maintain bladder/bowel control (emptying, urges), organ support, and stabilization of the spine/pelvis. Pelvic issues that originate from cancer treatment vary from scar tissue restriction or swelling, fibrosis causing narrowing and hardening of tissues, sexual issues, and lymphedema, among other issues. While some patients may not display symptoms at all, others can develop issues immediately after treatment, or even months after treatment has ended.
There are over 15 million cancer survivors in the United States. In the next 10 years, this number will increase to over 20 million. The need for trained practitioners to treat patients with cancer diagnoses will only be increasing in the future. Join H&W on August 15-16 in Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1 and learn to be part of an interdisciplinary oncology team.

How do healthcare practitioners improve patient satisfaction? Patient satisfaction is a cognitive evaluation of an emotional reaction to their health-care experience. According to multiple studies, the most significant predictor of patient satisfaction is the quality of their conversations with their medical practitioners.
Patients care about:
- Being listened to
- Being treated courteously and respectfully
- Being involved in decisions about their healthcare
- Receiving clear explanations about their medical status and treatment
This is good news because they are all factors that you can control. Practitioners who take the time to communicate clearly, listen intently, understand each patient as an individual, and respond compassionately can improve their patients’ satisfaction and treatment outcomes. As Lauren Mansell stated in an interview with H&W, you have to “know what questions to ask patients for treatment. Our patients often feel alone, are frustrated with medical treatments, and feel like no one can address their symptoms.”
When patients are facing a difficult or new medical situation, they are in a threat state. This means that emotions get triggered, the limbic system gets activated, and the prefrontal cortex starts to deactivate. This results in patients who are not thinking clearly, listening well, or who appreciate a different mindset.
Herman & Wallace offers courses on treating the pelvic floor, and also the whole patient. Strengthen your clinical interactions with one of their courses:
- Sexual Interviewing for Pelvic Health Therapists – with Mia Fine, MS, LMFT, CST, CIIP
- Trauma Awareness for the Pelvic Therapist – with Lauren Mansell DPT, CLT, PRPC
- Inclusive Care for Gender and Sexual Minorities – with Brianna Durand, PT, DPT
One of the most important things that a practitioner can learn is to never assume that you know how your patient feels or identifies. No two people are the same. Faculty member, Brianna Durand shares that “Ultimately, the best method to providing compassionate and competent care is to minimize your assumptions.” Brianna shares this example in a recent interview, “if you find yourself assuming someone’s gender identity based on their name or appearance, I’d challenge you to practice using the gender-neutral they/them pronoun until you learn how they identify. If you are unsure, it is okay to privately ask them!”
Faculty member, Mia Fine further stresses that “It is important that providers be aware of their own biases and be introduced to the various sexual health resources available to providers and patients.” Listen to your patient to understand what they are saying and feeling. Do not respond defensively. Remember that this can feel like a threatening situation for patients.
Happy patients are more likely to return to your practice in the future, recommend your practice to their friends, and pay their bills on time and in full. Patients want to have quality interactions with a healthcare provider who cares about them. As a practitioner, your satisfied patient is more likely to make follow-up appointments and maintain their prescribed treatment plan, which can lead to more positive outcomes.
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://hermanwallace.com/