This week The Pelvic Rehab Report is featuring faculty member (and senior TA) Mora Pluchino, teaching assistant Amanda Moe, and faculty member Dawn Sandalcidi on the topic of pediatric issues from infancy through adolescence. Our first guest blogger, Mora Pluchino, PT, DPT, PRPC has published two books. The first of which is titled The Poop Train: Helping Your Child Understand Their Digestive System. This is a rhyming, kid-friendly book to help children understand how their poop is made. It has resources in the back to help parents and caregivers manage a child's digestive system for optimal function including proper voiding positions, ideas for activities to help voiding, fiber recommendations, fiber-filled food options, and belly massage instructions. Her second book, Practically Perfect Pelvic Health 101: A Visual Tour of the Pelvic Floor is a visual tour of the pelvic floor to help all genders and all ages understand general pelvic health. You can find Mora online at https://www.practicallyperfectpt.com/ and on Instagram @practicallyperfectpt.
As a pelvic health specialist, I treat the pelvic floors for all humans of all ages. I am frequently asked the question “Why would a child need pelvic floor therapy?” The response is “So many reasons!”
Colic, gastroesophageal reflux disorder (GERD), and constipation are the top reasons for visits to a pediatrician in the first year (Indrio Et Al, 2014). As the mother of a child that struggled with all of these things, I can attest to the quality of life impact these diagnoses can create. A pelvic health specialist can help caregivers to manage these conditions with manual therapy, gross motor development assistance, and other infant care ideas to help manage the infant’s gastrointestinal system for better comfort and function.
Sillen (2001) reports that the neonatal bladder is controlled by neuronal pathways connecting with the cerebral cortex. The neonatal bladder function is characterized by small, frequent voids of varying volumes (Sillen 2001). Preterm infants had slightly different results thought to be due to an immature nervous system and this interrupted voiding disappeared for most as the children approached potty training age (Sillen, 2001). Still, infants born prematurely may be more at risk for pelvic floor issues!
What does this mean? There is a certain point in every child’s life where the bladder function, nervous system, and cognitive awareness match up. Ideally, this allows them to learn to hold and then void waste on a toilet. When toddlers are seen for pelvic floor issues, it is usually due to problems that arise during the potty training phase if they haven’t carried along with another pelvic floor issue from infancy. Pediatric pelvic floor issues, if not addressed early on, can continue on into preschool and elementary-aged children.
Pediatric Incontinence and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, instructed by Dawn Salicidi, reviews the basics of pediatric pelvic floor treatment. Pediatric pelvic floor issues can be divided into three categories: storage, voiding, and “other.” Storage issues include things like: increased or decreased voiding frequency, continuous incontinence, intermittent incontinence, enuresis, urgency, nocturia, constipation, and encopresis. Voiding dysfunctions present with hesitancy, straining, weak stream, intermittency, and dysuria. Other pediatric pelvic floor issues include symptoms like excessive holding, incomplete emptying, post micturition dribble, spraying, and pain in the bladder/ urethral/ genital areas.
Pediatric pelvic health requires the knowledge and skills used for treating adults with the additional abilities to relate to the child and their caregivers to help them manage and improve their symptoms. There is no age limit on the benefits of pelvic floor treatment!
Join us on Wednesday for the next installment of the pediatric pelvic floor three-part series: Pee Problems in Pre-Teens and Teens by Amanda Moe, DPT, PRPC. Amanda has written a book, Pelvic PT for ME: Storybook Explanation of Pelvic Physical Therapy for Children. You can find Amanda on Instagram @amandampelvicpt. The series will conclude on Friday with an interview with long-time faculty member, Dawn Sandalcidi PT, RCMT, BCB-PMD. Dawn Sandalcidi is a trailblazer in the field of Pediatric Bowel and Bladder Disorders and can be found on Instagram @kidsbowelbladder.
References:
- Indrio F, Di Mauro A, Riezzo G, et al. Prophylactic Use of a Probiotic in the Prevention of Colic, Regurgitation, and Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2014;168(3):228–233.
- Sillén U. Bladder function in healthy neonates and its development during infancy. J Urol. 2001 Dec;166(6):2376-81.

The Birth Healing Summit is a virtual summit that runs from April 4th through April 14th. Faculty member Nari Clemons will be speaking on Sunday, April 10th!
H&W is partnering again this year to bring the Birth Healing Summit virtually to you. Lectures throughout the summit present practical information, instruction, and tools that can be implemented in your practice right away. The summit is scheduled to run from April 4th to April 14th with 2 recordings going live each day with the intention to help practitioners to help moms heal body, mind, and spirit after birth! Also, twice during the summit, there will be a LIVE Facebook Q & A which is a great opportunity to speak to the experts and ask any questions you may have.
You can register for the summit now or get more information on the website here:
https://courses.instituteforbirthhealing.com/birth-healing-summit/ibh/77
As physical therapists and bodyworkers, the majority of training is focused on anatomy, physiology, and techniques to apply force to the body. While this is an effective way to treat the body, the summit is going to explore “out-of-the-box” solutions to achieve deeper healing. All 20 interviews will introduce you to a new approach to treating the common postpartum issues that women face.
These interviews are so packed with valuable information, instruction, and tools that you will want to listen to them over and over again. The All-Access Pass – Video or Video Plus, will allow you to review each at your own convenience or refer back to the information for a specific client case. It’s like having a reference library at your fingertips whenever you need it.
DAILY ACCESS: You receive 20 interviews with experts, plus their gifts for FREE!
Here is how it works:
- Starting April 4th, 2 speaker video-recorded interviews will be released each day.
- You will have 48hr to view, learn and enjoy the interviews.
- Sorry, no CEU’s available
VIDEO ALL-ACCESS PASS: You receive immediate access to all 20 interviews and the gifts.
Here is how it works:
- Starting March 21, you can purchase to gain full access to all the video-recorded interviews and gifts.
- You will have lifetime access to learn and enjoy the interviews.
- Sorry, no CEU’s available.
VIDEO PLUS ALL-ACCESS PASS: You receive immediate access to all 20 interviews and the gifts.
Here is how it works:
- Starting March 21, you can purchase to gain full access to all the video-recorded, audio, and transcripts plus the gifts.
- You will have lifetime access to learn and enjoy the interviews.
- Sorry, no CEU’s available.
Herman & Wallace's own Nari Clemons will be one of the 20 speakers talking about 'Mediation and Intention as Tools to Decrease Burnout' which is close to her heart! If you join Nari's lecture and enjoy the subject, she also co-instructs a course with Jennafer Vande Vegte for H&W to further deep dive into this topic called Boundaries, Self-Care, and Meditation which can be found on the H&W Online Courses page.
A few of the other lecturers and topics that you may be interested in:
- Lynn Schulte, PT - Pregnancy and Postpartum Impact on the Organs
- Rachel Shapiro, CNM - The Uterosacral LIgament - Sex and Postpartum Wellness
- Kathleen Kendall Tackett A New Paradigm for Depression in New Mothers
- Raylene Phillips, MD - Preventing and Minimizing Birth Trauma
- Rixa Freeze - Making Breech Birth Safe Again
Better support your client's pregnancy and labor and speed up their recovery by listening in. H&W hopes to see you at the Summit! Join the Summit Here: https://courses.instituteforbirthhealing.com/birth-healing-summit/ibh/77
This week Jennafer Vande Vegte and Nari Clemons sat down to share their course Boundaries, Self-Care, and Meditation with us to give a peek into the why, what, and how of it all.
What are boundaries? Boundaries are when we need to set a limit. It’s that capacity to say here’s where I need to draw the line so that I stay grounded and centered and feel good about myself. Self-care is what we do to replenish those energy reserves every day. To replenish our joy. To replenish our sense of awe and gratitude. Then meditation is a beautiful way to rewire the brain. To get to the reasons and roots of why we are getting depleted, we need to have a high level of honesty and introspection.
This is a course that gives you that permission and a lot of tangible tools. Nari shares that students have told her that "all of the other courses give us manual skills, but this course changed my life." Jen adds to this, "BUT you got to put in the work. This course is science and research-based and used in a way to transform lives." Part one is a deep dive into the science of the brain. Pain, trauma, PTSD and how that changes the brain, and how that has changed the brains of patients and of us. Meditation practices are explained from a scientific perspective about how they can come in and rewire the nervous system and help your patterns.
Part two is about a month later and gets a little bit softer. In this portion, Nari and Jenn focus on relationships, not just with our patients but with ourselves and the people that we love in our lives. How to construct healthy relationships and build that patient shared responsibility model in our practices. They also dive into the visualization of what we want in our practices and lives, self-care, and meditation. The course comes to a close with case studies and an action plan to bring what you’ve learned into the clinic. They’ve also established an online network where you can sign up for continued community. We’re all going through this journey together.
Boundaries, Self-Care, and Meditation Part 1 is scheduled for April 24th.
Boundaries, Self-Care, and Meditation Part 2 is scheduled for June 12th.
Steve Dischiavi sits down with Holly Tanner to discuss his remote course - Athletes and Pelvic Rehabilitation.
Can you tell us a little bit about yourself and your background?
I’ve been with Herman & Wallace now for about 10 years teaching various forms of this course [Athletes & Pelvic Rehabilitation] in terms of the pelvic floor content bridging the sports medicine world. With me not being an internal physical therapist, it’s been kind of a unique situation having been involved with H&W for so long.
I’m a manually trained orthopedic and sports PT, board-certified through the APTA, Athletic Trainer, PT. I’ve got my masters in PT, went back and got my doctoral degree in PT and now I’m pursuing my Ph.D. and doing some research. My professional background includes ten years of treating outpatient ortho and running clinics for big corporate entity types of places. Then I went for ten years of pro sports with the NHL.
This is really how I got linked into H&W because of all of the hip and pelvic disorders I was dealing with and interacting with pelvic floor therapists. That’s where the blend of pelvic floor content merging with sports medicine came into play for my course Athletes & Pelvic Rehabilitation & Pelvic Rehabilitation.
If I’m an internal pelvic health practitioner, why would I want to go take a course with someone who doesn’t even do that?
I’ve always respected that question. When I look at my course the thing that will attract the experienced physical therapist that is doing internal pelvic health care, would be the amount of consideration that goes into the design of the therapeutic exercise. Specifically how some of the latest research should be impacting the exercises directed at the pelvic floor. For example, those are the relationships between the lower extremity and the pelvic and the lower back, and how does the lumbopelvic-hip complex influence the pelvic floor. When we start looking at exercise prescriptions, specifically for the athletic population, the massive amount of complexity that goes into athletic movement typically is not reflected in the therapeutic exercises in the way we deliver them.
I tie those two roles together in an update on some of the most contemporary evidence concerning lumbopelvic-hip exercise prescription with the specific implications to the pelvic floor, and what should the pelvic floor therapist be thinking about when they start prescribing more global appreciation of exercises specific to that region.
Many of the people who take the Athlete course are first-time H&W course takers. What I see sometimes that they say is that oftentimes they are not internal pelvic floor practitioners. They don’t have the career trajectory to want to do internal work, but like myself, they know that the pelvic floor is an integral part of how athletes perform. I provide a kinematic vision from the entire lower extremity kinematic chain, up through the lumbopelvic-hip region, and how simple concepts like length-tension relationships can alter how the pelvic floor functions.
What is the philosophy that shows up in shifting the chronic pain experience?
One of the unique patterns that we see is that when the exercises are delivered more rotationally when the joint is loaded it seems to have a very interesting effect on the pelvic floor itself. So some of these same benefits that you get in the hip you see in your pelvic floor and other parts of the body. The transitional positions such as half and tall kneeling offer great opportunities to get the best of both worlds where you can be in a relatively stable pattern but still be loaded in the pelvic and the hip joint. It allows a nice transition of exercises between lower-level stability exercises and higher-level athletic-looking exercises.
A lot of times by the end of the course people will say that seems to be the transition that they really like. Now they see a way to get their patients off the table but not doing such high-level exercises that are aggravating to the patient. These transitional positions are a nice place to see some of these neurologic changes in the lumbopelvic hip region and carry over to more athletic maneuvers.
Athletes and Pelvic Rehabilitation is scheduled five more times this year in 2022!

Most people spend their days alternating between sitting and standing, changing positions constantly. How many of us take the time to think about the position of our coccyx, ilia, or sacrum? The coccyx typically is minimally weight-bearing in sitting, about 10%, just like the fibula. However, it can become a major pain generator if the biomechanics of the ilia, sacrum, and femoral head positions are not quite right.
Coccydynia and Painful Sitting is a course that can be related to all populations that physical therapists treat. A lot of patients will state “my pain is worse with sitting” which can mean thoracic pain, low back/sacral pain, and even lower extremity radicular pain.
Coccyx pain patients often have more long-standing pain conditions than other patient types. For the most part, the medical community does not know what to do with this tiny bone that causes all types of havoc with patient pain levels. Lila shares that "Sometimes treating a traumatic coccydynia patient seems so simple and I am bewildered as to why patients are suffering so long - and other times, their story is so complex that I wonder if I can truly help."
Lila Abbate discussed this in her past blog, Case Studies in Coccyx Pain. She wrote that "The longer I am a physical therapist, the more important the initial evaluation has become. Our first visit with the patient is time together that really helps me to create a treatment hypothesis. This examination helps me to put together an algorithm for treatment.
I hear their story and repeat back their sequence of events in paraphrase. Then I ask if there is any other relevant information, no matter how small or simple, that they need to tell me? Some will say, I know it sounds weird, but it all started after I twisted my ankle or hurt my shoulder (or something like that). I assure them that we have the whole rest of the visit together and they can chime in with any relevant details."
Determining the onset of coccyx pain will help you gauge the level of improvement you can expect to achieve. Coccyx literature states that patients who have had coccyx pain for 6 months or greater will have less chance for resolution of their symptoms. However, none of the literature includes true osteopathic physical therapy treatment, so I am very biased and feel that this statement is untrue."
The remote course Coccydynia and Painful Sitting is very orthopedically-based which takes Lila Abbate's love of manual, osteopathic treatment and combines it with the women’s health internal treatment aspects so that practitioners are able to move more quickly to get patients back on the path to improved function and recovery. The course looks at patients from a holistic approach from the top of their heads down to their feet. In taking on this topic, the course hones basic observation skills, using some of Lila's favorite tools: the Hesch Method, the Integrated Systems Model, and traditional osteopathic and mobilization approaches.
This course is designed to spark your orthopedic mindset, encouraging the clinician to evaluate the coccyx more holistically.
- What are the joints doing?
- How does it change from sitting to standing? Standing to sitting?
- What is the difference from sitting upright to slump activities?
Working through the basics and the obvious with failed results takes practitioners to the next step of critical thinking about how the patient presents, what seems to be lacking, and how to correct them biomechanically to achieve pain-free sitting?
This remote course provides 5.5 contact hours and the registration fee is $175. The 2022 scheduled course dates are:
Practitioners who have taken Sacroiliac Joint Current Concepts, Bowel Pathology, Sacral Nerve Manual Assessment and Treatment, Yoga for Pelvic Pain, or Ramona Horton's Mobilization of the Myofascial System courses may be interested in attending this course.

Blog by Deanna Vaughn, PT, DPT who practices at Core and Pelvic Physical Therapy Clinic in Conway, Arkansas, this article was originally located at https://whatsupdownthere.info/colorectal-cancer-the-gut-and-the-butt/.
Colorectal cancer refers to cancerous cells within the colon or rectum. Need a quick anatomy review? Keep reading then!
The colon is another name for the large intestine, which is the long tube (nearly 5 FEET!) surrounding the small intestines (that snaky, jumbled tube in the middle of our bodies, which you can see below in the picture). It’s comprised of segments: the cecum (the little pouch that joins the small intestine to the large intestine) in the right lower abdomen, the ascending colon starting at the right lower part of your abdomen (coming off the cecum), and up to about the right side of your ribcage; the transverse colon that loops underneath the stomach and ribcage from right to left; the descending colon that extends down from the left side of your ribcage to the lower part of your left abdomen; and then the sigmoid colon that loops (in an s-shape) along the lower abdomen to the center of the body. At the end of the colon is the rectum, which pretty much connects the colon to the actual anus/anal opening for wastes to leave the body.
That being said, colorectal cancer can affect any part or segment of the colon and the rectum. If you have a family history of colorectal cancer, or if you have an inflammatory bowel disease (like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis), then you may be at a higher risk for colorectal cancer. Other risk factors are the same for virtually any other health condition – genetics, no regular physical activity, poor diet, tobacco use, high alcohol consumption, etc.
So how would we know if it’s colorectal cancer – or precancerous cells, and how do we decrease our risk?
That’s where screening comes into play! Just like how someone may see their gynecologist annually and undergo the PAP smear every 1-3 years to check for any gynecological cancer (like cervical or labial cancer), someone may see their colorectal or gastrointestinal (GI) provider to check for colorectal cancer or disorders. Regular screening takes place around age 45 (although a person may be screened earlier if they are at higher risk or had a previous history of cancer).
What does screening look like?
There are a few tests that screen for colorectal cancer. These tests include stool tests, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and colonoscopy.
Stool tests – This pretty much involves you taking a sample of your stool via test kit provided to you, and returning it to your doctor/lab, where your stool is checked for any blood or other abnormal findings.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy – A thin, short tube with a light is inserted into the rectum. This allows your doctor to see any polyps or cancer within the rectum and lower part of the colon.
Colonoscopy – This is like the sigmoidoscopy, but with a longer tube. The longer tube allows your doctor to check for polyps/cancer inside the rectum and the entire length of the colon. Your doctor can also remove some polyps during this procedure if indicated.
Most people without any symptoms, abnormal findings or outstanding personal or family history of colorectal cancer will have these screening tests performed anywhere from 5-10 years.
What are the symptoms?
This is not an exhaustive list, but some symptoms may include:
- Bleeding, pain, and/or discomfort within the rectum/anus
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal pain and bloating
- Nausea/vomiting
- Difficulty or incomplete bowel evacuation
- Hemorrhoids
- Altered bowel habits (such as sudden constipation, diarrhea, change in stool consistency)
Now what are our treatment options?
Besides preventative measures – such as getting regular physical activity, improving our diet, etc., treatment looks similar to any other cancer treatment. This may look like chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and/or surgery. Surgery may be indicated to remove polyps/tumors, or parts of the colon or rectum to eliminate cancerous growths. Thankfully though, regular screening of the colorectal region can find precancerous/cancerous cells early. Oftentimes, such as during a colonoscopy, your colorectal provider may go ahead and remove polyps that are abnormal or deemed precancerous at that time!
Now what about pelvic physical therapy? Can it possibly help?
Well, this is another condition (like Pelvic Congestion Syndrome in the previous blog post), where pelvic physical therapy is not the initial go-to or main treatment option. Individuals with colorectal cancer vary in several ways depending on staging/severity and overall health. Once again, pelvic therapy is a nice resource to utilize if you’re needing or wanting ways to manage your bowel symptoms.
Ways that pelvic PT CAN help may include: Teaching appropriate toileting – positioning to straighten out the anorectal angle and allow stool to pass more easily from the rectum; mechanics, such as exhaling smoothly when pushing for a bowel movement to prevent straining; Improving pelvic floor muscle function (strength, endurance, coordination) so that your body can delay defecation as needed and calm down bowel urges; and overall promoting health bowel habits by supporting your nutrition and keeping bowel movements regular.
Whether or not you (or someone you know) have colorectal cancer, developing healthy and safe bowel habits is key to a better quality of life. Working with your doctor and/or your team of providers is important in making sure your needs are addressed, but feel free to reach out to your local pelvic PT if you want more resources or guidance – even things like, “So, how SHOULD I be pooping??”
References & Resources
Brenner H, Chen C. The colorectal cancer epidemic: challenges and opportunities for primary, secondary and tertiary prevention. Br J Cancer. 2018;119(7):785-792. doi:10.1038/s41416-018-0264-x
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/colon-rectal-cancer.html
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14501-colorectal-colon-cancer
Kuipers EJ, Grady WM, Lieberman D, et al. Colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15065. Published 2015 Nov 5. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2015.65
Leslie A, Steele RJC. Management of colorectal cancerPostgraduate Medical Journal 2002;78:473-478. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/pmj.78.922.473
Mármol I, Sánchez-de-Diego C, Pradilla Dieste A, Cerrada E, Rodriguez Yoldi MJ. Colorectal Carcinoma: A General Overview and Future Perspectives in Colorectal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(1):197. Published 2017 Jan 19. doi:10.3390/ijms18010197
You YN, Lee LD, Deschner BW, Shibata D. Colorectal Cancer in the Adolescent and Young Adult Population. JCO Oncol Pract. 2020;16(1):19-27. doi:10.1200/JOP.19.00153

Tara Sullivan, PT, DPT, PRPC, WCS, IF is on faculty with Herman & Wallace. She created Sexual Medicine in Pelvic Rehab and co-created Pain Science for the Chronic Pelvic Pain Population which she instructs alongside co-creator Alyson N Lowrey, PT, DPT, OCS. Tara started in the healthcare field as a massage therapist, practicing over ten years including three years of teaching massage and anatomy and physiology. Tara has specialized exclusively in Pelvic Floor Dysfunction treating bowel, bladder, sexual dysfunctions, and pelvic pain since 2012. She is adjunct faculty speaking at the annual conference for the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health (ISSWSH) and teaches an elective course at Northern Arizona University (NAU) and Franklin Pierce University on Pelvic Health. Tara is very passionate about creating awareness on Pelvic Floor Dysfunction and recently launched her website pelvicfloorspecialist.com to continue educating the public and other healthcare professionals.
You may have heard of Jessica Pin. She’s been making headlines lately with the unconventional ways she is going about changing what medical texts and schools teach about the clitoris…..which is currently very little. According to Pin, who has a bachelor’s degree in biomedical engineering, the average textbook has over 50 pages more dedicated to the penis than compared to the clitoris. Jessica Pin started her journey to create awareness of clitoral anatomy because at 17 years old she had a labiaplasty leaving her with sensory loss. Jessica’s activism has so far changed 8 medical texts to include detailed anatomy of the clitoris in hopes knowledge of this anatomy is understood well, as it is critical prior to performing surgery near the clitoris.
Loss of clitoral function can also occur after labiaplasty, biopsies, cosmetic surgeries, and repair. As pelvic rehab providers, there is a level of responsibility we have to help shift the narrative. How often have we seen or heard similar stories of young patients undergoing cosmetic surgeries to try to ‘look normal’ or apologize for the way they look? We have such a unique position to spend time educating our patients and treating sexual dysfunctions across the spectrum.
The clitoris is analogous to the penis so what is the cause of this disparity? It could be that, traditionally, the focus has been on penetrative intercourse which largely overlooks that the clitoris is the primary sexual organ of the female sexual response and that 81.6% of women don’t orgasm from intercourse alone (without additional clitoral stimulation). Only 18.4% of women report that intercourse alone is sufficient to orgasm (Herbenick, et al. 2018).
The clitoris has historically been omitted from anatomical textbooks and then ‘rediscovered’ throughout medical history (O’connell, 1998). If you look at the 1948 Grey’s Anatomy textbook you will see that the clitoris was left out. Anatomical information centralized around the medical field has been historically male-dominated, affecting how the world discusses and understands anatomy and their bodies even in the current day. In 2005 Wade, Kremer and Brown ran a study on college students and found that 29% of women and 25% of men could not identify the clitoris on a diagram of the vulva. We need to revolutionize female sexuality in general, change the focus from the linear model where penetrative sex and orgasm are the focus as it’s been traditionally taught.
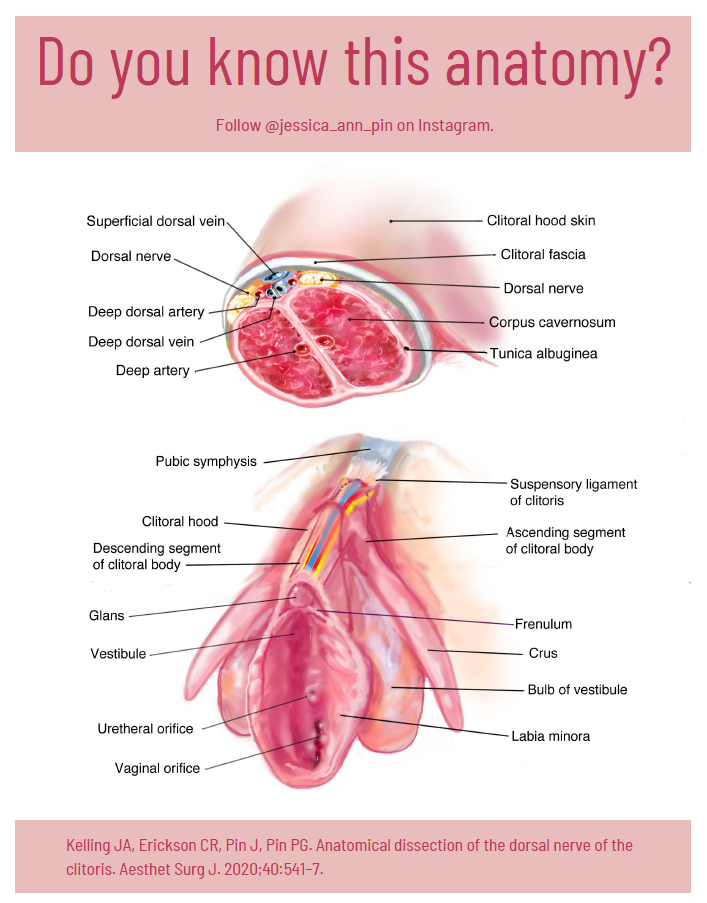
The full clitoris goes far beyond the crown which is the external tip. The clitoris actually extends several inches into the body where it branches into a shape similar to a wishbone. A description that I love is from Latham Thomas, “It’s all this amazing erectile tissue that wraps around, and it all engorges when it’s stimulated. Pound for pound, if you have a vulva, you actually have the same amount of erectile tissue that people with penises have, but it’s just internal.” These clitoral legs are responsible for the sensations where the front wall of the vagina connects to the paraurethral glands (the G-spot) and for female ejaculation.
I authored the Herman & Wallace Sexual Medicine in Pelvic Rehab course for practitioners to have a platform to learn proper anatomy, identify misconceptions, and understand that sexuality is circular with satisfaction as the focus. With the understanding of ‘normal’ anatomy and function, we can help our patients with sexual dysfunctions return to a healthy sexual lifestyle.
To sign the petition to get the nerves of the clitoris into the American College of OB/GYN curriculum go to:
Sexual Medicine in Pelvic Rehab is a two-day, remote continuing education course designed for pelvic rehab specialists who want to expand their knowledge, experience and treatment in sexual health and dysfunction. This course provides a thorough introduction to pelvic floor sexual function, dysfunction, and treatment interventions for the gender and sexual spectrum, as well as an evidence-based perspective on the value of physical therapy interventions for patients with chronic pelvic pain related to sexual conditions, disorders, and multiple approaches for the treatment of sexual dysfunction including understanding medical diagnosis and management.
Lecture topics include hymen myths, female squirting, G-spot, prostate gland, female and male sexual response cycles, hormone influence on sexual function, anatomy and physiology of pelvic floor muscles in sexual arousal, orgasm. As well as the function and specific dysfunction treated by physical therapy in detail including vaginismus, dyspareunia, erectile dysfunction, hard flaccid, prostatitis, post-prostatectomy; as well as recognizing medical conditions such as persistent genital arousal disorder (PGAD), hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) and dermatological conditions such as lichen sclerosis and lichen planus. Upon completion of the course, participants will be able to confidently treat sexual dysfunction related to the pelvic floor as well as refer to medical providers as needed and instruct patients in the proper application of self-treatment and diet/lifestyle modifications.
Course dates in 2022 include:
Top Homogenous Image: Internal genitalia depicting homology (Carrellas, B. and Sprinkle, A., 2017).
Bottom Clitoral Anatomy Image: Jessica Pin, https://drive.google.com/file/d/1fS1HfBWYqXAEBu_jnAPuiulTE3nqIYYQ/view
O'Connell, H.E., Hutson, J.M., Anderson, C.R. and Plenter, R.J., 1998. Anatomical relationship between urethra and clitoris. The Journal of Urology, 159(6), pp.1892–1897.
Herbenick, D., Tsung, Chieh F., Arter, J. Women's Experiences With Genital Touching, Sexual Pleasure, and Orgasm: Results From a U.S. Probability Sample of Women Ages 18 to 94. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/0092623X.2017.1346530
Wade, L.D., Kremer, E.C. and Brown, J., 2005. The incidental orgasm: The presence of clitoral knowledge and the absence of orgasm for women. Women & Health, 42(1), pp.117–138.

Megan Kranenburg, PT, DPT, WCS created the course Doula Services and Pelvic Rehab Therapy to present the unique challenges of merging a rehab practice with Doula services. Megan is a physical therapist who has balanced her solo outpatient pelvic health practice and Doula work since 2016. She lives and works in the nexus of Doula training near Seattle, Washington - which has provided plenty of opportunities to observe and participate in birth conversations and process the experience through the Physical Therapist's mind and heart.
As a pelvic floor practitioner, you may know that nearly 24% of women in the United States have pelvic floor dysfunction (as reported by the National Institutes of Health) and that this frequency increases with age. Childbirth can contribute to pelvic floor dysfunction, and it can be beneficial for pelvic therapists to know the doula's toolkit
So what is a doula? Doulas are often the first and sometimes the only people with whom a birthing person will feel comfortable discussing pelvic floor-related issues. Dona International defines a doula as a trained professional who provides continuous physical, emotional, and informational support to a mother before, during, and shortly after childbirth to help her achieve the healthiest, most satisfying experience possible.
Doulas can offer position ideas for comfort and labor progression, while their skilled hands can assist a mispositioned baby find its way through the pelvis. They can also support the birthing parent in learning how to push safely, effectively and protect the pelvic floor for birth. Doulas may hear several different symptoms of pelvic floor conditions from their clients through the perinatal experience. Two examples of natural birth/ pushing that a doula and pelvic therapist can spot or assist with include:
- Long hours of pushing can contribute to long-term muscle weakness and damage as well as lead to incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse.
- Uncoordinated pushing can result in weaker pelvic floor muscles that can last for several months postpartum. This weakness can also contribute to incontinence.
Similarly, Sara Reardon shared in a blog for Doula Trainings International a few symptoms of pelvic floor conditions that doulas may hear from their clients and can be looking out for throughout the birthing experience (1):
- Pain above the vagina that is sharp or achy and is exacerbated when rolling over in bed, or standing on while leg while getting dressed. This can be pubic symphysis dysfunction due to ligament relaxation.
- Pain in the back or lower back on one side that is sharp and is felt with a deep lunge, or when standing for a long time. This can be sacroiliac joint dysfunction due to ligament relaxation.
- Heaviness or pressure in the vagina that is worse at the end of the day, after exercise, or when standing. This can be a prolapse of pelvic laxity/varicose veins/swelling.
- Leakage of urine or poop, constipation, hemorrhoids and straining with bowel movements, incomplete bladder emptying, urinary urgency.
During vaginal birth, the baby passes through the ‘levator hiatus’ in the pelvic floor. This process can damage the fascia, muscles, connective tissues, and nerves. The levator muscles are stretched by 1.5 to more than 3 times their normal length as the baby passes through, depending on the size of both baby and pelvic floor muscle opening. (2) After this fascia is stretched, or torn, it doesn't heal like before. This fascia is attached to the bone and supports the urethra, vagina, and rectum.
Pelvic therapists and doulas can both make a big difference in the health of their clients. The following simple list is a very basic list that can be shared with clients that can make a difference in their healing.
- Breath - Inhale for the count of 2. Exhale for the count of 4. Repeat. Allow the exhale to be longer than your inhale.
- Nutrition - Choose nourishing whole foods. Collagen and mineral-rich foods, good quality protein, zinc, vitamin C are critical for tissue integrity and supporting new connective tissue repair.
- Hydrate - Easy & often. Don't wait until the end of the day to hydrate. Manage fluids throughout the day.
- Movement - Start with a good walk and build up from there. Spend time sitting on the floor with your baby and practice getting up from there.
- Sleep when the baby sleeps. Regular sleep and deep restorative rest are important for healing, recovery, and supporting mental energy.
- Each birth story is important and valid.
Doula Services and Pelvic Rehab Therapy is scheduled for April 3rd, August 6th, and December 10th this year. This is a four-hour, beginner-level course. Practitioner's who register are recommended to have completed Pelvic Floor Level 1, and the following reading:
- Preparing for A Gentle Birth, Calais-Germaine
- Reviving your Sex Life After Childbirth, Wallace
- The Birth Partner, Penny Simkin
- 5 Pelvic Health Lessons For Doulas From The Vagina Whisperer. The DTI Team. Doula Trainings International. Nov 5, 2018. https://doulatrainingsinternational.com/5-pelvic-health-lessons-for-doulas-from-the-vagina-whisperer/
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Damage. Australasian Birth Trauma Association. https://www.birthtrauma.org.au/physical-birth-trauma/pelvic-floor-muscle-damage/#:~:text=The%20levator%20muscles%20are%20stretched,and%20pelvic%20floor%20muscle%20opening.&text=In%20many%20women%2C%20these%20muscles,sometimes%20torn%20off%20the%20bone.

In a 2018 article by Holly Tanner, she explains how managing a medical crisis such as a cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming for an individual. ‘Faced with choices about medical options, dealing with disruptions in work, home, and family life often leaves little energy left to consider sexual health and intimacy. Maintaining closeness, however, is often a goal within a partnership and can aid in sustaining a relationship through such a crisis.” Research shows that cancer treatment is disruptive to sexual health. Intimacy is a larger concept that may be fostered even when sexual activity is impaired or interrupted.
Prostate cancer treatment can change relational roles, finances, work-life, independence, and other factors including hormone levels. (1) Exhaustion (on the part of the patient and the caregiver), role changes, changes in libido, and performance anxiety can create further challenges. (1, 3, 4) Recovery of intimacy is possible, and reframing of sexual health may need to take place. Most importantly, these issues need to be talked about, as a renegotiation of intimacy may need to take place after a diagnosis or treatment of prostate cancer. (2)
If a patient brings up sexual health, or the practitioner encourages the conversation, many research-based suggestions can be provided to encourage recovery of intimacy including:
• Redefining sex to include other sexual practices beyond penetration, such as massage or touching, cuddling, talking, use of vibrators, medication, aids such as pumps (5)
• Participation in couples therapy to understand their partner’s needs, address loss, be educated about sexual function (7)
• Participation in “sensate focus” activities (developed by Masters & Johnson in the 1970s as “touch opportunities”) with appropriate guidance (6)
Holly continues to share that “Within the context of this information, there is an opportunity to refer the patient to a provider who specializes in sexual health and function. While some rehabilitation professionals are taking additional training to be able to provide a level of sexual health education and counseling, most pelvic health providers do not have the breadth and depth of training required to provide counseling techniques related to sexual health - we can, however, get the conversation started, which in the end may be most important.”
Courses of Interest:
- A colorectal or male pelvic cancer diagnosis has multiple systems that are affected by cancer treatment. The rehabilitation professional that works with the pelvic oncology patient needs to competently navigate treatment techniques for all of these systems, as well as be confident in treating a patient in a personal area. This two-day course will address specific cancer types including prostate cancer, penile cancer, and testicular cancer. Additional cancer types covered include colorectal cancer and anal cancer.
Trauma Awareness for the Pelvic Therapist - Remote Course - Apr 9-10, 2022
- Bring their increased awareness of trauma to the successful, holistic treatment of patients with pelvic pain, sexual dysfunction, bowel dysfunction, and bladder dysfunction.
Sexual Medicine in Pelvic Rehab - Remote Course - Apr 9-10, 2022
- This course provides a thorough introduction to pelvic floor sexual function, dysfunction and treatment interventions for males and females of all sexual orientations, as well as an evidence-based perspective on the value of physical therapy interventions for patients with chronic pelvic pain related to sexual conditions, disorders, and multiple approaches for the treatment of sexual dysfunction including understanding medical diagnosis and management.
Male Pelvic Floor Function, Dysfunction, and Treatment - Satellite Lab Course - April 23-24 2022
- Discuss sexual anatomy and physiology, prostate issues, and look at the research describing models of intimacy and what worked for couples who did learn to renegotiate intimacy after prostate cancer. Participants will be able to describe the relationships between pelvic muscle function and men’s sexual health, including the evidence that demonstrates pelvic muscle rehabilitation's positive impact on erectile function.
1. Beck, A. M., Robinson, J. W., & Carlson, L. E. (2009, April). Sexual intimacy in heterosexual couples after prostate cancer treatment: What we know and what we still need to learn. In Urologic oncology: seminars and original investigations (Vol. 27, No. 2, pp. 137-143). Elsevier.
2. Gilbert, E., Ussher, J. M., & Perz, J. (2010). Renegotiating sexuality and intimacy in the context of cancer: the experiences of carers. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 39(4), 998-1009.
3. Hawkins, Y., Ussher, J., Gilbert, E., Perz, J., Sandoval, M., & Sundquist, K. (2009). Changes in sexuality and intimacy after the diagnosis and treatment of cancer: the experience of partners in a sexual relationship with a person with cancer. Cancer Nursing, 32(4), 271-280.
4. Higano, C. S. (2012). Sexuality and intimacy after definitive treatment and subsequent androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 30(30), 3720-3725.
5. Ussher, J. M., Perz, J., Gilbert, E., Wong, W. T., & Hobbs, K. (2013). Renegotiating sex and intimacy after cancer: resisting the coital imperative. Cancer Nursing, 36(6), 454-462.
6. Weiner, L., Avery-Clark, C. (2017). Sensate Focus in Sex Therapy: The Illustrated Manual. Routledge, New York.
7. Wittmann, D., Carolan, M., Given, B., Skolarus, T. A., An, L., Palapattu, G., & Montie, J. E. (2014). Exploring the role of the partner in couples’ sexual recovery after surgery for prostate cancer. Supportive Care in Cancer, 22(9), 2509-2515.

Faculty member Christine Stewart, PT, CMPT began her career specializing in orthopedics and manual therapy and became interested in women’s health after the birth of her second child. Christine joined Olathe Health in 2010 to further focus on women’s health and obtain her CMPT from the North American Institute of Manual Therapy. She also went through Diane Lee's integrated systems model in 2018. Her course, Menopause Transitions and Pelvic Rehab is designed for the clinician that wants to understand the multitude of changes that are experienced in the menopause transition and how they affect the aging process.
Menopause. The M-word, the second puberty, is the final frontier of a hormonal roller coaster when there are twelve consecutive months with no menstruation. A time of celebration, right? No more cramps, hygiene products, menstrual cups, or moodiness – FREEDOM! Not so fast my fellow clinician!
The body goes through some serious, hormonal loop-the-loops leading up to the cessation of ovulation. Perimenopause is the stretch leading up to the final cycle and this stretch can feel like yoga on steroids. It can last TEN years, not including symptoms experienced after the transition takes place. Changes in cycle length, flow, anovulation, and yes, even ovulating twice are all stages of perimenopause. (Hale et al., 2009). These changes translate into symptoms: sleeplessness, brain fog, anxiety, palpitations, fatigue, painful intercourse, and joint stiffness are just a few things that can be experienced during this time (Lewis, 2021).
This transition can begin for patients during their mid-thirties, more commonly it begins during their forties, but eventually, all people that ovulate will experience it. For some, perimenopause can be much more challenging than after menopause. The perimenopause hormone guessing game begins. Some months, progesterone makes an appearance. The next month, mostly estrogen, and some months - neither are around very much at all. If there is an abrupt change in ovulation, such as with a complete hysterectomy, the symptoms will most likely be intensified due to the abrupt loss of hormones. (Gunter, 2020). Dealing with the changes of menopause can be challenging in a variety of ways (like a two-year-old wailing for a candy bar in the checkout line), but many things can help ease this transition.
With fluctuating hormones also comes changes to many systems in the body. Estrogen receptors are everywhere, and when hormone levels are changing, so does the body’s internal workings. Glucose metabolism, bone physiology, brain, and urogenital function are just some of the systems affected (Shifren et al., 2014). Perimenopause is not just a time of altered periods. It is also a critical time in a person’s health where an increased incidence of heart disease, diabetes, and bone loss can begin (Lewis 2021).
Preparing for menopause should be on our radar for patients in their twenties, thirties, and early forties before the process starts. Establishing healthy habits earlier instead of later can help for a more successful transition, however, it is never too late! Knowing the signs and symptoms of this phase can help us guide patients and ourselves to a better understanding of what is happening with the body in this adaptation. We can make recommendations on lifestyle, exercise, and meditation, as well as refer them to other knowledgeable providers when needed.
I have had countless patients sent to me for urinary frequency, incontinence, or painful intercourse who are in this transition, but no one has talked to them about what is happening to their bodies. You may be thinking to yourself, these patients have doctors. Why aren’t they getting the information from their physician? After all, these providers have had years of training. The reality is sometimes doctors do not receive the necessary education to treat menopausal patients.
In a survey of postgraduate trainees in internal medicine, family medicine, and obstetrics/gynecology, 90% felt unprepared to manage women experiencing menopause (Reid, 2021). Insert jaw drop here. As pelvic health providers, we can help to fill this knowledge gap and be a conduit to explaining the process. We can empower patients with education, treatments, and recommendations to flourish in this critical phase of life.
The menopause transition can be a time of great uncertainty. Not only are patients’ lives transforming as their children grow and their parents age, but their bodies are changing as well. We can ease their burden in this period of adaptation. By calming their fears through education, we can assure them that indeed, they are not losing their minds.
Knowledge is power, and I am all in when it comes to empowering patients. They can learn that menopause is a phase and does not define who they are as a person. It is possible to survive and come out on the other side still thriving, while learning how to cope during the process. There is hope!

Menopause Transitions and Pelvic Rehab is an excellent opportunity to understand the physiological consequences to the body as hormones decline, in order to assist our patients in lifestyle habits for successful aging. Lecture topics include cardiovascular changes, metabolic syndrome, bone loss and sarcopenia, neurological changes (headache, brain fog, sleeplessness), Alzheimer’s risk, urogenital changes, as well as symptoms and treatment options. These include hormone replacement, non-hormonal options, dietary choices, and exercise considerations.
Menopause Transitions and Pelvic Rehab course dates include April 9-10th and August 27-28th.By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://hermanwallace.com/









































