You wouldn't place a newborn in a crib without knowing the legs were firmly attached at the right angle to the base. You wouldn't jump on a hammock if the poles or trees were not firmly intact and upright to support the sling. Why would you treat a pregnant woman without checking if her hips were working optimally in proper alignment to support the pelvis, inside which a new life is developing? Let's hope higher level clinicians spend the extra effort to learn about the surrounding areas that affect our specialty, whether it is pelvic floor or spine or sports medicine.
 In 2015, Branco et al., published a study entitled, “Three-Dimensional Kinetic Adaptations of Gait throughout Pregnancy and Postpartum.” Eleven pregnant women voluntarily participated in this descriptive longitudinal study. Ground reaction forces (GRF), joint moments of force in the sagittal, frontal, and transverse planes, and joint power in those same 3 planes were measured and assessed during gait over the course of the first, second, and third trimesters as well as 6 months post-partum. The authors found pregnancy does influence the kinetic variables of all the lower extremity joints; however, the hip joint experiences the most notable changes. As pregnancy progressed, a decrease in the mechanical load was found, with a decrease in the GRF and sagittal plane joint moments and joint powers. The vertical GRF showed the peaks of braking propulsion decreases from late pregnancy to the postpartum period. A significant reduction of hip extensor activity during loading response was detected in the sagittal plane. Ultimately, throughout pregnancy, physical activity needs to be performed in order to develop or maintain stability of the body via the lower quarter, particularly the hips.
In 2015, Branco et al., published a study entitled, “Three-Dimensional Kinetic Adaptations of Gait throughout Pregnancy and Postpartum.” Eleven pregnant women voluntarily participated in this descriptive longitudinal study. Ground reaction forces (GRF), joint moments of force in the sagittal, frontal, and transverse planes, and joint power in those same 3 planes were measured and assessed during gait over the course of the first, second, and third trimesters as well as 6 months post-partum. The authors found pregnancy does influence the kinetic variables of all the lower extremity joints; however, the hip joint experiences the most notable changes. As pregnancy progressed, a decrease in the mechanical load was found, with a decrease in the GRF and sagittal plane joint moments and joint powers. The vertical GRF showed the peaks of braking propulsion decreases from late pregnancy to the postpartum period. A significant reduction of hip extensor activity during loading response was detected in the sagittal plane. Ultimately, throughout pregnancy, physical activity needs to be performed in order to develop or maintain stability of the body via the lower quarter, particularly the hips.
The same authors, in 2013, studied gait analysis in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Branco et al., performed a 3-dimensional gait analysis of 22 pregnant women and 12 non-pregnant women to discern kinetic differences in the groups. Nineteen dependent variables were measured, and no change was noted between 2nd and 3rd trimesters or the control group for walking speed, stride width, right-/left-step time, cycle time and time of support, or flight phases. Comparing the 2nd versus 3rd trimester, a decrease in stride and right-/left-step lengths decreased. The 2nd and 3rd trimesters both showed a significant decrease in right hip extension and adduction during the stance phase when compared to the control group. In this study, the authors also noted increased left knee flexion and decreased right ankle plantar flexion during gait from the 2nd to the 3rd trimester. The bottom line in this study, just as the more recent one suggests, pregnant women need a higher degree of lower quarter stability to ambulate efficiently throughout pregnancy.
Physical therapists are movement specialists with a unique opportunity to analyze how humans function, whether athletes or pregnant women (or even a pregnant athlete). How the hips move and whether or not proper muscles are firing can affect anyone’s gait. The extra demands on the pregnant body require more specific analysis of kinetics by therapists, thus directing the protocols for rehabilitation of this population. It should behoove every pelvic floor specialist, in particular, to attend a course like “Biomechanical Assessment of the Hip and Pelvis" or "Care of the Pregnant Patient" in order to provide patients with the optimal support for the natural “crib” women provide during pregnancy.
Branco, M., Santos-Rocha, R., Vieira, F., Aguiar, L., & Veloso, A. P. (2015). Three-Dimensional Kinetic Adaptations of Gait throughout Pregnancy and Postpartum. Scientifica, 2015, 580374. http://doi.org/10.1155/2015/580374
Branco, M., Santos-Rocha, R., Aguiar, L., Vieira, F., & Veloso, A. (2013). Kinematic Analysis of Gait in the Second and Third Trimesters of Pregnancy.Journal of Pregnancy, 2013, 718095. http://doi.org/10.1155/2013/718095
Posture is a concept that rehab clinicians have long hung our hats on, and yet updated models of evaluation and care take into account the truth that there are plenty of humans functioning in poor postures who do not complain of musculoskeletal pain or other dysfunctions. Is postural dysfunction always, or never, causative? As with many things in life, the answer is likely somewhere in between. If our patient arrives at the clinic with a dysfunctional posture and improving their alignment eases discomfort and improves function, we have provided help with addressing posture. It is also likely that we have spent a bit too much time lecturing on the elusive “ideal” posture, when in fact dynamic and adaptive postures are more often occurring throughout a person’s day. Certainly computer postures add to a patient’s movement challenge, and we continue to learn more about the best ways for patients to manage the otherwise potentially static and unhealthy positions that add to many of our patients’ issues.
 In regards to the pelvic floor, does changing standing lumbopelvic posture affect pelvic floor muscle (PFM) activation? This is the question asked by researchers from Queen’s University in Canada. (Capson et al., 2011) Sixteen women ages 22-41 who had never given birth and who were continent participated in the study. They were assessed completing five tasks in three different postures: normal lumbopelvic posture, hyperlordosis, and hypolordosis. The tasks included quiet standing, maximal effort cough, Valsalva maneuver, pelvic floor maximal voluntary contraction, and a load-catching activity. A vaginal sensor was to use to collect electromyographic activity of the pelvic floor, and sensors were placed on trunk muscles including the rectus abdominus, external and internal obliques, and erector spinae. A perineometer was utilized separately to record manometry measures, and 3D motion analysis was used to position women in the appropriate lumbopelvic angles. Key results of the investigation are summarized below:
In regards to the pelvic floor, does changing standing lumbopelvic posture affect pelvic floor muscle (PFM) activation? This is the question asked by researchers from Queen’s University in Canada. (Capson et al., 2011) Sixteen women ages 22-41 who had never given birth and who were continent participated in the study. They were assessed completing five tasks in three different postures: normal lumbopelvic posture, hyperlordosis, and hypolordosis. The tasks included quiet standing, maximal effort cough, Valsalva maneuver, pelvic floor maximal voluntary contraction, and a load-catching activity. A vaginal sensor was to use to collect electromyographic activity of the pelvic floor, and sensors were placed on trunk muscles including the rectus abdominus, external and internal obliques, and erector spinae. A perineometer was utilized separately to record manometry measures, and 3D motion analysis was used to position women in the appropriate lumbopelvic angles. Key results of the investigation are summarized below:
- Baseline EMG activity of the PFMs and the trunk muscles was significantly lower in supine versus standing
- PFM EMG activity in standing hypolordotic was higher than normal or typical posture
- Trunk muscle EMG activity did not significantly change during the 3 quiet standing postures
- For maximal PFM contraction and for cough, Valsalva, and load-catching, lower EMG activity was measured in standing in hyperlordotic or hypolordotic postures compared to “normal” or habitual posture
- With cough, all muscles except the erector muscles demonstrated increased activity
- In general, EMG activity was increased in trunk muscles when the subjects were in their habitual posture
- Related to timing of the rectus abdominus (RA) muscles, the RA were activated 106 ms before the PFM
- In standing, the intravaginal pressure was significantly higher in the hypolordotic posture compared to hyperlordotic posture
How can we put this valuable research to work in the clinic? This study validates a typical EMG activity finding of increased activity during standing versus lying, which makes sense given the pelvic tasks of working against gravity. In addition, it may be the case that our patients can generate an optimal amount of pelvic muscle contraction (when strengthening) in a more neutral posture. It may also be worth considering that for our patients who are chronically holding, perhaps a tendency for them to be in a hypolordotic posture is perpetuating their dysfunction. The data on timing of trunk and pelvic floor muscles was less consistent, although not less interesting. This research can also be implemented as an evaluation and intervention in the clinic- let’s be sure that we are using methods of feedback such as EMG, real-time ultrasound, or pressure biofeedback in various and functional positions. Then we can find out what seems to work best for our patient, whether the goal is to increase or decrease muscle activity and function.
Capson, A. C., Nashed, J., & Mclean, L. (2011). The role of lumbopelvic posture in pelvic floor muscle activation in continent women. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology21(1), 166-177.
Assuring patients with chronic pain they are not crazy by explaining the neurophysiology behind what is happening in their brain and body can be life changing. Increasing our patients’ knowledge about physical conditions can reduce anxiety and provide hope. As a healthcare provider, being confident in your differential diagnosis skills can help narrow down the physical source of pain, weed out the psychological components, and connect the dots to the neurological influence on the patient’s persistent symptoms.
 A 2015 article in Pain Medicine (Gurian et al) found a direct association between pain sensitivity and treatment of chronic pelvic pain. The study involved 58 women with at least 6 months of pelvic pain, and they were evaluated on pain threshold using transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation before treatment and 6 months after a multidisciplinary approach to treatment of the pelvic pain. Pain intensity was also evaluated using the visual analog scale and the McGill questionnaire. Depending on the specific condition, treatment included manual therapy, physical therapy, pain medications, laparoscopy, oral contraceptives, nutrition intervention, or psychological support. After receiving treatment for 6 months, the pain threshold mean improved from 14.2 to 17.4. The effect sizes of 0.86 in the group with pain reduction and 0.53 in the group not achieving pain reduction were both within the 95% confidence interval. The authors concluded in this study that central sensitization does occur in patients with chronic pelvic pain, and treatment can reduce the general pain sensitivity of the patient.
A 2015 article in Pain Medicine (Gurian et al) found a direct association between pain sensitivity and treatment of chronic pelvic pain. The study involved 58 women with at least 6 months of pelvic pain, and they were evaluated on pain threshold using transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation before treatment and 6 months after a multidisciplinary approach to treatment of the pelvic pain. Pain intensity was also evaluated using the visual analog scale and the McGill questionnaire. Depending on the specific condition, treatment included manual therapy, physical therapy, pain medications, laparoscopy, oral contraceptives, nutrition intervention, or psychological support. After receiving treatment for 6 months, the pain threshold mean improved from 14.2 to 17.4. The effect sizes of 0.86 in the group with pain reduction and 0.53 in the group not achieving pain reduction were both within the 95% confidence interval. The authors concluded in this study that central sensitization does occur in patients with chronic pelvic pain, and treatment can reduce the general pain sensitivity of the patient.
Kutch et al., (2015) performed a study regarding the change in men’s resting state of neuromotor connectivity as affected by chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), showing men are also subject to central sensitization. Fifty-five men (28 males with pelvic pain for at least 3 months and 27 healthy males) completed the study, with resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging detecting the functional connectivity of the pelvis with the motor cortex (pelvic-motor). The right posterior insula and pelvic-motor functional connectivity was found to be significantly different in men with chronic pelvic pain and prostatitis versus the healthy control group. Contraction of the pelvic floor corresponded with activation of the medial aspect of the motor cortex, while the left motor cortex was more associated with contraction of the right hand. The authors concluded this relationship may explain the viscerosensory and motor processing changes that occur in men with CP/CPPS and could be the most important marker of brain function alteration in this group of patients.
As more research is being done on the neurophysiological level of pain, more truth can support the “it’s all in your head” accusation. However, it is a positive light to shed for a patient. The brain is powerful and controls how pain is perceived globally. Proper treatment of a chronic pelvic floor condition, for women and men, can help reduce stress on the brain and lessen pain sensitivity and perception in our patients. Never let a patient pursue the self-perception that they are crazy. Explain central sensitization and how sometimes the brain wins in the war of “mind over matter”; however, give them hope, explaining how the proper treatment can lessen the intensity of the battle wounds.
Maria Beatriz Ferreira Gurian, Omero Benedicto Poli Neto, Julio Cesar Rosa e Silva, Antonio Alberto Nogueira, Francisco Jose Candido dos Reis. (2015). Reduction of Pain Sensitivity is Associated with the Response to Treatment in Women with Chronic Pelvic Pain. Pain Medicine. 16 (5) 849-854; DOI: 10.1111/pme.12625
Kutch, J. J., Yani, M. S., Asavasopon, S., Kirages, D. J., Rana, M., Cosand, L., … Mayer, E. A. (2015). Altered resting state neuromotor connectivity in men with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: A MAPP: Research Network Neuroimaging Study. NeuroImage : Clinical, 8, 493–502. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2015.05.013
III. Postpartum
Nourishing my baby and myself, a complicated dichotomy
 The care I received from the doctors, nurses, and hospital staff during labor, delivery, and postpartum period was excellent. I felt all the staff members explained all procedures for myself and the baby. The labor and delivery nurses were helpful and compassionate. They showed me how to breastfeed the baby, assisted me with skin to skin contact, and taught my husband and I how to care for the baby when we took her home. The birth center site at the hospital was amazing. I had an individual birthing suite with a bathroom, a television, a bathtub and a place for my husband to sleep. Health care for the baby and I following delivery continued to be excellent. I had a surgical follow up one week later with my doctor and another postpartum visit at 6 weeks. At each visit I was given The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (a scale to help identify postpartum depression) as well as educational pamphlets on self-care following a cesarean delivery. The only complaints I had that required assistance from a health care provider was with getting baby to latch with breast feeding and neck and shoulder pain from breast feeding the baby. I took it upon myself to work on core and hip exercises I would give a postpartum patient who had undergone a cesarean delivery and was working on my scar tissue to prevent problems with bladder, bowel, abdomen, and uterus. I sought some massage for my neck and shoulders and did my physical therapy exercises for my neck and shoulders. I sought a lactation consultant for the latching issues with breast feeding. Seeking care helped resolve these issues which reduced my neck and shoulder pain and helping me enjoy breastfeeding my baby.
The care I received from the doctors, nurses, and hospital staff during labor, delivery, and postpartum period was excellent. I felt all the staff members explained all procedures for myself and the baby. The labor and delivery nurses were helpful and compassionate. They showed me how to breastfeed the baby, assisted me with skin to skin contact, and taught my husband and I how to care for the baby when we took her home. The birth center site at the hospital was amazing. I had an individual birthing suite with a bathroom, a television, a bathtub and a place for my husband to sleep. Health care for the baby and I following delivery continued to be excellent. I had a surgical follow up one week later with my doctor and another postpartum visit at 6 weeks. At each visit I was given The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (a scale to help identify postpartum depression) as well as educational pamphlets on self-care following a cesarean delivery. The only complaints I had that required assistance from a health care provider was with getting baby to latch with breast feeding and neck and shoulder pain from breast feeding the baby. I took it upon myself to work on core and hip exercises I would give a postpartum patient who had undergone a cesarean delivery and was working on my scar tissue to prevent problems with bladder, bowel, abdomen, and uterus. I sought some massage for my neck and shoulders and did my physical therapy exercises for my neck and shoulders. I sought a lactation consultant for the latching issues with breast feeding. Seeking care helped resolve these issues which reduced my neck and shoulder pain and helping me enjoy breastfeeding my baby.
Before having my daughter, I had preconceived notions about postpartum care. For the last ten years since I started working with women’s health patients I have heard repeatedly from my patients that they felt they did not receive comprehensive postpartum care. Many of these women hopped from health care provider to health care provider, sometimes taking years to resolve orthopedic or pelvic floor problems from their pregnancy or labor and delivery experience. Quality postpartum care was my soap box issue and still is. That being said, I was very satisfied with my postpartum health care experience. My experience revealed that support and education about postpartum problems as well as proactive healthcare for theses challenges is becoming mainstream. I have always felt that women in our country need better post-partum care and I am happy to see improvements being made. We may forget between the constant baby changing, soothing, and feedings that mom needs some care too. I am not sure that we always remember that there have been 9 months of physiologic changes occurring to a woman’s body. Additionally, physical trauma that occurs with caesarean or vaginal delivery. A mother may need physical therapy for exercises to strength abdominals or back, help for bowel or bladder problems, manual therapy for painful intercourse, or scar tissue work for abdominals or pelvic floor.
I think as a society we are getting more aware of the influence of hormones, crying babies, sleep deprivation, and a heavy work load can overwhelm a postpartum mother. Based on my experience only, I think we are doing a better job of monitoring postpartum depression, pain management, and pelvic floor problems. I was so pleased at the availability of information and counseling opportunities presented to me during my birthing and postpartum experience. I received so much encouragement and permission to seek help from others during my postpartum healing.
Now that patients are being routinely counseled on postpartum self-care for mind and body we need to help them achieve successful outcomes. As health care providers, we should help postpartum patients decide how to include self-care with their new routine with baby. Caring for a baby takes a lot of time! My postpartum experience was likely similar to other women, where I had very little time to do all the “things I should be doing.” (For me this included neck, shoulder, abdominal, back, and pelvic exercises. As well as attending pediatrician, massage therapy, and lactation appointments.) The baby needs to feed constantly. By the time you feed, change, and soothe the baby (and pump if needed) it is almost time to do it again. You may never have more than an hour to get things done or get some sleep. As a mother there are many novel challenges to face, skills to learn, and emotional stress from fatigue and hormones. On top of all that, oh yeah, you should exercise, eat healthy, and if you are lucky shower and sleep! The point is, being a mother is challenging and we are all doing the best job we can. It is difficult to care for your baby while taking care of yourself. Reflecting back on my “birth story” has helped me empathize with my patients but also helped me to see that as health care providers, we should continue to provide education to our patients on self-care and continue to encourage them to seek care for their problems. However, to really help our patients successfully heal, we need to help them figure out how postpartum self-care blends into their new life with baby.
II. Labor and Delivery
The Baby Always Has a Different Plan
Towards the end of my pregnancy, my doctor ordered an ultrasound to make sure the baby was growing appropriately. This was precautionary as the baby had measured small the last couple appointments. The ultrasound gave us some important information. Baby K was growing appropriately, however, she was breech. At this point, she should have already flipped into the cephalic (head down) position, and it was unlikely that she would turn further along in my pregnancy. I knew what this meant… “C-section” (cesarean). Like so many women before me, this was not what I wanted for my birth plan. Having a planned cesarean had not really crossed my mind. I figured it would only be some kind of emergency that would result in this outcome. Instantly I thought of all the patients I have treated over the years who had cesarean delivery. I thought of abdominal adhesions and scar tissue mobility work that would need to be done postpartum. Naturally, as a physical therapist, I also thought of all the mobility challenges this would bring after baby. Having a cesarean would change my post-partum recovery; I would need more help with lifting, carrying, and we have so many stairs in our house! I know this may sound crazy… but what saddened me the most about cesarean delivery was that I was not going to experience what labor felt like. I felt cheated, in a weird way, I was looking forward to it, almost like a rite of passage. I wanted to analyze labor and delivery from a patient’s standpoint, not just as a therapist. I thought it would help me relate to patients and friends who have experienced labor. All that being said, a scheduled C-section was happening unless that baby miraculously flipped.
 My doctor suggested a version, which is a procedure where your doctor tries to manually turn your baby using an external technique. I had heard it is painful, but I pride myself on being a pretty tough woman who has dealt with some pain, I can do this! Needless to say, the version was painful… Very painful! As a matter of fact, the most painful procedure I have ever encountered. After trying about four times to turn the baby, my doctor asked me if we should try one more time. Although I was miserable, I asked if they thought the baby was close to being in the right position. The looks on my husband’s and doctor’s faces told me that she hadn’t moved at all. We gave it one more try, but that stubborn baby really liked the spot she was in. The plan was to proceed with the scheduled C-section at 39 weeks, unless I went into labor first, then it would be an emergency cesarean delivery.
My doctor suggested a version, which is a procedure where your doctor tries to manually turn your baby using an external technique. I had heard it is painful, but I pride myself on being a pretty tough woman who has dealt with some pain, I can do this! Needless to say, the version was painful… Very painful! As a matter of fact, the most painful procedure I have ever encountered. After trying about four times to turn the baby, my doctor asked me if we should try one more time. Although I was miserable, I asked if they thought the baby was close to being in the right position. The looks on my husband’s and doctor’s faces told me that she hadn’t moved at all. We gave it one more try, but that stubborn baby really liked the spot she was in. The plan was to proceed with the scheduled C-section at 39 weeks, unless I went into labor first, then it would be an emergency cesarean delivery.
At 39 weeks, I woke up the morning of the planned cesarean and thought, “it’s a good day to have a baby”. I was excited to finally meet this little princess, but a little nervous about the cesarean delivery. I was trying not to think about what was going to happen to my abdomen and uterus. I was hoping Baby K would handle all of this safely, and she would be well. My plan for the procedure was distraction, not to think about what was happening, as I knew too much. Sometimes ignorance is bliss. I did not want to think of every unfortunate story I had heard about “spinals”, and “cesareans gone wrong”, so I kept telling myself to trust my doctors and relax. After all, this is what they do every day, and they are good at it. I wasn’t the biggest fan of the numbness and tingling I felt in my legs, as well as the lack of motor control in the lower half of my body once they administered the spinal, but it did the trick.
All I felt during the caesarean was just some tugging on my abdomen as the doctor worked to get baby out and complete the procedure. Luckily, it was all happening behind a partition while my husband held my hand and we told jokes to relieve our nerves. All of a sudden, there was a loud cry, and I felt instant relief. It was my baby, and she had healthy lungs! My doctor popped around the screen and showed me my beautiful brown-haired baby. Next, my husband and the nurses cut the cord and took care of baby. Once she was cleared and safe, they plopped her on my chest. Like a moth to a flame, that baby wriggled herself right onto my breast. It was the purest form of instinct I have ever witnessed. How did that little baby that just entered this world have the innate knowledge to nourish, and the strength to find her food source. It was amazing! Overall, no matter how much you research and plan for labor and delivery, it likely won’t turn out how you plan it. The positive is that our bodies have been delivering babies forever, so trust in your body, and trust in those around you helping with the delivery. The labor and delivery experience is innate.
The following is the first in a three-part blog series which chronicles the peripartum journey of Rachel Kilgore.
I. Pregnancy
 In April, I had my first child, a sweet and healthy baby girl. Reflecting on the last year, what a ride! I have had many of my friends, family members, patients, and acquaintances discuss the journey and challenges of motherhood with me, however, experiencing it first hand was a memorable voyage. I thought I was very prepared and knew what I was getting into, but as usual, nothing compares to first-hand knowledge and experience. From an academic standpoint, I had done my research on everything from conception, what to expect each trimester of pregnancy, and reviewed the many options for labor and delivery. I even was lucky enough to assist in the Herman and Wallace Care for the Post-Partum Patient course with Holly Tanner while I was pregnant! As a practitioner, I love treating pregnant and post-partum patients, it is one of my favorite populations to treat. I love helping these strong, motivated women with pain relief and to teach them management skills to adapt to a new lifestyle and a changed body that has unique musculoskeletal needs.
In April, I had my first child, a sweet and healthy baby girl. Reflecting on the last year, what a ride! I have had many of my friends, family members, patients, and acquaintances discuss the journey and challenges of motherhood with me, however, experiencing it first hand was a memorable voyage. I thought I was very prepared and knew what I was getting into, but as usual, nothing compares to first-hand knowledge and experience. From an academic standpoint, I had done my research on everything from conception, what to expect each trimester of pregnancy, and reviewed the many options for labor and delivery. I even was lucky enough to assist in the Herman and Wallace Care for the Post-Partum Patient course with Holly Tanner while I was pregnant! As a practitioner, I love treating pregnant and post-partum patients, it is one of my favorite populations to treat. I love helping these strong, motivated women with pain relief and to teach them management skills to adapt to a new lifestyle and a changed body that has unique musculoskeletal needs.
First Trimester: Information, Nausea, and Fatigue
I had always had a preconceived notion that I would exercise diligently and eat super healthy through my pregnancy. After all, that was how my lifestyle was before pregnancy, why should it change? That lasted about 6 weeks, until 24-hour episodes of nausea and vomiting overwhelmed me, which continued until the start of the second trimester. I basically just tried to make it through the day without vomiting at work, and would go straight to bed whenever I had the chance. I even had to miss several days of work! I thought it was termed “morning sickness” implying that it went away after morning, but apparently it should be renamed to “forever nausea” as that is what it felt like at the time. Because of the nausea, I wanted nothing to do with food, which in turn lead to constant concern about the baby not getting enough nourishment. Of course, my regular activity levels plummeted. In addition to nausea was constant fear of miscarriage and whether my regular activities were somehow harmful to my baby. Instead of ice cream and pickles, I craved information. What should I be doing, and what should I not be doing?
Second Trimester: Return of Energy, Excitement, Planning and Doing!
When the first day of the second trimester hit, the nausea just went away. I was ecstatic! I got my energy back and was finally enjoying the pregnancy again! I was able to exercise regularly and eat healthy, two of my favorite things. Everything was going well, and it was time to start figuring out this whole baby thing. Luckily, most of my friends are mothers themselves, and they helped guide me. They directed me to great resources to satisfy my quest for knowledge about everything I needed to know for pregnancy, labor delivery, and the baby itself. They helped me decipher what all these baby products were, and what do you actually need. All the fun stuff was happening! We painted the baby’s room, ordered furniture, and planned a baby shower.
Third trimester: Waiting, Exhaustion, Heart Burn, and Reduced Mobility
Everything that happens to my patients happens to me. Third trimester was when I started to really “feel pregnant”. Daily mobility became challenging. I never realized how many times in a workday I show patients correct lifting mechanics or how often I set things on the ground or pick up weights. I started to dread every time I had to pick up something. At work, I would drop my pen on the ground so many times, and why had I never noticed that I did it so often? Luckily, I used my “physical therapy knowledge and skills” and did things I tell my pregnant patients to do; the results were minimal problems with musculoskeletal pain. Techniques such as: Using proper mechanics throughout my day, pulling in my core, and wearing a maternity support if my back was hurting a little. I never really developed severe back pain as is the case for many pregnant women. I completed hip and trunk exercises I usually give my pregnant patients and found they were easy to do and made me feel better... shocking right? Of course I was doing my kegels too! While my musculoskeletal system was doing well, my gastrointestinal system was not. I had never really had heart burn before, but now had it constantly, and found it to be very frustrating and depressing. I love cooking and eating but neither are enjoyable when you have heartburn. The heartburn was so bad it would wake me up every night coughing and chocking on my own acid reflux. Between lack of sleep, heartburn, and reduced mobility, I was getting pretty excited to be done with pregnancy and to finally meet “Baby K” as we had begun calling her. Overall, being pregnant was a very informative experience for me as a person and as a clinician. I often hear my patients tell me of their uncomfortable symptoms during pregnancy involving their musculoskeletal and gastrointestinal systems, however, now I empathize on another level.
Susannah Haarmann, PT, CLT, WCS is the author and instructor of Physical Therapy Treatment for the Breast Oncology Patient. Join her this September 24-25 in Stockton, CA to learn about the various diagnostic tests, medical and surgical interventions to provide appropriate and optimal therapeutic interventions for breast cancer patients.
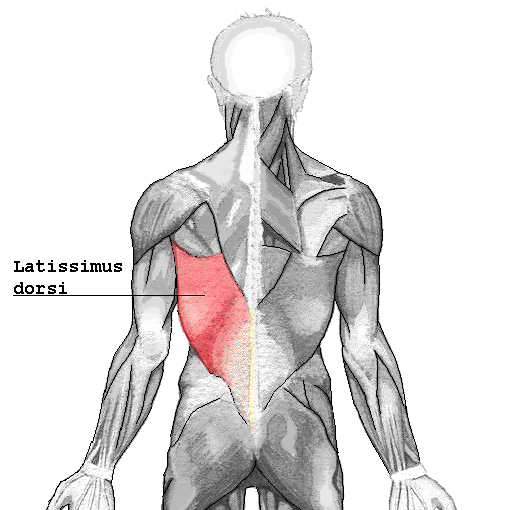 I turned to the literature and found prominent articles discussing breast reconstruction and giving minimal consequence to shoulder function after resection of the latissimus dorsi muscle. As a physical therapist, this left me in a quandary, “Really? Harvesting a portion of the broadest muscle of the back then threading it through the axilla to recreate the breast mound won’t have an impact on shoulder function or back pain? Impressive!” However, this did not correlate with my clinical findings. Often, scapulohumeral rhythm was altered, range of motion restricted and activities limited due to pain and fatigue. Scrutinizing the literature, I found that those articles were mostly unsubstantiated. Here is a quick summary of two systematic reviews published in 2014 addressing what the research really found pertaining to shoulder function after ‘lat flap’ reconstruction:
I turned to the literature and found prominent articles discussing breast reconstruction and giving minimal consequence to shoulder function after resection of the latissimus dorsi muscle. As a physical therapist, this left me in a quandary, “Really? Harvesting a portion of the broadest muscle of the back then threading it through the axilla to recreate the breast mound won’t have an impact on shoulder function or back pain? Impressive!” However, this did not correlate with my clinical findings. Often, scapulohumeral rhythm was altered, range of motion restricted and activities limited due to pain and fatigue. Scrutinizing the literature, I found that those articles were mostly unsubstantiated. Here is a quick summary of two systematic reviews published in 2014 addressing what the research really found pertaining to shoulder function after ‘lat flap’ reconstruction:
Patient impressions:
- Reported incidence of overall functional impairment is 41%. 8
- Overhead activities, lifting and pushing objects and high-level activities such as sport and housework were the most cumbersome. 1,7
- Subjective deficits did not resolve based on length of follow-up. 1
Strength:
- Greatest deficits are noted with reconstruction on the dominant side. 4
- Extension of the shoulder is the most common strength deficit followed by adduction then internal rotation. 8
- Objective strength deficits typically resolved within a year. 8,9
- Rehab should be ordered pro-actively. 4
Range of Motion:
- Active flexion is the most common restriction followed by abduction. 8
- Rarely were these restrictions severe. 5,6
- Restrictions were greatest post-operatively likely due to alterations in shoulder biomechanics, scar formation and post-operative pain.
- Discrepancies were found regarding resolution of range of motion without rehab. 5,8
- No clinically significant functional morbidity was found when therapy was provided from post-op day one. 2,3
Other reported complications that may impact function:
- Taratino, Banic and Fischer noted that capsular contracture was the most significant and recurrent complication in their study.10
- 50% reported post-operative numbness and tightness.1
- Scar tissue adhesions were associated with functional limitations.2,3
In conclusion, is it feasible to say that the latissimus dorsi muscle bears little consequence to function after reconstruction? I’m going to trust what the researchers performing the systematic reviews say:
- Physicians and researchers Lee and Mun state the following; “over 20 percent of the patients undergoing latissimus dorsi muscle transfer suffered from considerable disability…7% of patients changed their job postoperatively. These results suggest that considerable discomfort, even to the extent of limitation on daily activity, can be developed after latissimus dorsi muscle harvest, as opposed to the previous assumption that latissimus dorsi muscle harvest may not lead to serious disability” .8
- Smith does give merit to the fact that most strength deficits resolve within 6 to 12 months due to other muscles compensating for function, however, she states “standardization of physical therapy protocols is imperative as it appears to have a measurable positive impact.” Immediately after this statement she remarks that physical therapy is rarely included in the physician’s plan of care.9
I guess it is time we start talking to our surgical oncologists and plastic surgeons.
1. Adams, Jr., W., Lipschitz, A., Ansari, M., Kenkel, J., & Rohrich, R. J. (2004). Functional donor site morbidity following LD muscle flap transfer. Annals of Plastic Surgery, 53(1), 6–11.
2. de Oliveira, R., Nascimento, S., Derchain, S. & Sarian, L. (2013). Immediate breast reconstruction with a latissimus dorsi flap has no detrimental effects on shoulder motion or postsurgical complications up to 1 year after surgery. Plas¬tic and Reconstructive Surgery, 131(5), 673e–680e.
3. de Oliveira, R. R., Pinto e Silva, M. P., Costa Gurgel, M. S., Pas¬tori-Filho, L., & Sarian, L. O. (2010). Immediate breast re¬construction with transverse latissimus dorsi flap does not affect the short-term recovery of shoulder range of motion after mastectomy. Annals of Plastic Surgery, 64(4), 402– 408.
4. Forthomme, B., Heymans, O., Jacquemin, D., Klinkenberg, S., Hoff¬mann, S., Grandjean, F. X.,...Croisier, J. L. (2010). Shoulder function after latissimus dorsi transfer in breast reconstruc-tion. Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging, 30, 406– 412.
5. Giordano, S., Kääriäinen, M., Alavaikko, J., Kaistila, T. & Kuok¬kanen, H. (2011). Latissimus dorsi free flap harvesting may affect the shoulder joint in long run. Scandinavian Journal of Surgery, 100, 202–207.
6. Hamdi, M., Decorte, T., Demuynck, M., Defrene, B., Fredricks, A., VanMaele, G.,...Monstrey, S. (2008). Shoulder func¬tion after harvesting a thoracodorsal artery perforator flap. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 122(4), 1111–1117.
7. Koh, C. E., & Morrison, W. A. (2009). Functional impairment af¬ter latissimus dorsi flap. Australian Journal of Surgery, 79, 42–47. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-2197.2008.04797.x
8. Lee, K.T., Mun, G.H., (2014).A systematic review of functional donor-site morbidity after latissimus dorsi muscle transfer, Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 134: 303.
9. Smith, S., (2014). Functional morbidity following latissimus dorsi flap breast reconstruction. J Adv Pract Oncol, 5, 181–187.
10. Tarantino, I., Banic, A., & Fischer, T. (2006). Evaluation of late results in breast reconstruction by latissimus dorsi flap and prosthesis implantation. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 117(5), 1387–1394.
Nancy Cullinane PT, MHS, WCS is today's guest blogger. Nancy has been practicing pelvic rehabilitation since 1994 and she is eager to share her knowledge with the medical community at large. Thank you, Nancy, for contributing this excellent article!
Clinically valid research on the efficacy and safety of therapeutic exercise and activities for individuals with osteoporosis or vertebral fractures is scarce, posing barriers for health care providers and patients seeking to utilize exercise as a means to improve function or reduce fracture risk1,2. However, what evidence does exist strongly supports the use of exercise for the treatment of low Bone Mineral Density (BMD), thoracic kyphosis, and fall risk reduction, three themes that connect repeatedly in the body of literature addressing osteoporosis intervention.
 Sinaki et al3 reported that osteoporotic women who participated in a prone back extensor strength exercise routine for 2 years experienced vertebral compression fracture at a 1% rate, while a control group experienced fracture rates of 4%. Back strength was significantly higher in the exercise group and at 10 years, the exercise group had lost 16% of their baseline strength, while the control group had lost 27%. In another study, Hongo correlated decreased back muscle strength with an increased thoracic kyphosis, which is associated with more fractures and less quality of life. Greater spine strength correlated to greater BMD4. Likewise, Mika reported that kyphosis deformity was more related to muscle weakness than to reduced BMD5. While strength is clearly a priority in choosing therapeutic exercise for this population, fall and fracture prevention is a critical component of treatment for them as well. Liu-Ambrose identified quadricep muscle weakness and balance deficit statistically more likely in an osteoporotic group versus non osteoporotics6. In a different study, Liu-Ambrose demonstrated exercise-induced reductions in fall risk that were maintained in older women following three different types of exercise over a six month timeframe. Fall risk was 43% lower in a resistance-exercise training group; 40% lower in a balance training exercise group, and 37% less in a general stretching exercise group7.
Sinaki et al3 reported that osteoporotic women who participated in a prone back extensor strength exercise routine for 2 years experienced vertebral compression fracture at a 1% rate, while a control group experienced fracture rates of 4%. Back strength was significantly higher in the exercise group and at 10 years, the exercise group had lost 16% of their baseline strength, while the control group had lost 27%. In another study, Hongo correlated decreased back muscle strength with an increased thoracic kyphosis, which is associated with more fractures and less quality of life. Greater spine strength correlated to greater BMD4. Likewise, Mika reported that kyphosis deformity was more related to muscle weakness than to reduced BMD5. While strength is clearly a priority in choosing therapeutic exercise for this population, fall and fracture prevention is a critical component of treatment for them as well. Liu-Ambrose identified quadricep muscle weakness and balance deficit statistically more likely in an osteoporotic group versus non osteoporotics6. In a different study, Liu-Ambrose demonstrated exercise-induced reductions in fall risk that were maintained in older women following three different types of exercise over a six month timeframe. Fall risk was 43% lower in a resistance-exercise training group; 40% lower in a balance training exercise group, and 37% less in a general stretching exercise group7.
These studies allow us to unequivocally conclude that spinal extensor strengthening and therapeutic activities aimed at improving balance and decreasing fall risk are tantamount as therapeutic interventions for osteoporosis. But postural education/modification and weight bearing activities aimed at stimulating osteoblast production intended to improve BMD are a reasonable component of an osteoporosis treatment plan, despite the lack of concrete evidence for them. Nutrition and mineral supplementation with calcium and vitamin D have been shown to reduce morbidities, and hence we should incorporate this education into our treatment plans as well8, 9. Studies on the efficacy of vibration platforms hold promise, but thus far, have not been substantiated as an evidence-based intervention to improve BMD.
Too Fit To Fracture: outcomes of a Delphi consensus process on physical activity and exercise recommendations for adults with osteoporosis with or without vertebral fractures1,2 is a multiple-part publication in the journal Osteoporosis International, based upon an international consensus process by expert researchers and clinicians in the osteoporosis field. These publications include exercise and physical activity recommendations for individuals with osteoporosis based upon a separation of patients into to three groups: osteoporosis based on BMD without fracture; osteoporosis with one vertebral fracture; and osteoporosis with multiple spine fractures, hyperkyphosis and pain. This group of experts emphasize the importance of teaching safe performance of ADLs with respect to bodymechanics as a priority to accompany strength, balance, fall & fracture prevention, nutrition and pharmacotherapy management. They promote establishment of an individualized program for each patient with adaptable variations of these concepts, with the most accommodation allotted for individuals with multiple vertebral compression fractures. An example of such an adaptation is altering prone back extensions such as those documented in the studies by Sinaki and Hongo, into supine shoulder presses, thus strengthening the back extensors in a less gravitationally demanding posture. Osteoporosis Canada has adapted the main concepts from these publications into a patient-friendly, instructional website with reproducible handouts at http://www.osteoporosis.ca/osteoporosis-and-you/too-fit-to-fracture/
A firm conclusion from the Too Fit to Fracture project is that higher quality outcomes studies are desperately needed to assist all healthcare providers in managing osteoporosis more effectively and comprehensively, and to do so prior to the onset of debilitating fractures that tend to produce serious comorbidities.
1. Giangregorio et al. Too Fit to Fracture: exercise recommendations for individuals with osteoporosis or osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Osteoporosis International. 2014; 25(3): 821-835
2. Giangregorio et al. Too Fit to Fracture: outcomes of a Delphi consensus process on physical activity and exercise recommendations for adults with osteoporosis with or without vertebral fracture. Osteoporosis International. 2015; 26(3):891-910
3. Sinaki et al. Stronger back muscles reduce the incidence of vertebral fractures: a prospective 10 year follow-up of postmenopausal women. Bone. 2002; 30: 836-841 4. Hongo et al. Effect of low-intensity back exercise on quality of life and back extensor strength in patients with osteoporosis; a randomized controlled trial.Osteoporosis International. 2007; 10: 1389-1395
5. Mika et al. Differences in thoracic kyphosis and in back muscle strength in women with bone loss due to osteoporosis. Spine. 2005; 30(2): 241-246
6. Liu-Ambrose et al. Older women with osteoporosis have increased postural sway and weaker quadriceps strength than counterparts with normal bone mass: overlooked determinants of fracture risk? J Gerontology, Series A Biolog Sci Med Sci. 2003; 58(9): M862-866
7. Liu-Ambrose et al. The beneficial effects of group-based exercise on fall risk profile and physical activity persist 1 year post intervention in older women with low bone mass: follow-up after withdrawal of exercise. J Am Geriat Soc. 2005; 53 (10): 1767-1773
8. Ensrud et al. Weight change and fractures in older women: study of osteoporotic fractures research group. Archives Int Med. 1997; 157 (8): 857-863
9. Kemmler et al. Exercise effects on fitness and bone mineral density in early postmenopausal women: 1-year EFOPS results. Med and Sci in Sports Ex. 2002; 34 (12): 2115-2123
In manual therapy training, we do not learn just one position to mobilize a joint, so why should pelvic floor muscle training be limited by the standard training methods? There is almost always at least one patient in the clinic that fails to respond to the “normal” treatment and requires a twist on conventional therapy to get over a dysfunction. Thankfully, classes like “Integrative Techniques for Pelvic Floor and Core Function” provide clinicians with the extra tools that might help even just one patient with lingering symptoms.
 In 2014, Tenfelde and Janusek considered yoga as a treatment for urge urinary incontinence in women, referring to it as a “biobehavioral approach.” The article reviews the benefits of yoga as it relates to improving the quality of life of women with urge urinary incontinence. Yoga may improve sympatho-vagal balance, which would lower inflammation and possibly psychological stress; therefore, the authors suggested yoga can reduce the severity and distress of urge UI symptoms and their effect on daily living. Since patho-physiologic inflammation within the bladder is commonly found, being able to minimize that inflammation through yoga techniques that activate the efferent vagus nerve (which releases acetylcholine) could help decrease urge UI symptoms. The breathing aspect of yoga can reduce UI symptoms as it modulates neuro-endocrine stress response symptoms, thus reducing activation of psychological and physiologic stress and inflammation associated with stress. The authors concluded the mind-body approach of yoga still requires systematic evaluation regarding its effect on pelvic floor dysfunction but offers a promising method for affecting inflammatory pathways.
In 2014, Tenfelde and Janusek considered yoga as a treatment for urge urinary incontinence in women, referring to it as a “biobehavioral approach.” The article reviews the benefits of yoga as it relates to improving the quality of life of women with urge urinary incontinence. Yoga may improve sympatho-vagal balance, which would lower inflammation and possibly psychological stress; therefore, the authors suggested yoga can reduce the severity and distress of urge UI symptoms and their effect on daily living. Since patho-physiologic inflammation within the bladder is commonly found, being able to minimize that inflammation through yoga techniques that activate the efferent vagus nerve (which releases acetylcholine) could help decrease urge UI symptoms. The breathing aspect of yoga can reduce UI symptoms as it modulates neuro-endocrine stress response symptoms, thus reducing activation of psychological and physiologic stress and inflammation associated with stress. The authors concluded the mind-body approach of yoga still requires systematic evaluation regarding its effect on pelvic floor dysfunction but offers a promising method for affecting inflammatory pathways.
Pang and Ali (2015) focused on complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) treatments for interstitial cystitis (IC) and bladder pain syndrome (BPS). Since conventional therapy has not been definitely determined for the IC/BPS population, CAM has been increasingly used as an optional treatment. Two of the treatments under the CAM umbrella include yoga (mind-body therapy) and Qigong (an energy therapy). Yoga can contribute to IC/BPS symptom relief via mechanisms that relax the pelvic floor muscle. Actual yoga poses of benefit include frog pose, fish pose, half-shoulder stand and alternate nostril breathing. According to a systematic review, Qigong and Tai Chi can improve function, immunity, stress, and quality of life. Qigong has been effective in managing chronic pain, although not specifically evidenced with IC/BPS groups. Qigong has also been shown to reduce stress and anxiety and activate the brain region that suppresses pain. The CAM gives a multimodal approach for treating IC/BPS, and this has been recommended by the International Consultation on Incontinence Research Society.
Evidence is emerging in every area of treatment these days, so it is only a matter of time before randomized controlled trials regarding alternative treatment methods for the pelvic floor begin to fill pages of our professional journals. Yoga, Qigong, Tai Chi, biologically based therapies, manipulative and body-based approaches, and whole medical systems all offer safe, effective treatment options for the IC/BPS and urinary incontinence patient populations. The more we use these extra treatment tools and document the results, the more likely we will see clinical trials proving their efficacy.
Tenfelde, S and Janusek, L. (2014). Yoga: A Biobehavioral Approach to Reduce Symptom Distress in Women with Urge Urinary Incontinence. THE JOURNAL OF ALTERNATIVE AND COMPLEMENTARY MEDICINE. 20 (10), 737–742. http://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2013.0308
Pang, R., & Ali, A. (2015). The Chinese approach to complementary and alternative medicine treatment for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome.Translational Andrology and Urology, 4(6), 653–661. http://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.08.10
Dr. Dischiavi is a Herman & Wallace faculty member who authored and teaches Biomechanical Assessment of the Hip & Pelvis: Manual Movement Therapy and the Myofascial Sling System, available this August in Boston, MA.
STEM is an acronym for science, technology, engineering, and math. These fields are deeply intertwined and taking this approach could potentially be a way to facilitate the physical therapist’s appreciation of human movement.
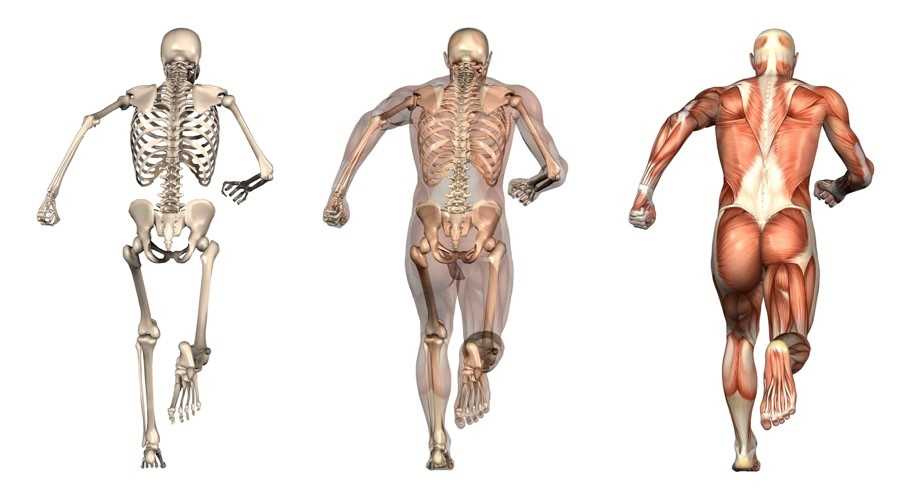
 Science: I would bet most physical therapists would agree that science is the cornerstone of our profession. It is time to look across all the landscapes of science to better understand the physical principles that govern movement. Biotensegrity is a great example of how science from a field such as cellular biology can help possibly explain how we maintain an erect posture when the rigid bony structure of our skeleton is only connected from bone to bone by soft tissues [1]. The brain and central nervous system regulates muscle tone, and it is resting muscle tone that give our bodies the ability to be upright. Without resting muscle tone, we would crumple to the ground as a heap of bones within a bag of skin. Since the CNS can either up or down regulate muscle tone, this allows us to create the rigidity we need to accomplish higher level movements such as sport, and then return to a resting state after the movements are performed (see running skeleton picture below). This theory of organismic support was bred within the scientific field of cellular biology, and can potentially be applied effectively to the human organism. As physical therapists, I agree we need to be skeptical of new ideas, but we also need to embrace the idea that the physical sciences have applied to nature for centuries, and it is possible these various scientific fields can help us unlock new ideas and allow us to look at things through a different lens.
Science: I would bet most physical therapists would agree that science is the cornerstone of our profession. It is time to look across all the landscapes of science to better understand the physical principles that govern movement. Biotensegrity is a great example of how science from a field such as cellular biology can help possibly explain how we maintain an erect posture when the rigid bony structure of our skeleton is only connected from bone to bone by soft tissues [1]. The brain and central nervous system regulates muscle tone, and it is resting muscle tone that give our bodies the ability to be upright. Without resting muscle tone, we would crumple to the ground as a heap of bones within a bag of skin. Since the CNS can either up or down regulate muscle tone, this allows us to create the rigidity we need to accomplish higher level movements such as sport, and then return to a resting state after the movements are performed (see running skeleton picture below). This theory of organismic support was bred within the scientific field of cellular biology, and can potentially be applied effectively to the human organism. As physical therapists, I agree we need to be skeptical of new ideas, but we also need to embrace the idea that the physical sciences have applied to nature for centuries, and it is possible these various scientific fields can help us unlock new ideas and allow us to look at things through a different lens.
 Technology: As not only a practicing physical therapist, but as a newly appointed assistant professor within a budding physical therapy program it is my duty to embrace evidence based practice. I believe without question, when evidence that is sound exists it should help direct patient care. It is also clear that our tests and measures that are currently being utilized to help develop new evidence are lacking, specifically with regard to human movement and sport performance.
Technology: As not only a practicing physical therapist, but as a newly appointed assistant professor within a budding physical therapy program it is my duty to embrace evidence based practice. I believe without question, when evidence that is sound exists it should help direct patient care. It is also clear that our tests and measures that are currently being utilized to help develop new evidence are lacking, specifically with regard to human movement and sport performance.
Sports performance is such a complex system (more on this later) we can’t expect to study things such as injury prevention at slow speeds utilizing maneuvers that aren’t even seen in the sport itself. Recently, Bahr [2] suggested that screening for sports injuries is pretty much a futile effort as he titled his article “Why screening tests to predict injury do not work - and probably never will…: a critical review.” Eventually technology will need to be developed that can measure high speed movement across multiple planes and ranges of motion, and essentially capture the complex spiraling that occurs with human movement and the bodies effort to attenuate ground reaction forces. This concept can be illustrated in the current work of Tak and Langhout [3] who have developed a novel approach to measure hip ROM in soccer players. They have essentially performed a thorough needs analysis of the kicking motion and determined that the classical method of measuring hip ROM doesn’t take into account the body’s need to spiral itself to gain the energy in the system needed to kick a ball [Fig 1]. This global understanding of the dynamic integration of the kinetic chain (which is covered in my hip course!) is what has led them to design this new method to measure hip ROM. Now, we will need technological advancements to capture, record, and measure these types of positions across three planes and at high speeds to establish the data that will eventually lead to evidence that will translate into sport. This is a great example of how clinical innovation sometimes precedes actual evidence to support its use. As William Blake was quoted as saying “what is now proven was once only imagined.”
 Engineering: Structural engineering should be included in every physical therapy education program. There are many basic structural engineering principles that directly apply to a physical therapists practice. For example, the principal of elastics is frequently discussed within structural engineering. Elastics describes to what extent deformation is proportional to the forces applied to a particular material. In physical therapy muscles are that particular material, muscles must have elasticity and extensibility, not flexibility! In elastics, a rubber band is often used as a simple example to explain this engineering concept.
Engineering: Structural engineering should be included in every physical therapy education program. There are many basic structural engineering principles that directly apply to a physical therapists practice. For example, the principal of elastics is frequently discussed within structural engineering. Elastics describes to what extent deformation is proportional to the forces applied to a particular material. In physical therapy muscles are that particular material, muscles must have elasticity and extensibility, not flexibility! In elastics, a rubber band is often used as a simple example to explain this engineering concept.
A rubber band will elongate and develop potential energy until release and then unleash kinetic energy. Our human movement system relies heavily on the principle of elastics. The rectus femoris is a two-joint muscle across the hip. During gait and running the rectus femoris is elongated as the hip moves into extension, this elongation builds its potential energy until the foot comes off the ground to initiate the swing phase, and the kinetic energy released in the system allows momentum to carry the lower extremity forward.
 I would add that possibly the twisting created by the contralateral counter trunk rotation and reciprocating arm and leg swing that accompanies the hip extension is what creates tension throughout the entire anterior chain, similar to why Tak and Langhout feel its important to take up all soft tissue slack three dimensionally to effectively measure hip ROM needed for a soccer kick. It is considering that the elasticity in the entire system (organism) is needed to create an efficient human movement, which is kicking a ball in this example. When the body utilizes passive lengthening of muscle chains, as in elastics, it allows the body to move more efficiently. This is described by Chu [4] who reports that in the pitching motion maximizing force development in the large muscles of the core and legs produces more than 51%- 55% of the kinetic energy that is transferred to the hand [Fig 2]. The thoracolumbar fascia is involved in the kinetic chain during throwing activities and connects the lower limbs through the gluteus maximus muscle to the upper limbs through the latissimus dorsi. This idea of a dynamic integration of the kinetic chain is the main concept of the exercise portion of my hip course!
I would add that possibly the twisting created by the contralateral counter trunk rotation and reciprocating arm and leg swing that accompanies the hip extension is what creates tension throughout the entire anterior chain, similar to why Tak and Langhout feel its important to take up all soft tissue slack three dimensionally to effectively measure hip ROM needed for a soccer kick. It is considering that the elasticity in the entire system (organism) is needed to create an efficient human movement, which is kicking a ball in this example. When the body utilizes passive lengthening of muscle chains, as in elastics, it allows the body to move more efficiently. This is described by Chu [4] who reports that in the pitching motion maximizing force development in the large muscles of the core and legs produces more than 51%- 55% of the kinetic energy that is transferred to the hand [Fig 2]. The thoracolumbar fascia is involved in the kinetic chain during throwing activities and connects the lower limbs through the gluteus maximus muscle to the upper limbs through the latissimus dorsi. This idea of a dynamic integration of the kinetic chain is the main concept of the exercise portion of my hip course!
 Math: The dynamic systems theory is an area of mathematics that most physical therapists probably don’t consider during everyday treatment. Little do they know, every treatment decision we as therapists make for our patient/clients has some root found in the dynamic systems theory. In fact, it is a fitting description when this theory is applied to human movement. Human movement is an incredibly complex system comprised of many different systems all working at the same time. Paul Glazier recently offered a Grand Unified Theory (GUT) for sports performance [5] and he discusses in detail the various systems and dynamic elements involved in sports performance from musculoskeletal, to neural, to cognitive, environmental, hormonal, and emotional just to name a few. The systems at work during sport when combined are exponential and most likely infinite. This is why it is so difficult to try and capture all these dynamic systems in a laboratory setting with the current technology available. In my hip course offered through Herman & Wallace I offer a novel paradigm to help clinicians construct therapeutic exercise programs using the hip as a cornerstone to human movement. I try to compact these various systems into 8 overlapping elements related to sport performance. When each of these 8 components are “exploded” as you might see in an engineering schematic where an engine is exploded to see all the parts that make the engine or more simply explained using a cheeseburger as the example [Fig 3]. Sure its easy to spot the cheeseburger when its whole just like when you see an athlete on the field running it seems obvious. Once the cheeseburger is “exploded” you can now isolate each sub-element included in your cheeseburger. This cheeseburger example is an obvious over-simplification, but if we exploded the bun to see the underlying grain and the seeds and so on…you now start to get an idea of how deep and intertwined all these subsystems are. Interestingly, the engine and the cheeseburger have finite parts and fit together, the human system has different parts in different systems depending on the sport and who might be playing it, under ever-changing scenery, and so on. So you can now see how the 8 components I outline in my course can house many different aspects of these dynamic systems. Although, I think this is progress with regard to the current state of the evidence, specifically with regard to utilizing the hip during movement, there are other systems at work that clinicians simply cannot control, such as gender, hormonal, environmental, etc…The idea is to try to identify and then manipulate modifiable factors whenever possible. These concepts are more clearly described and implemented in my hip course! Please come and check it out, and let me know what you think!
Math: The dynamic systems theory is an area of mathematics that most physical therapists probably don’t consider during everyday treatment. Little do they know, every treatment decision we as therapists make for our patient/clients has some root found in the dynamic systems theory. In fact, it is a fitting description when this theory is applied to human movement. Human movement is an incredibly complex system comprised of many different systems all working at the same time. Paul Glazier recently offered a Grand Unified Theory (GUT) for sports performance [5] and he discusses in detail the various systems and dynamic elements involved in sports performance from musculoskeletal, to neural, to cognitive, environmental, hormonal, and emotional just to name a few. The systems at work during sport when combined are exponential and most likely infinite. This is why it is so difficult to try and capture all these dynamic systems in a laboratory setting with the current technology available. In my hip course offered through Herman & Wallace I offer a novel paradigm to help clinicians construct therapeutic exercise programs using the hip as a cornerstone to human movement. I try to compact these various systems into 8 overlapping elements related to sport performance. When each of these 8 components are “exploded” as you might see in an engineering schematic where an engine is exploded to see all the parts that make the engine or more simply explained using a cheeseburger as the example [Fig 3]. Sure its easy to spot the cheeseburger when its whole just like when you see an athlete on the field running it seems obvious. Once the cheeseburger is “exploded” you can now isolate each sub-element included in your cheeseburger. This cheeseburger example is an obvious over-simplification, but if we exploded the bun to see the underlying grain and the seeds and so on…you now start to get an idea of how deep and intertwined all these subsystems are. Interestingly, the engine and the cheeseburger have finite parts and fit together, the human system has different parts in different systems depending on the sport and who might be playing it, under ever-changing scenery, and so on. So you can now see how the 8 components I outline in my course can house many different aspects of these dynamic systems. Although, I think this is progress with regard to the current state of the evidence, specifically with regard to utilizing the hip during movement, there are other systems at work that clinicians simply cannot control, such as gender, hormonal, environmental, etc…The idea is to try to identify and then manipulate modifiable factors whenever possible. These concepts are more clearly described and implemented in my hip course! Please come and check it out, and let me know what you think!
I’m hoping the STEM approach can possibly make it into physical therapy curriculums to illustrate to future physical therapists that there are many different disciplines at work with regard to physical therapy, and taking a global view of these elements can certainly be worthwhile.
1. Ingber, D.E., N. Wang, and D. Stamenovic, Tensegrity, cellular biophysics, and the mechanics of living systems. Rep Prog Phys, 2014. 77(4): p. 046603.
2. Bahr, R., Why screening tests to predict injury do not work-and probably never will...: a critical review. Br J Sports Med, 2016.
3. Tak, I., et al., Hip Range of Motion Is Lower in Professional Soccer Players With Hip and Groin Symptoms or Previous Injuries, Independent of Cam Deformities. Am J Sports Med, 2016. 44(3): p. 682-8.
4. Chu, S.K., et al., The Kinetic Chain Revisited: New Concepts on Throwing Mechanics and Injury. PM R, 2016. 8(3 Suppl): p. S69-77.
5. Glazier, P.S., Towards a Grand Unified Theory of sports performance. Hum Mov Sci, 2015.
Figure 1

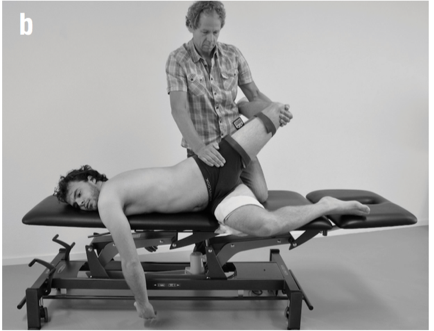
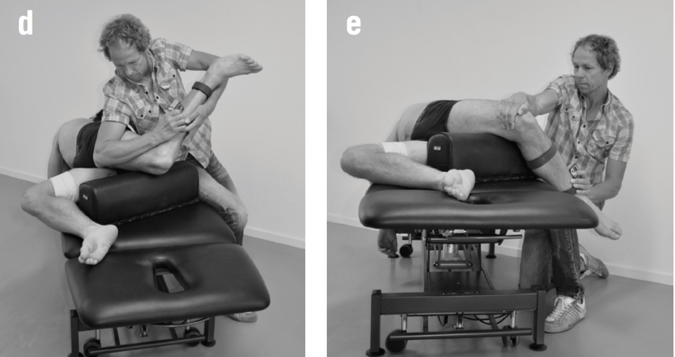
Figure 2
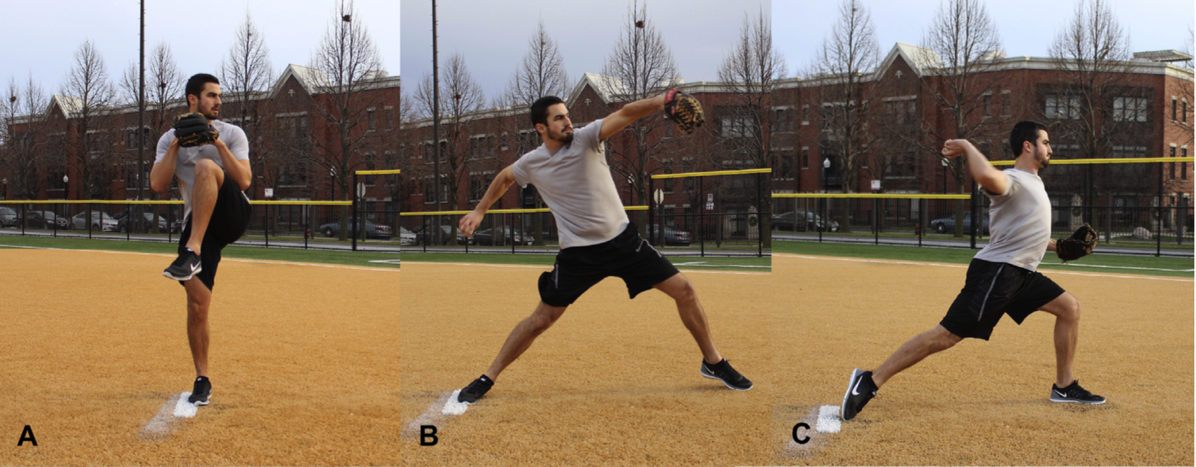

Figure 3

Figure 4
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://hermanwallace.com/